
Jessen's icosahedron
Encyclopedia
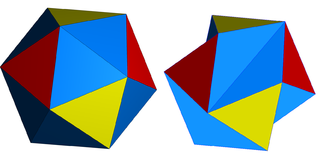
Polyhedron
In elementary geometry a polyhedron is a geometric solid in three dimensions with flat faces and straight edges...
with the same number of vertices, edges and faces as the regular icosahedron
Icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids....
. It was introduced by Børge Jessen
Børge Jessen
Børge Christian Jessen was a Danish mathematician best known for his work in analysis, specifically on zeta function, and in geometry, specifically on Hilbert's third problem....
in 1967 and has several geometric properties:
- it is vertex-transitive (or isogonal),
- it has only rightRight angleIn geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle that bisects the angle formed by two halves of a straight line. More precisely, if a ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the adjacent angles are equal, then they are right angles...
dihedral angleDihedral angleIn geometry, a dihedral or torsion angle is the angle between two planes.The dihedral angle of two planes can be seen by looking at the planes "edge on", i.e., along their line of intersection...
s, - it is (continuously) rigid but not infinitesimallyInfinitesimalInfinitesimals have been used to express the idea of objects so small that there is no way to see them or to measure them. The word infinitesimal comes from a 17th century Modern Latin coinage infinitesimus, which originally referred to the "infinite-th" item in a series.In common speech, an...
rigid, - as with the simpler Schönhardt polyhedronSchönhardt polyhedronIn geometry, the Schönhardt polyhedron is the simplest non-convex polyhedron that cannot be triangulated into tetrahedra without adding new vertices...
, its interior cannot be triangulated into tetrahedraTetrahedronIn geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids...
without adding new verticesVertex (geometry)In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
, - it is scissors congruentHilbert's third problemThe third on Hilbert's list of mathematical problems, presented in 1900, is the easiest one. The problem is related to the following question: given any two polyhedra of equal volume, is it always possible to cut the first into finitely many polyhedral pieces which can be reassembled to yield the...
to a cube.
Although a shape resembling Jessen's icosahedron can be formed by keeping the vertices of a regular icosahedron in their original positions and replacing some of its faces, the resulting polyhedron does not have right-angled dihedrals. The vertices of Jessen's icosahedron are perturbed from these positions in order to give all the dihedrals right angles.

