
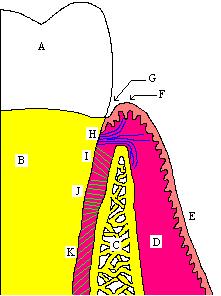
Junctional epithelium
Encyclopedia
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus
Gingiva
The gingiva , or gums, consists of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth.-General description:...
. It attaches to the surface of the tooth with hemidesmosome
Hemidesmosome
Hemidesmosomes are very small stud- or rivet-like structures on the inner basal surface of keratinocytes in the epidermis of skin. They are similar in form to desmosomes when visualized by electron microscopy. While desmosomes link two cells together, hemidesmosomes attach one cell to the...
s and is, on average, roughly 1 mm in width, constituting about one half of the biologic width.
The junctional epithelium lies immediately apical
Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry
There are numerous commonly used terms of relationship and comparison that refer to different aspects of teeth and are frequently utilized in articles about dentistry...
to the sulcular epithelium
Sulcular epithelium
The sulcular epithelium is that epithelium which lines the gingival sulcus. It is apically bounded by the junctional epithelium and meets the epithelium of the oral cavity at the height of the free gingival margin. The sulcular epithelium is nonkeratinized....
, which lines the gingival sulcus
Gingival sulcus
The gingival sulcus is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding gingival tissue and is lined by sulcular epithelium. The depth of the sulcus is bounded by two entities: apically by the gingival fibers of the connective tissue attachment and coronally by the free gingival...
from the base to the free gingival margin
Free gingival margin
The free gingival margin is the interface between the sulcular epithelium and the epithelium of the oral cavity. This interface exists at the most coronal point of the gingiva, otherwise known as the crest of the marginal gingiva....
, where it interfaces with the epithelium of the oral cavity.
Cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
in the junctional epithelium tend to have wide inter-cellular spaces, to allow the transmission of white blood cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
s from blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s to the bottom of the gingival sulcus, to help prevent disease. Damage to the junctional epithelium results in it being irregular in texture, rather than smooth, and the formation of "pocket" epithelium, which is a primary symptom of gum disease.

