
KDE
Encyclopedia
KDE is an international free software
community producing an integrated set of cross-platform
applications designed to run on Linux
, FreeBSD
, Microsoft Windows
, Solaris and Mac OS X systems. It is best known for its Plasma Desktop, a desktop environment
provided as the default working environment on many Linux distributions, such as Kubuntu
, Pardus
and openSUSE
.
The goal of the community is to provide basic desktop functions and applications for daily needs as well as tools and documentation for developers to write stand-alone applications for the system. In this regard, the KDE project serves as an umbrella project for many standalone applications and smaller projects that are based on KDE technology. These include Calligra Suite, digiKam
, Rekonq
, K3b
and many others.
KDE software is based on the Qt framework. The original GPL
version of this toolkit only existed for the X11 platform, but with the release of Qt 4, LGPL
versions are available for all platforms. This allows KDE software based on Qt 4 to also be distributed to Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X
.
 KDE was founded in 1996 by Matthias Ettrich
KDE was founded in 1996 by Matthias Ettrich
, who was then a student at the Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen
. At the time, he was troubled by certain aspects of the Unix
desktop. Among his concerns was that none of the applications
looked, felt, or worked alike. He proposed the creation of not merely a set of applications but a desktop environment in which users could expect things to look, feel, and work consistently. He also wanted to make this desktop easy to use; one of his complaints about desktop applications of the time was that his girlfriend could not use them. His initial Usenet
post spurred a lot of interest, and the KDE project was born.
The name KDE was intended as a wordplay on the existing Common Desktop Environment
, available for Unix systems. CDE was an X11-based user environment jointly developed by HP, IBM, and Sun through the X/Open
consortium, with an interface and productivity tools based on the Motif
graphical widget toolkit. It was supposed to be an intuitively easy-to-use desktop computer
environment. The K was originally suggested to stand for "Kool", but it was quickly decided that the K should stand for nothing in particular. The KDE initialism is therefore expanded to "K Desktop Environment".
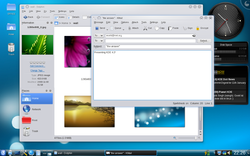 Matthias Ettrich chose to use Trolltech’s
Matthias Ettrich chose to use Trolltech’s
Qt framework for the KDE project. Other programmers quickly started developing KDE/Qt applications, and by early 1997, a few applications were being released. On 12 July 1998 the first version of the desktop environment, called KDE 1.0, was released.
Q Public License
(QPL) and a commercial license for proprietary software developers. The same year, the KDE Free Qt foundation was created which guarantees that Qt would fall under a variant of the very liberal BSD license should Trolltech cease to exist or no free version of Qt be released during 12 months.
Debate continued about compatibility with the GNU General Public License (GPL), hence in September 2000 Trolltech made the Unix version of the Qt libraries available under the GPL in addition to the QPL which eliminated the concerns of the Free Software Foundation
. Trolltech continued to require licenses for developing proprietary software
with Qt. The core libraries of KDE are collectively licensed under the GNU LGPL but the only way for proprietary software to make use of them was to be developed under the terms of the Qt proprietary license.
Starting with Qt 4.5, Qt was also made available under the LGPL version 2.1, now allowing proprietary applications to legally use the open source Qt version.
of the KDE project components, motivated by the perceived shift from building a desktop environment to a complete project around a community of "people who create software". The rebranding focused on de-emphasizing the desktop environment as "just another product", and emphasizing both the community and the other technologies provided as KDE software. After the repositioning, the name KDE no longer stands for K Desktop Environment, as it now acts as an umbrella brand for software produced by the community. What would have been previously known as KDE 4.4 will now be referred as "KDE Software Compilation 4.4" (abbreviated "KDE SC 4.4"). Regardless, many users still refer to it as KDE 4.
, which is a German non-profit organization, and help organizing the conferences and meetings of the community members. KDE e.V. helps running the servers needed by the KDE community. It owns the trademark
on KDE and the logo. It pays for travel to meetings, and subsidizes events. The working groups are a structure which will formalize some roles within KDE and enhance coordination within KDE, communication between parts of KDE. KDE e.V. has no influence on development. KDE e.V. logo has been contributed by David Vignoni
. The three flags on top of the logo represent the three main tasks of the KDE e.V.: supporting the community, representing the community, and governing the community.
The KDE community's developer meetings, servers and related events are frequently sponsored by individuals, universities, and businesses. The supporting members of the KDE e.V. are extraordinary members supporting the KDE through financial or material contributions. Supporting members are entitled to display the "Member of KDE" logo on their website or in printed materials. The Patron of KDE is the highest level of supporting member. The patrons of KDE also are entitled to display the exclusive "Patron of KDE" logo on their website or in printed materials. On 15 October 2006, it was announced that Mark Shuttleworth
had become the first Patron of KDE. On 7 July 2007, it was announced that Intel Corporation and Novell had also become patrons of KDE. In January 2010, Google became a supporting member. On 9 June 2010, KDE e.V. launched the "Join the Game" campaign. This campaign promotes the idea of becoming a supporting member for individuals. It is made available for those who would like to support KDE, but do not have enough time to do so. Georg Greve, founder of the Free Software Foundation Europe
(FSFE) was first to 'join the game'.
KDE-AR (KDE Argentina) is the group of KDE developers and users in Argentina, was officially opened in 22 November 2008 at the meeting in IRC channel. They can organize release parties on holidays to celebrate released of new version of the KDE SC since 4.2. KDE-AR has their own mailing lists and IRC channel.
KDE Brasil is composed by several local groups in Brazil, like KDE-MG, Live Blue, KDE Piauí, and KDE-RS. The main goals of local groups are regional promotion and direction of contributions of members, and still maintaining harmony with the KDE Brazil community. KDE-MG is a local group in Minas Gerais
. The idea of structuring the group was arose during the FISL (Fórum Internacional Software Livre) 10. Live Blue is a KDE working group in Bahia
. KDE Piauí is a group of users and contributors of KDE in the Piauí
. The ideia was born during the Software Freedom Day Teresina 2009 and has concretized during the Akademy-Br 2010, where the group was officially created. KDE-RS is a group of KDE users from Rio Grande do Sul
. KDE Lovelace is a Brazilian female group of users and contributors in KDE.
KDE España was registered as an association under the Spanish law in 2009. The aim is stimulating the development and use of the KDE software in Spain. The supreme governing body is general assembly, which is ordinary or extraordinary. The ordinary general assembly is held at least once a year. The extraordinary general assembly is held as necessary. The board consists of president, vice president, secretary, treasurer and members. Current board are Albert Astals Cid (president), Alejandro Fiestas Olivares (vice president), Aleix Pol i Gonzàlez (secretary), and José Millán Soto (treasurer). In addition, KDE España is the official representative of KDE e.V. in Spain.
KDE.in (KDE India) was founded in 2005, provide Indian KDE developers and users with a community hub to coordinate with and support each other. Besides making efforts in the internationalization and localization, a major aim is to foster the creation and adaptation of KDE applications to needs specific to India.
is Japanese local users' group of KDE. The membership type of the association are and . About 15 member is active staff. The officers include one , two and one accountant. Currently, president is , vice presidents are and . The association will hold an annual general assembly in December. It's activities include message translation to Japanese, making patch for multilingualization, and exchanging information about KDE/Qt.
KDE GB is a KDE community with a constitution in Britain. At October 2010 meeting they agreed to register as a charity. KDE-ir (فارسی KDE) is a Persian KDE community. Korean KDE Users Group was started in 1999. The group's work is mostly translation.
s, and conferences. The community has the Code of Conduct for acceptable behaviour within the community.
The mailing list
s are one of the main communication channels, and most problems are discussed on here. The community has several mailing lists, has two general user lists: Kde for discussion of users, and Kde-announce for version updates, security patches and other changes. And two general development lists: Kde-devel, for communication of application developers, and Kde-core-devel for communication of development of KDE Platform
. Many applications also have specific mailing lists.
KDE Community Forums is also activity in discuss. The forums have Brainstorm for user submit ideas to developers. The wish can be approved or disapproved by other users. Every few months, the highest-voted features will then be submitted to the developers. The forums have IRC bots that can announce new threads and posts on IRC channels, briding forum posts to mailinglist messages and offering RSS feeds.
KDE has three wikis: UserBase, TechBase and Community Wiki. UserBase provides documentation for end user. It contains tutorials, links to where to get more help, as well as an application catalogue. The logo is designed by Eugene Trounev. TechBase provides technical documentation for developers and system administrators. Community Wiki provides a place for coordinating community teams. It is used for publishing and sharing community-internal information.
And IRC
channels is real-time discuss way. Planet KDE is made from the blogs of KDE's contributors. KDE.News
is the website of office news announcements. KDE Buzz tracks identi.ca, Twitter, Picasa, Flickr and YouTube to show social media activity concerning KDE. KDE Pastebin allows for posting of source code snippets and uses syntax highlighting which adds ease to reviewing code. The pastes can be password protected. And use RSS notification to get aware of new posts. KDE Bug Tracking System provides anyone, who report bugs that was found in the software. Bug tracking uses Bugzilla
. Behind KDE is a site that interviews contributor of KDE.
is a green dragon named Konqi
. Konqi has a girlfriend named Katie. Konqi and Katie made their costumed appearance at the KDE 4.0 Release Event and Camp KDE 2010. Konqi also appeared on the KDE software's about dialog. Kandalf the wizard was the former mascot for the KDE community during its 1.x and 2.x versions, but he was dropped owing to copyright issues (his resemblance to Gandalf
).
KDE has community identity guidelines (CIG) for definitions and recommendations which help the community to establish a unique, characteristic, and appealing design. The KDE official logo displays the white trademarked K-Gear shape on a blue square with mitred corners.Copying of the KDE Logo is subject to the LGPL. Some local community logos are derivations of the official logo. The KDE software labels are used by producers of software to show that they are part of the KDE community or that they use the KDE Platform. There are three labels available. The Powered by KDE label is used to show that an application derives its strength from the KDE community and from the KDE development platform. The Built on the KDE Platform label indicates that the application uses the KDE platform. The Part of the KDE family label is used by application authors to identify themselves as being part of the KDE community.
Many KDE applications have a K in the name, mostly as an initial letter. The K in many KDE applications is obtained by spelling a word which originally begins with C or Q differently, for example Konsole
and Kaffeine
. Also, some just prefix a commonly used word with a K, for instance KGet
. Among KDE SC 4 applications and technologies, however, the trend is not to have a K in the name at all, such as Stage and Dolphin
.
Like many free/open source software projects, KDE is primarily a volunteer effort, although various companies, such as Novell
, Nokia
, and Mandriva
, employ developers to work on the project. Since a large number of individuals contribute to KDE in various ways (e.g. code, translation, artwork), organization of such a project is complex.
is made on the KDE Core Team. These are developers who have made significant contributions to KDE over a long period of time. This team communicates using the kde-core-devel mailing list, which is publicly archived and readable, but joining requires approval. KDE does not have a single central leader who can veto important decisions. Instead, the KDE core team consisting of several dozen contributors takes decisions. The decisions do not take a formal vote, but through discussions. The Developers also organize alongside topical teams. For example, the KDE Edu team
develops free educational software. While these teams work mostly independent and do not all follow a common release schedule. Each team has its own messaging channels, both on IRC and on the mailinglists. And they have mentor program which helps beginner to get start.
Currently KDE community uses the Git
repository. KDE Projects site gives an overview of all projects within Git repository. QuickGit is another repository browser. It shows all the git repositories. ReviewBoard site gives patch review. Commitfilter will send an email with each commit for the projects you want to watch, without either getting tons of mails or getting infrequent and redundant information. English Breakfast Network (EBN) is a collection of machines that do automated KDE source artifact quality checking. The EBN provides KDE API documentation validation, user documentation validation, source code checking. It is operated by Adriaan de Groot
and Allen Winter. Commit-Digest site gives a weekly overview of the development activity. LXR indexes classes and methods used in KDE.
Season of KDE (SoK) is a program for people could not get accepted into Google Summer of Code. They will have a mentor from the KDE community to help them if any question arises or if they do not know how to continue.
On 20 July 2009, KDE announced that the one millionth commit has been made to its Subversion repository. On October 11, 2009, Cornelius Schumacher
, a main developer within KDE, wrote about the estimated cost (using the COCOMO
model with SLOCCount) to develop KDE software package with 4,273,291 LoC, which would be about US$175,364,716. This estimation does not include Qt, Calligra Suite, Amarok, Digikam
, and other applications that are not part of KDE core.
The work can be measured in figures:
make KDE accessible to all users, including those with physical handicaps. The Artists team has designed most of the artwork used by the software like icons, wallpapers and themes. They have also produced graphics for t-shirts and websites. Discuss of the team is most active on the IRC channel. The Bugsquad team keeps track of incoming bugs. They verify that a
bug exists, that it is reproducible, and that the reporter has given enough
information. The goal is to help developers notice valid bugs quicker, and to save their time. The Documentation team writing documentation for application. The team uses the DocBook
format and custom tools to create documentation. The Localization team translate KDE software into many different languages. This team works beside the Documentation team. The Marketing and Promotion team manages marketing and promotion. The team writes news articles, release announcements and other webpages on KDE websites. The articles of KDE.News is submitted by the team. It also has channels at social media sites for communication and promotion. They also attend conference events. The Research team is to improve the collaboration with external parties to achieve more funded research. They support community members by providing information, navigating bureaucracies, and matching research partners. The usability team has written a Human Interface Guideline
(HIG) for the developers and they do regular reviews of KDE applications. The HIG provides a standardized layout. The Web team maintains KDE’s web presence. The KDE Women help women to contribute and encourage women to give talks at conferences.
The Release team defines and executes the official software releases. The Team is responsible for setting release schedules for the official releases. This includes release dates, deadlines for individual release steps and restrictions for code changes. The Release Team coordinates release dates with the marketing and press efforts of KDE. The release team is composed of Module Coordinators, Marketing Team liaison, and the people who actually do the work of tagging and creating the releases.
is the annual world summit, held each summer at varying venues in Europe. The primary goals of Akademy are to act as a community building event, to communicate the achievements of community, and to provide a platform for collaboration with community and industry partners. Secondary goals are to engage local people, and to provide space for getting together to write code. KDE e.V.
assist with procedures, advice and organization. Akademy including conference, KDE e.V. general assembly, marathon coding sessions, BOFs (birds of a feather
sessions) and social program. BOFs are meet to discuss specific sub-projects or issues.
The KDE community held KDE One that was first conference in Arnsberg
, Germany in 1997 to discuss the first KDE release. Initially, each conference was numbered after the release, and not regular hold. Since 2003 the conferences were hold one a year. And they were named Akademy since 2004.
The yearly Akademy conference gives Akademy Awards, are awards that the KDE community gives to KDE contributors. Their purpose is to recognize outstanding contribution to KDE. There are three awards, best application, best non-application and jury's award. As always the winners are chosen by the winners from the previous year. First winners received a framed picture of Konqi
signed by all attending KDE developers.
Camp KDE is another annual contributor’s conference of the KDE community. The event provides a regional opportunity for contributors and enthusiasts to gather and share their experiences. It's free to all participants. It is intended to ensure that KDE in the world is not simply seen as being Euro-centric. The KDE e.V. helps travel and accommodation subsidies for presenters, BoF leaders, organizers or core contributor. It is held in the North America since 2009.
In January 2008, KDE 4.0 Release Event was held at the Google headquarters in Mountain View, California, USA to celebrate the release of KDE SC 4.0. The community realized that there was a strong demand for KDE events in the Americas, therefore Camp KDE was produced.
Camp KDE 2009 was the premiere meeting of the KDE Americas, was held at the Travellers Beach Resort in Negril, Jamaica, sponsored by Google, Inte, iXsystem, KDE e.V. and Kitware. The event included 1-2 days of presentations, BoF meetings and hackathon
sessions. Camp KDE 2010 took place at the University of California San Diego (UCSD) in La Jolla, USA. The schedule included presentations, BoFs, hackathons and a day trip. It started with a short introduction by Jeff Mitchell, who was the principal organizer of the conference, talked a bit of history about Camp KDE and some statistics about the KDE community. The talks of the event were relatively well attended, and an increase over the previous year to around 70 people. On 1/19, the social event was a tour of a local brewery. Camp KDE 2011 was held at Hotel Kabuki in San Francisco, USA, was co-located with the Linux Foundation Collaboration Summit. The schedule included presentations, hackathons and a party at Noisebridge. The conference opened with a introduction spoken by Celeste Lyn Paul
.
Akademy-es is a conference for Spanish community since 2006, aimed at Spanish speakers. The event is organized by Spanish local organization. KDE España organizes the event since 2008. The annual KDE España Assembly took place during the event.
Akademy-es 2006 was held at Espai Jove Bocanord in Barcelona, organized by Badopi. Akademy-es 2007 was hosted by Hispalinux, Wireless Zaragoza, and the Zaragoza council. Akademy-es 2008 was held at University of A Coruña
, was organized by the KDE España and GPUL, sponsored by Oficina de Software Libre de la Universidad de Coruña, Mancomun, Igalia, Qt Software and eyeOs. Akademy-es 2009 was held in the University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. Akademy-es 2010 was held in the Engineering Technical School of Bilbao, was organized by KDE España and Itsas. There were approximately 80 participants. The KDE España Assembly elected the new board consists of Albert Astals Cid (president), Rafael Fernández López (vice president), Aleix Pol (secretary), and José Millán Soto (treasurer). Akademy-es 2011 was organized by KDE España, was sponsored by Google and Nokia, and was supported by the Linux and Todo-Linux magazines. The event was held in the in two different locations: the Polytechnic University of Catalunya for presentations of fist day, The School of Sant Marc de Sarrià for last two day.
conf.KDE.in is the first KDE and Qt conference in India. The conference was organized by KDE India, was held at R.V. College of Engineering in Bengaluru, India. The first three days of the event had talks, tutorials and interactive sessions. The last two days were a focused code sprint. The conference was opened by its main organiser Pradeepto Bhattacharya, over 300 people were at the opening talks. The Lighting of the Auspicious Lamp ceremony was performed to open the conference. The first session was by Lydia Pintscher who talk "So much to do – so little time". At the event, Project Neon announced return on Mar 11, 2011, provides nightly builds of the KDE Software Compilation. Closing the conference was keynote speaker and old-time KDE developer Sirtaj.
Día KDE (KDE Day) is a Argentinian event focused on KDE. It gives talks and workshops. The purpose of the event are: spread the free software movement among the population of Argentina, bringing to it the KDE community and environment developed by it, to know and strengthen KDE-AR, and generally bring the community together to have fun. The event is free.
Release party is a party, which celebrates released of new version of the KDE SC (twice a year). KDE also participates other conferences that around free software.
. They also create a sprint landing page on the community wiki, which give a brief summary of the sprint and link to relevant material.
KDE PIM Meeting is the annual meeting of KDE PIM team, held in Osnabrück
, Germany since 2003. Akonadi Sprint is anther meeting of KDE PIM team since 2007; it focus on Akonadi
. Calligra Sprint is the meeting of designers and developers of Calligra Suite. Usually the meetings are held in Berlin
, Germany. Krita Sprint is the meeting of Krita
team since 2009. KDE Education Meeting is the meeting of KDE Edu team
. KDE Marble sprint is the meeting of Marble team, held in Nürnberg, Germany. KDE Games Sprint is the meeting of KDE Games team. KDE Imaging Sprint is a sprint for KDE photography applications. Tokamak is the meeting of designers and developers of Plasma, KWin
, and Oxygen
since 2008. KDE Finances Sprint is the meeting of developers from KMyMoney
, Kraft and Skrooge. Promo sprint is the meeting, which discuses KDE Marketing and Promo.
consists of the libraries and services needed to run KDE applications. libraries include: Solid
, Nepomuk
, Phonon
, etc. Packages include: kdelibs, kdepimlibs and kdebase-runtime. The libraries must be licensed under one of the LGPL, BSD license, MIT License
and X11 license. While the Platform is mainly written in C++, it includes bindings for other programming languages.
, KDM, Plasma core libraries, Klipper
, KSysguard
, and System Settings
. There are different available GUI
environments: Plasma Desktop for desktop computers, Plasma Netbook for netbooks, Plasma Mobile for smartphones and Plasma Tablet for Tablet PCs.
, KTorrent
, Kexi
and KDE Partition Manager
. KDE applications can potentially be portable between operating systems and independent of a particular workspace or desktop environment. Some brands identify application suites built up from several applications, such as KDE Network
, KDE Graphics
and KDE Utilities
. Some applications are part of the regular Software Compilation releases, others are part of Extragear and release to their own schedule.
systems, Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows. CMake
serves as the build tool. This allows KDE to support a wider range of platforms, including Microsoft Windows. GNU gettext is used for translation. Doxygen
is used to generate api documentation.
syntax highlighting in Kate
and accessing Wikipedia
content within KDE applications, such as Amarok and Marble.
On 4 April 2008, the KDE e.V.
and Wikimedia Deutschland have opened shared offices in Frankfurt
. In September 2009 KDE e.V. moved to shared offices with Free Software Foundation Europe
in Berlin, so Wikimedia Foundation now uses the Frankfurt offices for themselves.
(FSFE).
On 22 August 2008, KDE e.V. and FSFE announced that after working with FSFE’s Freedom Task Force one and a half years KDE adopts FSFE’s Fiduciary Licence Agreement. Using that, KDE developers can – on a voluntary basis – assign their copyrights to KDE e.V.
In September 2009, KDE e.V. and FSFE moved into shared offices in Berlin.
Nokia use Calligra Suite as base for their Office Viewer application for Maemo
/MeeGo
. They have also been contracting KO GmbH to bring MS Office 2007 file format filters to Calligra. Nokia also employs several KDE developers directly – either to use KDE software for MeeGo (e.g. KCal) or as sponsorship.
The software development and consulting companies Intevation GmbH of Germany and the Swedish KDAB use Qt and KDE software – especially Kontact
and Akonadi
for Kolab
– for their services and products, therefore both employ KDE developers.
, an effort to standardize Unix desktop interoperability.
Since 2009, GNOME
and KDE co-host their conferences Akademy and GUADEC every two years under the Desktop Summit label.
In December 2010 KDE e.V. became a licensee of the Open Invention Network
.
Many Linux distribution
s and other free operating systems are involved in the development and distribution of the software, and are therefore also active in the KDE community. These include commercial distributors such as Novell, Mandriva, Red Hat, or Canonical, but also government-funded non-commercial organizations such as the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey with its Linux distribution Pardus.
Germany uses KDE software in its embassies around the world, representing around 11,000 systems. Through use of Pardus, a local Linux distribution, many sections of the Turkish government make use of KDE software, including the Turkish Armed Forces
, Ministry of Foreign Affairs
, Ministry of National Defence
, Turkish Police, and the SGK (Social Security Institution of Turkey), although these departments often do not exclusively use Pardus as their operating system. The CERN
(European Organization for Nuclear Research) built the Large Hadron Collider
in Switzerland, one of the world’s largest science experiments, using KDE software.
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
community producing an integrated set of cross-platform
Cross-platform
In computing, cross-platform, or multi-platform, is an attribute conferred to computer software or computing methods and concepts that are implemented and inter-operate on multiple computer platforms...
applications designed to run on Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
, FreeBSD
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free Unix-like operating system descended from AT&T UNIX via BSD UNIX. Although for legal reasons FreeBSD cannot be called “UNIX”, as the direct descendant of BSD UNIX , FreeBSD’s internals and system APIs are UNIX-compliant...
, Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
, Solaris and Mac OS X systems. It is best known for its Plasma Desktop, a desktop environment
Desktop environment
In graphical computing, a desktop environment commonly refers to a style of graphical user interface derived from the desktop metaphor that is seen on most modern personal computers. These GUIs help the user in easily accessing, configuring, and modifying many important and frequently accessed...
provided as the default working environment on many Linux distributions, such as Kubuntu
Kubuntu
Kubuntu is an official derivative of the Ubuntu operating system using the KDE Plasma Desktop instead of the Unity graphical environment. It is part of the Ubuntu project and uses the same underlying system. It is possible to install both the KDE Plasma Desktop as well as the Unity desktop on...
, Pardus
Pardus (operating system)
Pardus is a Linux distribution developed with support from the Turkish government. Pardus’ main focus is office-related work, including the use in Turkish government agencies. Despite that, Pardus ships in several languages. Its ease of use and availability free of charge spawned numerous...
and openSUSE
OpenSUSE
openSUSE is a general purpose operating system built on top of the Linux kernel, developed by the community-supported openSUSE Project and sponsored by SUSE...
.
The goal of the community is to provide basic desktop functions and applications for daily needs as well as tools and documentation for developers to write stand-alone applications for the system. In this regard, the KDE project serves as an umbrella project for many standalone applications and smaller projects that are based on KDE technology. These include Calligra Suite, digiKam
DigiKam
digiKam is an image organizer and editor using KDE Platform. It runs on most known desktop environments and window managers if the required libraries are installed. It supports all major image file formats, and can organize collections of photographs in directory-based albums, or dynamic albums by...
, Rekonq
Rekonq
rekonq is a lightweight, QtWebKit-based web browser developed inside the free software project KDE. It is the default web browser in Kubuntu 10.10 and Chakra GNU/Linux.rekonq has been officially included into KDE Extragear the 2010-05-25...
, K3b
K3b
K3b is a CD and DVD authoring application by KDE for Unix-like computer operating systems. It provides a graphical user interface to perform most CD/DVD burning tasks like creating an Audio CD from a set of audio files or copying a CD/DVD, as well as more advanced tasks such as burning eMoviX...
and many others.
KDE software is based on the Qt framework. The original GPL
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....
version of this toolkit only existed for the X11 platform, but with the release of Qt 4, LGPL
GNU Lesser General Public License
The GNU Lesser General Public License or LGPL is a free software license published by the Free Software Foundation . It was designed as a compromise between the strong-copyleft GNU General Public License or GPL and permissive licenses such as the BSD licenses and the MIT License...
versions are available for all platforms. This allows KDE software based on Qt 4 to also be distributed to Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
.
Origins

Matthias Ettrich
Matthias Ettrich is a German computer scientist known for his contributions to the KDE and LyX projects.- School :...
, who was then a student at the Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen
Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen
Eberhard Karls University, Tübingen is a public university located in the city of Tübingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of Germany's oldest universities, internationally noted in medicine, natural sciences and the humanities. In the area of German Studies it has been ranked first among...
. At the time, he was troubled by certain aspects of the Unix
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
desktop. Among his concerns was that none of the applications
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
looked, felt, or worked alike. He proposed the creation of not merely a set of applications but a desktop environment in which users could expect things to look, feel, and work consistently. He also wanted to make this desktop easy to use; one of his complaints about desktop applications of the time was that his girlfriend could not use them. His initial Usenet
Usenet
Usenet is a worldwide distributed Internet discussion system. It developed from the general purpose UUCP architecture of the same name.Duke University graduate students Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979 and it was established in 1980...
post spurred a lot of interest, and the KDE project was born.
The name KDE was intended as a wordplay on the existing Common Desktop Environment
Common Desktop Environment
The Common Desktop Environment is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit.- Corporate history :...
, available for Unix systems. CDE was an X11-based user environment jointly developed by HP, IBM, and Sun through the X/Open
X/Open
X/Open Company, Ltd. was a consortium founded by several European UNIX systems manufacturers in 1984 to identify and promote open standards in the field of information technology. More specifically, the original aim was to define a single specification for operating systems derived from UNIX, to...
consortium, with an interface and productivity tools based on the Motif
Motif (widget toolkit)
In computing, Motif refers to both a graphical user interface specification and the widget toolkit for building applications that follow that specification under the X Window System on Unix and other POSIX-compliant systems. It emerged in the 1980s as Unix workstations were on the rise, as a...
graphical widget toolkit. It was supposed to be an intuitively easy-to-use desktop computer
environment. The K was originally suggested to stand for "Kool", but it was quickly decided that the K should stand for nothing in particular. The KDE initialism is therefore expanded to "K Desktop Environment".
Product releases

Trolltech
Qt Development Frameworks is an Oslo, Norway-based software company best known for its Qt toolkit and application framework. Qt Development Frameworks is a wholly owned subsidiary of Nokia Corporation...
Qt framework for the KDE project. Other programmers quickly started developing KDE/Qt applications, and by early 1997, a few applications were being released. On 12 July 1998 the first version of the desktop environment, called KDE 1.0, was released.
| Version | Date | Information |
|---|---|---|
| October 14, 1996 | KDE development announced | |
| 1.0 | July 12, 1998 | |
| 2.0 | October 23, 2000 | |
| 3.0 | April 3, 2002 | |
| 4.0 | January 11, 2008 |
Licensing
In November 1998, the Qt framework was dual-licensed under the free and open sourceFree and open source software
Free and open-source software or free/libre/open-source software is software that is liberally licensed to grant users the right to use, study, change, and improve its design through the availability of its source code...
Q Public License
Q Public License
The Q Public License is a non-copyleft license, created by Trolltech for its free edition of the Qt. It was used until Qt 3.0, as Trolltech toolkit version 4.0 was released under GPL version 2...
(QPL) and a commercial license for proprietary software developers. The same year, the KDE Free Qt foundation was created which guarantees that Qt would fall under a variant of the very liberal BSD license should Trolltech cease to exist or no free version of Qt be released during 12 months.
Debate continued about compatibility with the GNU General Public License (GPL), hence in September 2000 Trolltech made the Unix version of the Qt libraries available under the GPL in addition to the QPL which eliminated the concerns of the Free Software Foundation
Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation is a non-profit corporation founded by Richard Stallman on 4 October 1985 to support the free software movement, a copyleft-based movement which aims to promote the universal freedom to create, distribute and modify computer software...
. Trolltech continued to require licenses for developing proprietary software
Proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
with Qt. The core libraries of KDE are collectively licensed under the GNU LGPL but the only way for proprietary software to make use of them was to be developed under the terms of the Qt proprietary license.
Starting with Qt 4.5, Qt was also made available under the LGPL version 2.1, now allowing proprietary applications to legally use the open source Qt version.
Brand repositioning
On 24 November 2009 the KDE Marketing Team announced an official rebrandingRebranding
Rebranding is the creation of a new name, term, symbol, design, or a combination of them for an established brand with the intention of developing a differentiated position in the mind of stakeholders and competitors....
of the KDE project components, motivated by the perceived shift from building a desktop environment to a complete project around a community of "people who create software". The rebranding focused on de-emphasizing the desktop environment as "just another product", and emphasizing both the community and the other technologies provided as KDE software. After the repositioning, the name KDE no longer stands for K Desktop Environment, as it now acts as an umbrella brand for software produced by the community. What would have been previously known as KDE 4.4 will now be referred as "KDE Software Compilation 4.4" (abbreviated "KDE SC 4.4"). Regardless, many users still refer to it as KDE 4.
Organization
The financial and legal matters of KDE are handled by KDE e.V.KDE e.V.
KDE e.V. is a registered non-profit organization that represents the KDE community in the legal and financial entities. The association supports KDE’s work in cash, hardware, and other donations, and then the use of donations to help the KDE development, but not influence on development. “e.V.”...
, which is a German non-profit organization, and help organizing the conferences and meetings of the community members. KDE e.V. helps running the servers needed by the KDE community. It owns the trademark
Trademark
A trademark, trade mark, or trade-mark is a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity to identify that the products or services to consumers with which the trademark appears originate from a unique source, and to distinguish its products or...
on KDE and the logo. It pays for travel to meetings, and subsidizes events. The working groups are a structure which will formalize some roles within KDE and enhance coordination within KDE, communication between parts of KDE. KDE e.V. has no influence on development. KDE e.V. logo has been contributed by David Vignoni
David Vignoni
David Vignoni is a graphical artist who specialises in icon design.Vignoni is the creator of the Nuvola icon set, which have been used in many projects including script.aculo.us and Prototype JavaScript Framework. He has designed icons for several web sites, including , , and...
. The three flags on top of the logo represent the three main tasks of the KDE e.V.: supporting the community, representing the community, and governing the community.
The KDE community's developer meetings, servers and related events are frequently sponsored by individuals, universities, and businesses. The supporting members of the KDE e.V. are extraordinary members supporting the KDE through financial or material contributions. Supporting members are entitled to display the "Member of KDE" logo on their website or in printed materials. The Patron of KDE is the highest level of supporting member. The patrons of KDE also are entitled to display the exclusive "Patron of KDE" logo on their website or in printed materials. On 15 October 2006, it was announced that Mark Shuttleworth
Mark Shuttleworth
Mark Richard Shuttleworth is a South African entrepreneur who was the second self-funded space tourist. Shuttleworth founded Canonical Ltd. and as of 2010, provides leadership for the Ubuntu operating system...
had become the first Patron of KDE. On 7 July 2007, it was announced that Intel Corporation and Novell had also become patrons of KDE. In January 2010, Google became a supporting member. On 9 June 2010, KDE e.V. launched the "Join the Game" campaign. This campaign promotes the idea of becoming a supporting member for individuals. It is made available for those who would like to support KDE, but do not have enough time to do so. Georg Greve, founder of the Free Software Foundation Europe
Free Software Foundation Europe
The Free Software Foundation Europe was founded in 2001 as an official European sister organization of the U.S.-based Free Software Foundation to take care of all aspects of free software in Europe. FSF and FSFE are financially and legally separate entities.FSFE believes that access to and...
(FSFE) was first to 'join the game'.
Local community
In many countries, KDE has local branches. These are either informal organizations (KDE India) or like the KDE e.V., given a legal form (KDE France). The local organizations hosts and maintains a regional website, and organising local events, such as tradeshows, contributor meetings and social community meetings.KDE-AR (KDE Argentina) is the group of KDE developers and users in Argentina, was officially opened in 22 November 2008 at the meeting in IRC channel. They can organize release parties on holidays to celebrate released of new version of the KDE SC since 4.2. KDE-AR has their own mailing lists and IRC channel.
KDE Brasil is composed by several local groups in Brazil, like KDE-MG, Live Blue, KDE Piauí, and KDE-RS. The main goals of local groups are regional promotion and direction of contributions of members, and still maintaining harmony with the KDE Brazil community. KDE-MG is a local group in Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais is one of the 26 states of Brazil, of which it is the second most populous, the third richest, and the fourth largest in area. Minas Gerais is the Brazilian state with the largest number of Presidents of Brazil, the current one, Dilma Rousseff, being one of them. The capital is the...
. The idea of structuring the group was arose during the FISL (Fórum Internacional Software Livre) 10. Live Blue is a KDE working group in Bahia
Bahia
Bahia is one of the 26 states of Brazil, and is located in the northeastern part of the country on the Atlantic coast. It is the fourth most populous Brazilian state after São Paulo, Minas Gerais and Rio de Janeiro, and the fifth-largest in size...
. KDE Piauí is a group of users and contributors of KDE in the Piauí
Piauí
Piauí is one of the states of Brazil, located in the northeastern part of the country.Piauí has the shortest coastline of any of the non-landlocked Brazilian states at 66 km , and the capital, Teresina, is the only state capital in the north east to be located inland...
. The ideia was born during the Software Freedom Day Teresina 2009 and has concretized during the Akademy-Br 2010, where the group was officially created. KDE-RS is a group of KDE users from Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul is the southernmost state in Brazil, and the state with the fifth highest Human Development Index in the country. In this state is located the southernmost city in the country, Chuí, on the border with Uruguay. In the region of Bento Gonçalves and Caxias do Sul, the largest wine...
. KDE Lovelace is a Brazilian female group of users and contributors in KDE.
KDE España was registered as an association under the Spanish law in 2009. The aim is stimulating the development and use of the KDE software in Spain. The supreme governing body is general assembly, which is ordinary or extraordinary. The ordinary general assembly is held at least once a year. The extraordinary general assembly is held as necessary. The board consists of president, vice president, secretary, treasurer and members. Current board are Albert Astals Cid (president), Alejandro Fiestas Olivares (vice president), Aleix Pol i Gonzàlez (secretary), and José Millán Soto (treasurer). In addition, KDE España is the official representative of KDE e.V. in Spain.
KDE.in (KDE India) was founded in 2005, provide Indian KDE developers and users with a community hub to coordinate with and support each other. Besides making efforts in the internationalization and localization, a major aim is to foster the creation and adaptation of KDE applications to needs specific to India.
is Japanese local users' group of KDE. The membership type of the association are and . About 15 member is active staff. The officers include one , two and one accountant. Currently, president is , vice presidents are and . The association will hold an annual general assembly in December. It's activities include message translation to Japanese, making patch for multilingualization, and exchanging information about KDE/Qt.
KDE GB is a KDE community with a constitution in Britain. At October 2010 meeting they agreed to register as a charity. KDE-ir (فارسی KDE) is a Persian KDE community. Korean KDE Users Group was started in 1999. The group's work is mostly translation.
Communication
The communication within the community takes place via mailing lists, IRC, blogs, forums, news announcements, wikiWiki
A wiki is a website that allows the creation and editing of any number of interlinked web pages via a web browser using a simplified markup language or a WYSIWYG text editor. Wikis are typically powered by wiki software and are often used collaboratively by multiple users. Examples include...
s, and conferences. The community has the Code of Conduct for acceptable behaviour within the community.
The mailing list
Mailing list
A mailing list is a collection of names and addresses used by an individual or an organization to send material to multiple recipients. The term is often extended to include the people subscribed to such a list, so the group of subscribers is referred to as "the mailing list", or simply "the...
s are one of the main communication channels, and most problems are discussed on here. The community has several mailing lists, has two general user lists: Kde for discussion of users, and Kde-announce for version updates, security patches and other changes. And two general development lists: Kde-devel, for communication of application developers, and Kde-core-devel for communication of development of KDE Platform
KDE Platform
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
. Many applications also have specific mailing lists.
KDE Community Forums is also activity in discuss. The forums have Brainstorm for user submit ideas to developers. The wish can be approved or disapproved by other users. Every few months, the highest-voted features will then be submitted to the developers. The forums have IRC bots that can announce new threads and posts on IRC channels, briding forum posts to mailinglist messages and offering RSS feeds.
KDE has three wikis: UserBase, TechBase and Community Wiki. UserBase provides documentation for end user. It contains tutorials, links to where to get more help, as well as an application catalogue. The logo is designed by Eugene Trounev. TechBase provides technical documentation for developers and system administrators. Community Wiki provides a place for coordinating community teams. It is used for publishing and sharing community-internal information.
And IRC
Internet Relay Chat
Internet Relay Chat is a protocol for real-time Internet text messaging or synchronous conferencing. It is mainly designed for group communication in discussion forums, called channels, but also allows one-to-one communication via private message as well as chat and data transfer, including file...
channels is real-time discuss way. Planet KDE is made from the blogs of KDE's contributors. KDE.News
KDE Dot News
KDE.News is the official news website for the KDE community. It including KDE development and user news, discussions, feature articles and more. Most stories are summaries of things published elsewhere, some are interviews with KDE developers...
is the website of office news announcements. KDE Buzz tracks identi.ca, Twitter, Picasa, Flickr and YouTube to show social media activity concerning KDE. KDE Pastebin allows for posting of source code snippets and uses syntax highlighting which adds ease to reviewing code. The pastes can be password protected. And use RSS notification to get aware of new posts. KDE Bug Tracking System provides anyone, who report bugs that was found in the software. Bug tracking uses Bugzilla
Bugzilla
Bugzilla is a Web-based general-purpose bugtracker and testing tool originally developed and used by the Mozilla project, and licensed under the Mozilla Public License....
. Behind KDE is a site that interviews contributor of KDE.
Identity
The KDE community’s mascotMascot
The term mascot – defined as a term for any person, animal, or object thought to bring luck – colloquially includes anything used to represent a group with a common public identity, such as a school, professional sports team, society, military unit, or brand name...
is a green dragon named Konqi
Konqi
Konqi Konqueror is the current mascot for the KDE community, a small cheerful green dragon. He appears in KDE software, and on many websites, including the KDE homepage. The name "Konqi" was chosen after Konqueror, the KDE web- and file browser. His creator is Stefan Spatz. Konqi appears in 3.x...
. Konqi has a girlfriend named Katie. Konqi and Katie made their costumed appearance at the KDE 4.0 Release Event and Camp KDE 2010. Konqi also appeared on the KDE software's about dialog. Kandalf the wizard was the former mascot for the KDE community during its 1.x and 2.x versions, but he was dropped owing to copyright issues (his resemblance to Gandalf
Gandalf
Gandalf is a character in J. R. R. Tolkien's novels The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings. In these stories, Gandalf appears as a wizard, member and later the head of the order known as the Istari, as well as leader of the Fellowship of the Ring and the army of the West...
).
KDE has community identity guidelines (CIG) for definitions and recommendations which help the community to establish a unique, characteristic, and appealing design. The KDE official logo displays the white trademarked K-Gear shape on a blue square with mitred corners.Copying of the KDE Logo is subject to the LGPL. Some local community logos are derivations of the official logo. The KDE software labels are used by producers of software to show that they are part of the KDE community or that they use the KDE Platform. There are three labels available. The Powered by KDE label is used to show that an application derives its strength from the KDE community and from the KDE development platform. The Built on the KDE Platform label indicates that the application uses the KDE platform. The Part of the KDE family label is used by application authors to identify themselves as being part of the KDE community.
Many KDE applications have a K in the name, mostly as an initial letter. The K in many KDE applications is obtained by spelling a word which originally begins with C or Q differently, for example Konsole
Konsole
Konsole is a free terminal emulator which is part of KDE Software Compilation. Konsole was originally written by Lars Doelle.The KDE applications Konqueror, Krusader, Kate, Konversation, Dolphin and KDevelop use Konsole to provide embedded terminal functionality.- Features :* Tabbed terminals...
and Kaffeine
Kaffeine
Kaffeine is a media player for Unix-like operating systems running KDE.By default it uses xine-lib media framework but also supports GStreamer. It also supports the use of MPlayer project's binary codecs for proprietary formats...
. Also, some just prefix a commonly used word with a K, for instance KGet
KGet
KGet is a free download manager for KDE. By default it is the download manager used for Konqueror, but can also be used with Mozilla Firefox. KGet is part of the KDE Network package, and was featured by Tux Magazine and Free Software Magazine.-History:...
. Among KDE SC 4 applications and technologies, however, the trend is not to have a K in the name at all, such as Stage and Dolphin
Dolphin (software)
Dolphin is a free and open source software file manager for and part of the KDE Software Compilation. It is the default file manager in the current version, KDE Software Compilation 4, and can be optionally installed on K Desktop Environment 3...
.
Contributors
| Featured Partners | |
|---|---|
| Name | Work |
| Nuno Pinheiro Nuno Pinheiro (artist) Nuno Pinheiro is a Portuguese graphic designer and illustrator. He specializes in iconography, themes and user interface design. Nuno's works include general illustrations, UI design, Web design, corporate design as well as other work's in creative areas... |
Oxygen |
| David Vignoni David Vignoni David Vignoni is a graphical artist who specialises in icon design.Vignoni is the creator of the Nuvola icon set, which have been used in many projects including script.aculo.us and Prototype JavaScript Framework. He has designed icons for several web sites, including , , and... |
Oxygen |
| Eugene Trounev | Artists |
| Aaron Seigo Aaron Seigo Aaron Joseph Seigo is a Canadian open source software developer who lives in Zürich, Switzerland. He has been a KDE contributor since KDE 2 alphas release in 2000.... |
Develop |
| David Faure | Develop |
| Duncan Mac-Vicar Prett | Develop |
| Dirk Müller | Release, Develop |
| George Staikos | Develop |
| Lars Knoll | Develop |
| Volker Krause | Develop |
| Waldo Bastian | Develop |
| Sebastian Kügler | Marketing team liaison |
| Stuart Jarvis | Marketing and public relations |
Like many free/open source software projects, KDE is primarily a volunteer effort, although various companies, such as Novell
Novell
Novell, Inc. is a multinational software and services company. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of The Attachmate Group. It specializes in network operating systems, such as Novell NetWare; systems management solutions, such as Novell ZENworks; and collaboration solutions, such as Novell Groupwise...
, Nokia
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational communications corporation that is headquartered in Keilaniemi, Espoo, a city neighbouring Finland's capital Helsinki...
, and Mandriva
Mandriva
Mandriva S.A. is a publicly traded Linux and open source software company with its headquarters in Paris, France and development center in Curitiba, Brazil. Mandriva, S.A...
, employ developers to work on the project. Since a large number of individuals contribute to KDE in various ways (e.g. code, translation, artwork), organization of such a project is complex.
Development
The overall direction of the KDE PlatformKDE Platform
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
is made on the KDE Core Team. These are developers who have made significant contributions to KDE over a long period of time. This team communicates using the kde-core-devel mailing list, which is publicly archived and readable, but joining requires approval. KDE does not have a single central leader who can veto important decisions. Instead, the KDE core team consisting of several dozen contributors takes decisions. The decisions do not take a formal vote, but through discussions. The Developers also organize alongside topical teams. For example, the KDE Edu team
KDE Education Project
The KDE Education Project develops free educational software based on the KDE technologies.- History :The KDE Education project was started in July 2001.- List of software :This software is bundled in the kdeedu package.- Languages :...
develops free educational software. While these teams work mostly independent and do not all follow a common release schedule. Each team has its own messaging channels, both on IRC and on the mailinglists. And they have mentor program which helps beginner to get start.
Currently KDE community uses the Git
Git (software)
Git is a distributed revision control system with an emphasis on speed. Git was initially designed and developed by Linus Torvalds for Linux kernel development. Every Git working directory is a full-fledged repository with complete history and full revision tracking capabilities, not dependent on...
repository. KDE Projects site gives an overview of all projects within Git repository. QuickGit is another repository browser. It shows all the git repositories. ReviewBoard site gives patch review. Commitfilter will send an email with each commit for the projects you want to watch, without either getting tons of mails or getting infrequent and redundant information. English Breakfast Network (EBN) is a collection of machines that do automated KDE source artifact quality checking. The EBN provides KDE API documentation validation, user documentation validation, source code checking. It is operated by Adriaan de Groot
Adriaan de Groot (Software developer)
Adriaan de Groot is a researcher in software quality and formal verification. He lives in Nijmegen, Netherlands. He is KDE developer, member of KDE e.V. board and coordinator of KDE Netherlands. He's a KDE contributor since 2000. He work on portability, both to FreeBSD and to Solaris. Since 2007,...
and Allen Winter. Commit-Digest site gives a weekly overview of the development activity. LXR indexes classes and methods used in KDE.
Season of KDE (SoK) is a program for people could not get accepted into Google Summer of Code. They will have a mentor from the KDE community to help them if any question arises or if they do not know how to continue.
On 20 July 2009, KDE announced that the one millionth commit has been made to its Subversion repository. On October 11, 2009, Cornelius Schumacher
Cornelius Schumacher
Cornelius Schumacher is a German open source Software developer. He was born in Tübingen but lives in Erlangen, Germany. -Biography:...
, a main developer within KDE, wrote about the estimated cost (using the COCOMO
COCOMO
**********************************************************************************************The Constructive Cost Model is an algorithmic software cost estimation model developed by Barry W. Boehm...
model with SLOCCount) to develop KDE software package with 4,273,291 LoC, which would be about US$175,364,716. This estimation does not include Qt, Calligra Suite, Amarok, Digikam
DigiKam
digiKam is an image organizer and editor using KDE Platform. It runs on most known desktop environments and window managers if the required libraries are installed. It supports all major image file formats, and can organize collections of photographs in directory-based albums, or dynamic albums by...
, and other applications that are not part of KDE core.
The work can be measured in figures:
- Over 6 million lines of code. This does not include Qt.
- More than 1800 contributors help develop KDE. About 20 new developers contribute their first code each month.
- KDE is translated in over 108 languages.
- KDE has more than 114 official FTP mirrors in over 34 countries.
- The KDE community is the second largest Free Software community behind the Linux kernel community.
Other groups
The KDE community has many smaller teams working towards specific goals. The Accessibility teamKDE Accessibility Project
The goal of the KDE Accessibility Project is to ensure that the KDE Software Compilation is accessible to all users, including those with physical handicaps...
make KDE accessible to all users, including those with physical handicaps. The Artists team has designed most of the artwork used by the software like icons, wallpapers and themes. They have also produced graphics for t-shirts and websites. Discuss of the team is most active on the IRC channel. The Bugsquad team keeps track of incoming bugs. They verify that a
bug exists, that it is reproducible, and that the reporter has given enough
information. The goal is to help developers notice valid bugs quicker, and to save their time. The Documentation team writing documentation for application. The team uses the DocBook
DocBook
DocBook is a semantic markup language for technical documentation. It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software but it can be used for any other sort of documentation....
format and custom tools to create documentation. The Localization team translate KDE software into many different languages. This team works beside the Documentation team. The Marketing and Promotion team manages marketing and promotion. The team writes news articles, release announcements and other webpages on KDE websites. The articles of KDE.News is submitted by the team. It also has channels at social media sites for communication and promotion. They also attend conference events. The Research team is to improve the collaboration with external parties to achieve more funded research. They support community members by providing information, navigating bureaucracies, and matching research partners. The usability team has written a Human Interface Guideline
Human Interface Guidelines
Human interface guidelines are software development documents which offer application developers a set of recommendations. Their aim is to improve the experience for the users by making application interfaces more intuitive, learnable, and consistent. Most guides limit themselves to defining a...
(HIG) for the developers and they do regular reviews of KDE applications. The HIG provides a standardized layout. The Web team maintains KDE’s web presence. The KDE Women help women to contribute and encourage women to give talks at conferences.
The Release team defines and executes the official software releases. The Team is responsible for setting release schedules for the official releases. This includes release dates, deadlines for individual release steps and restrictions for code changes. The Release Team coordinates release dates with the marketing and press efforts of KDE. The release team is composed of Module Coordinators, Marketing Team liaison, and the people who actually do the work of tagging and creating the releases.
Activities
The two most important conferences of KDE are Akademy and Camp KDE. Each event is on a large scale, both thematically and geographically. Akademy-BR and Akademy-es are local community events.Akademy
AkademyAKademy
Akademy is an annual contributors and users conference of the KDE community. Akademy is held at varying venues in Europe....
is the annual world summit, held each summer at varying venues in Europe. The primary goals of Akademy are to act as a community building event, to communicate the achievements of community, and to provide a platform for collaboration with community and industry partners. Secondary goals are to engage local people, and to provide space for getting together to write code. KDE e.V.
KDE e.V.
KDE e.V. is a registered non-profit organization that represents the KDE community in the legal and financial entities. The association supports KDE’s work in cash, hardware, and other donations, and then the use of donations to help the KDE development, but not influence on development. “e.V.”...
assist with procedures, advice and organization. Akademy including conference, KDE e.V. general assembly, marathon coding sessions, BOFs (birds of a feather
Birds of a Feather (computing)
In computing, BoF can refer to:* An informal discussion group. Unlike special interest groups or working groups, BoFs are informal and often formed in an ad-hoc manner...
sessions) and social program. BOFs are meet to discuss specific sub-projects or issues.
The KDE community held KDE One that was first conference in Arnsberg
Arnsberg
Arnsberg is a town in the Hochsauerland district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the location of the Regierungsbezirk Arnsberg's administration and one of the three local administration offices of the Hochsauerlandkreis.-Geography:...
, Germany in 1997 to discuss the first KDE release. Initially, each conference was numbered after the release, and not regular hold. Since 2003 the conferences were hold one a year. And they were named Akademy since 2004.
The yearly Akademy conference gives Akademy Awards, are awards that the KDE community gives to KDE contributors. Their purpose is to recognize outstanding contribution to KDE. There are three awards, best application, best non-application and jury's award. As always the winners are chosen by the winners from the previous year. First winners received a framed picture of Konqi
Konqi
Konqi Konqueror is the current mascot for the KDE community, a small cheerful green dragon. He appears in KDE software, and on many websites, including the KDE homepage. The name "Konqi" was chosen after Konqueror, the KDE web- and file browser. His creator is Stefan Spatz. Konqi appears in 3.x...
signed by all attending KDE developers.
Camp KDE
| Year | Venue | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Negril Negril Negril is a small but widely dispersed beach resort town located across parts of two Jamaican parishes of Westmoreland and Hanover. Westmoreland is the westernmost parish in Jamaica, located on the south side of the island... , Jamaica Jamaica Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic... |
1/17-1/18 |
| 2010 | La Jolla, USA | 1/15-1/22 |
| 2011 | San Francisco, USA | 4/4-4/5 |
Camp KDE is another annual contributor’s conference of the KDE community. The event provides a regional opportunity for contributors and enthusiasts to gather and share their experiences. It's free to all participants. It is intended to ensure that KDE in the world is not simply seen as being Euro-centric. The KDE e.V. helps travel and accommodation subsidies for presenters, BoF leaders, organizers or core contributor. It is held in the North America since 2009.
In January 2008, KDE 4.0 Release Event was held at the Google headquarters in Mountain View, California, USA to celebrate the release of KDE SC 4.0. The community realized that there was a strong demand for KDE events in the Americas, therefore Camp KDE was produced.
Camp KDE 2009 was the premiere meeting of the KDE Americas, was held at the Travellers Beach Resort in Negril, Jamaica, sponsored by Google, Inte, iXsystem, KDE e.V. and Kitware. The event included 1-2 days of presentations, BoF meetings and hackathon
Hackathon
A hackathon, a hacker neologism, is an event when programmers meet to do collaborative computer programming. The spirit of a hackathon is to collaboratively build programs and applications. Hackathons are typically between several days and a week in length...
sessions. Camp KDE 2010 took place at the University of California San Diego (UCSD) in La Jolla, USA. The schedule included presentations, BoFs, hackathons and a day trip. It started with a short introduction by Jeff Mitchell, who was the principal organizer of the conference, talked a bit of history about Camp KDE and some statistics about the KDE community. The talks of the event were relatively well attended, and an increase over the previous year to around 70 people. On 1/19, the social event was a tour of a local brewery. Camp KDE 2011 was held at Hotel Kabuki in San Francisco, USA, was co-located with the Linux Foundation Collaboration Summit. The schedule included presentations, hackathons and a party at Noisebridge. The conference opened with a introduction spoken by Celeste Lyn Paul
Celeste Lyn Paul
Celeste Lyn Paul is an expert in interface design and usability. She is a contributor to KDE.-School:Celeste awarded B.A. in Multimedia at Duquesne University in 2003, and awarded M.S. in Interaction Design & Information Architecture at University of Baltimore in 2007...
.
Akademy-es
| Year | Venue | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Barcelona Barcelona Barcelona is the second largest city in Spain after Madrid, and the capital of Catalonia, with a population of 1,621,537 within its administrative limits on a land area of... |
3/3-3/5 |
| 2007 | Zaragoza Zaragoza Zaragoza , also called Saragossa in English, is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain... |
11/17-11/18 |
| 2008 | A Coruña A Coruña A Coruña or La Coruña is a city and municipality of Galicia, Spain. It is the second-largest city in the autonomous community and seventeenth overall in the country... |
11/21-11/23 |
| 2009 | Gran Canaria Gran Canaria Gran Canaria is the second most populous island of the Canary Islands, with a population of 838,397 which constitutes approximately 40% of the population of the archipelago... |
7/10-7/11 |
| 2010 | Bilbao Bilbao Bilbao ) is a Spanish municipality, capital of the province of Biscay, in the autonomous community of the Basque Country. With a population of 353,187 , it is the largest city of its autonomous community and the tenth largest in Spain... |
5/7-5/9 |
| 2011 | Barcelona | 5/20-5/22 |
Akademy-es is a conference for Spanish community since 2006, aimed at Spanish speakers. The event is organized by Spanish local organization. KDE España organizes the event since 2008. The annual KDE España Assembly took place during the event.
Akademy-es 2006 was held at Espai Jove Bocanord in Barcelona, organized by Badopi. Akademy-es 2007 was hosted by Hispalinux, Wireless Zaragoza, and the Zaragoza council. Akademy-es 2008 was held at University of A Coruña
University of A Coruña
The University of A Coruña is a public university located in the city of A Coruña, Galicia. Established in 1989, university departments are divided between two primary campuses in A Coruña and nearby Ferrol...
, was organized by the KDE España and GPUL, sponsored by Oficina de Software Libre de la Universidad de Coruña, Mancomun, Igalia, Qt Software and eyeOs. Akademy-es 2009 was held in the University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. Akademy-es 2010 was held in the Engineering Technical School of Bilbao, was organized by KDE España and Itsas. There were approximately 80 participants. The KDE España Assembly elected the new board consists of Albert Astals Cid (president), Rafael Fernández López (vice president), Aleix Pol (secretary), and José Millán Soto (treasurer). Akademy-es 2011 was organized by KDE España, was sponsored by Google and Nokia, and was supported by the Linux and Todo-Linux magazines. The event was held in the in two different locations: the Polytechnic University of Catalunya for presentations of fist day, The School of Sant Marc de Sarrià for last two day.
Other community events
Akademy-BR is addressed to Brazilian community since 2010. The purpose of the meeting is to gather and organize ideas Brazilian developers on how to help KDE in Brazil. Akademy-BR 2010 was organized by the local group named LiveBlue. There were thirty participants from all over the Brazil. Akademy-BR 2011 is organized by KDE-MG.| Akademy-BR | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Venue | Date |
| 2010 | Salvador Salvador, Bahia Salvador is the largest city on the northeast coast of Brazil and the capital of the Northeastern Brazilian state of Bahia. Salvador is also known as Brazil's capital of happiness due to its easygoing population and countless popular outdoor parties, including its street carnival. The first... |
4/9-4/11 |
| 2011 | São Paulo São Paulo São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among... |
11/12-11/15 |
| conf.KDE.in | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Venue | Date |
| 2011 | Bengaluru | 3/9-3/13 |
conf.KDE.in is the first KDE and Qt conference in India. The conference was organized by KDE India, was held at R.V. College of Engineering in Bengaluru, India. The first three days of the event had talks, tutorials and interactive sessions. The last two days were a focused code sprint. The conference was opened by its main organiser Pradeepto Bhattacharya, over 300 people were at the opening talks. The Lighting of the Auspicious Lamp ceremony was performed to open the conference. The first session was by Lydia Pintscher who talk "So much to do – so little time". At the event, Project Neon announced return on Mar 11, 2011, provides nightly builds of the KDE Software Compilation. Closing the conference was keynote speaker and old-time KDE developer Sirtaj.
Día KDE (KDE Day) is a Argentinian event focused on KDE. It gives talks and workshops. The purpose of the event are: spread the free software movement among the population of Argentina, bringing to it the KDE community and environment developed by it, to know and strengthen KDE-AR, and generally bring the community together to have fun. The event is free.
| Día KDE | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Venue | Date |
| 2011 | Rosario Rosario Rosario is the largest city in the province of Santa Fe, Argentina. It is located northwest of Buenos Aires, on the western shore of the Paraná River and has 1,159,004 residents as of the .... |
8/27 |
Release party is a party, which celebrates released of new version of the KDE SC (twice a year). KDE also participates other conferences that around free software.
Developer Sprints
In addition to Camp KDE and Akademy there are other conferences, which is called Developer Sprints. The Developer Sprints are focused gatherings of developers to work on a specific part of KDE. Usually there are 2–3 days meetings of around 10-15 people. The Developer Sprints include core people, but also least one or two newbie quota to get fresh developers into the community. They are supported by KDE e.V. financially and organizationally. It will also provide help and advice where needed and appropriate. The results of meetings are documented on the KDE.NewsKDE Dot News
KDE.News is the official news website for the KDE community. It including KDE development and user news, discussions, feature articles and more. Most stories are summaries of things published elsewhere, some are interviews with KDE developers...
. They also create a sprint landing page on the community wiki, which give a brief summary of the sprint and link to relevant material.
| Promo sprint | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Venue | Date |
| 2009 | Stuttgart Stuttgart Stuttgart is the capital of the state of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. The sixth-largest city in Germany, Stuttgart has a population of 600,038 while the metropolitan area has a population of 5.3 million .... , Germany |
|
| 2011 | Southampton Southampton Southampton is the largest city in the county of Hampshire on the south coast of England, and is situated south-west of London and north-west of Portsmouth. Southampton is a major port and the closest city to the New Forest... , England England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental... |
5/6-5/8 |
KDE PIM Meeting is the annual meeting of KDE PIM team, held in Osnabrück
Osnabrück
Osnabrück is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany, some 80 km NNE of Dortmund, 45 km NE of Münster, and some 100 km due west of Hanover. It lies in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest...
, Germany since 2003. Akonadi Sprint is anther meeting of KDE PIM team since 2007; it focus on Akonadi
Akonadi
Akonadi is a storage service for personal information management data and metadata named after the oracle goddess of justice in Ghana. It is one of the “pillars” behind the KDE SC 4 project, although it is designed to be used in any desktop environment...
. Calligra Sprint is the meeting of designers and developers of Calligra Suite. Usually the meetings are held in Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
, Germany. Krita Sprint is the meeting of Krita
Krita
Krita is the digital painting and illustration software included based on the KDE Platform and Calligra Suite libraries. Designed as a digital painting and illustration suite, Krita is free software and distributed under GNU General Public License...
team since 2009. KDE Education Meeting is the meeting of KDE Edu team
KDE Education Project
The KDE Education Project develops free educational software based on the KDE technologies.- History :The KDE Education project was started in July 2001.- List of software :This software is bundled in the kdeedu package.- Languages :...
. KDE Marble sprint is the meeting of Marble team, held in Nürnberg, Germany. KDE Games Sprint is the meeting of KDE Games team. KDE Imaging Sprint is a sprint for KDE photography applications. Tokamak is the meeting of designers and developers of Plasma, KWin
KWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System. It is an integral part of the KDE Software Compilation, although it can be used on its own or with other desktop environments.- History :- Look and feel :...
, and Oxygen
Oxygen Project
The Oxygen Project is a project created to give a visual refresh to KDE Plasma Workspaces.It consists of a set of computer icons, a window decoration for KWin, widget toolkit themes for GTK and Qt, and two themes for KDE Plasma Workspaces....
since 2008. KDE Finances Sprint is the meeting of developers from KMyMoney
KMyMoney
KMyMoney is the personal finance manager for KDE. It operates in a similar way to Microsoft Money. It supports different account types, categorisation of expenses and incomes, reconciliation of bank accounts and import/export to the “QIF” file format....
, Kraft and Skrooge. Promo sprint is the meeting, which discuses KDE Marketing and Promo.
Technology platform
The KDE technology platform consists of three parts: KDE Development Platform, KDE Workspace and KDE Applications.KDE Platform
KDE PlatformKDE Platform
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
consists of the libraries and services needed to run KDE applications. libraries include: Solid
Solid (KDE)
KDE Platform is a set of frameworks by KDE that serve as technological foundation for all KDE applications. Ever since KDE’s brand repositioning the Platform is released as separate product in sync with KDE’s Plasma Workspaces as part of the KDE Software Compilation 4...
, Nepomuk
NEPOMUK (framework)
NEPOMUK is an open-source software specification that is concerned with the development of a social semantic desktop that enriches and interconnects data from different desktop applications using semantic metadata stored as RDF...
, Phonon
Phonon (KDE)
Phonon is the multimedia API provided by Qt and is the standard abstraction for handling multimedia streams within the KDE Software Compilation 4....
, etc. Packages include: kdelibs, kdepimlibs and kdebase-runtime. The libraries must be licensed under one of the LGPL, BSD license, MIT License
MIT License
The MIT License is a free software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology . It is a permissive license, meaning that it permits reuse within proprietary software provided all copies of the licensed software include a copy of the MIT License terms...
and X11 license. While the Platform is mainly written in C++, it includes bindings for other programming languages.
Plasma Workspaces
The Plasma Workspaces provide the environment for running and managing applications. They include many components such as KWinKWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System. It is an integral part of the KDE Software Compilation, although it can be used on its own or with other desktop environments.- History :- Look and feel :...
, KDM, Plasma core libraries, Klipper
Klipper
Klipper is a clipboard manager for the KDE interface. It allows users of Unix-like operating systems running the KDE desktop environment to access a history of X Selections, any item of which can be reselected for pasting. It can also be used to react automatically if a certain text is selected...
, KSysguard
KDE System Guard
KDE System Guard, also known as KSysguard, is the KDE task manager and performance monitor. It can monitor both local and remote hosts. It can retrieve simple values or complex data such as tables and display this information in a variety of graphical displays. Displays can then be organized in...
, and System Settings
System Settings
System Settings is a KDE application which is used configure the system under KDE Plasma Workspaces. It replaces K Desktop Environment 3’s KControl.- Features :* Control Center for global KDE platform settings...
. There are different available GUI
Gui
Gui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
environments: Plasma Desktop for desktop computers, Plasma Netbook for netbooks, Plasma Mobile for smartphones and Plasma Tablet for Tablet PCs.
KDE Applications
KDE Applications are built on top of the KDE Platform like OkularOkular
Okular is the document viewer for KDE SC 4 . It is based on KPDF and it replaced KPDF, KGhostView, KFax, KFaxview and KDVI in KDE 4.Its functionality can be easily embedded in other applications....
, KTorrent
KTorrent
KTorrent is a BitTorrent client written in C++ for KDE using the Qt user interface toolkit. It is maintained in the KDE Extragear.- Features :*Upload and download speed capping / throttling & scheduling...
, Kexi
Kexi
Kexi is an integrated data management application, designed to fill the gap between spreadsheets and database solutions requiring more sophisticated development...
and KDE Partition Manager
KDE Partition Manager
KDE Partition Manager is a disk partitioning application for the KDE Platform. It was first released for KDE SC 4.1. It is released independently of the central KDE release cycle....
. KDE applications can potentially be portable between operating systems and independent of a particular workspace or desktop environment. Some brands identify application suites built up from several applications, such as KDE Network
Kdenetwork
- List of Software :* Filesharing - It provide some System Settings module of network file sharing* kdnssd* kfile-plugins - It provide KFile plug* KGet - Download manager* Kopete - Instant messaging* KPPP - Internet Dial-Up Tool...
, KDE Graphics
Kdegraphics
kdegraphics is a KDE software package to work with graphics.- List of software :* Gwenview : an image viewer.* kamera : digital camera io_slave for Konqueror.* kfile-plugins : provide meta information for graphic files....
and KDE Utilities
Kdeutils
Kdeutils is a KDE software package that contains utils.- List of component :* Ark - Archiving tool* KCalc - Calculator* KCharSelect - Character tool* KDELirc* KDiskFree - Disk space information* KFloppy- Floppy Formatter...
. Some applications are part of the regular Software Compilation releases, others are part of Extragear and release to their own schedule.
Implementation
Most KDE software uses the Qt framework which runs on most Unix and Unix-likeUnix-like
A Unix-like operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, while not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification....
systems, Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows. CMake
CMake
CMake is a cross-platform, open-source system for managing the build process of software using a compiler-independent method. It is designed to support directory hierarchies and applications that depend on multiple libraries, and for use in conjunction with native build environments such as Make,...
serves as the build tool. This allows KDE to support a wider range of platforms, including Microsoft Windows. GNU gettext is used for translation. Doxygen
Doxygen
Doxygen is a documentation generator for multiple programming languages.Doxygen is a tool for writing software reference documentation. The documentation is written within code, and is thus relatively easy to keep up to date...
is used to generate api documentation.
- KDE Software CompilationKDE Software CompilationThe KDE Software Compilation is a desktop environment and an associated range of KDE Applications produced by KDE. Prior to version 4.4, released in February 2010, the Software Compilation was known as KDE, which used to stand for K Desktop Environment until November 2009...
: KDE Software Compilation (KDE SC) is the coordinated releases of new software versions, gathering elements from the previous components to build an integrated core of software. The KDE SC is not a product as a single entity. - Calligra Suite: Integrated office suite.
- KDEWebdevKdewebdevKDEWebdev is a KDE software package to work with web development.- List of Software :* KFileReplace- Search & Replace Tool* KImageMapEditor - HTML Image Map Editor* KLinkStatus - Link Checker* Kommander - Dynamic Dialog Editor* KXSLDbg - XSLT Debugger...
: Web development tools. - KDE-ExtragearExtragearThe Extragear is a collection of KDE applications that are associated with the KDE project. Those applications are not part of the main KDE software compilation, which is released regularly, but they are still part of the project...
: Extragear is a collection of applications associated with KDE. Those applications are not part the official software compilation, but they are still part of the project. - KDE-Playground: This package contains pre-release and unstable software. It is a place for applications to mature.
Wikimedia
On 23 June 2005, chairman of the Wikimedia Foundation announced that the KDE community and the Wikimedia Foundation have begun efforts towards cooperation. Fruits of that cooperation are MediaWikiMediaWiki
MediaWiki is a popular free web-based wiki software application. Developed by the Wikimedia Foundation, it is used to run all of its projects, including Wikipedia, Wiktionary and Wikinews. Numerous other wikis around the world also use it to power their websites...
syntax highlighting in Kate
Kate (text editor)
In computing, Kate is a text editor by KDE. The name Kate is an acronym for KDE Advanced Text Editor.-History:Kate has been part of KDE Software Compilation since release 2.2 in 2001. Because of the KParts technology, it is possible to embed Kate as an editing component in other KDE applications...
and accessing Wikipedia
Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a free, web-based, collaborative, multilingual encyclopedia project supported by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its 20 million articles have been written collaboratively by volunteers around the world. Almost all of its articles can be edited by anyone with access to the site,...
content within KDE applications, such as Amarok and Marble.
On 4 April 2008, the KDE e.V.
KDE e.V.
KDE e.V. is a registered non-profit organization that represents the KDE community in the legal and financial entities. The association supports KDE’s work in cash, hardware, and other donations, and then the use of donations to help the KDE development, but not influence on development. “e.V.”...
and Wikimedia Deutschland have opened shared offices in Frankfurt
Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main , commonly known simply as Frankfurt, is the largest city in the German state of Hesse and the fifth-largest city in Germany, with a 2010 population of 688,249. The urban area had an estimated population of 2,300,000 in 2010...
. In September 2009 KDE e.V. moved to shared offices with Free Software Foundation Europe
Free Software Foundation Europe
The Free Software Foundation Europe was founded in 2001 as an official European sister organization of the U.S.-based Free Software Foundation to take care of all aspects of free software in Europe. FSF and FSFE are financially and legally separate entities.FSFE believes that access to and...
in Berlin, so Wikimedia Foundation now uses the Frankfurt offices for themselves.
Free Software Foundation Europe
In May 2006, KDE e.V. became an Associate Member of the Free Software Foundation EuropeFree Software Foundation Europe
The Free Software Foundation Europe was founded in 2001 as an official European sister organization of the U.S.-based Free Software Foundation to take care of all aspects of free software in Europe. FSF and FSFE are financially and legally separate entities.FSFE believes that access to and...
(FSFE).
On 22 August 2008, KDE e.V. and FSFE announced that after working with FSFE’s Freedom Task Force one and a half years KDE adopts FSFE’s Fiduciary Licence Agreement. Using that, KDE developers can – on a voluntary basis – assign their copyrights to KDE e.V.
In September 2009, KDE e.V. and FSFE moved into shared offices in Berlin.
Commercial enterprises
Several companies actively contribute to KDE, like Collabora, Erfrakon, Intevation GmbH, Kolab Konsortium, Klarälvdalens Datakonsult AB (KDAB), and KO GmbH.Nokia use Calligra Suite as base for their Office Viewer application for Maemo
Maemo
Maemo is a software platform developed by the Maemo community for smartphones and Internet tablets. It is based on the Debian Linux distribution, but has no relation to it...
/MeeGo
MeeGo
MeeGo is a Linux-based open source mobile operating system project. Primarily targeted at mobile devices and information appliances in the consumer electronics market, MeeGo is designed to act as an operating system for hardware platforms such as netbooks, entry-level desktops, nettops, tablet...
. They have also been contracting KO GmbH to bring MS Office 2007 file format filters to Calligra. Nokia also employs several KDE developers directly – either to use KDE software for MeeGo (e.g. KCal) or as sponsorship.
The software development and consulting companies Intevation GmbH of Germany and the Swedish KDAB use Qt and KDE software – especially Kontact
Kontact
KMail supports folders, filtering, viewing HTML mail, and international character sets. It can handle IMAP, IMAP IDLE, dIMAP, POP3, and local mailboxes for incoming mail. It can send mail via SMTP or sendmail...
and Akonadi
Akonadi
Akonadi is a storage service for personal information management data and metadata named after the oracle goddess of justice in Ghana. It is one of the “pillars” behind the KDE SC 4 project, although it is designed to be used in any desktop environment...
for Kolab
Kolab
Kolab is an open source groupware suite. It consists of the Kolab server and a wide variety of Kolab clients, including KDE PIM-Suite Kontact, Horde Webfrontend, Mozilla Thunderbird and Mozilla Lightning with SyncKolab extension and Microsoft Outlook with proprietary Kolab-Connector PlugIns.-Basic...
– for their services and products, therefore both employ KDE developers.
Others
KDE participates in freedesktop.orgFreedesktop.org
freedesktop.org is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free software desktop environments for the X Window System on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington from Red Hat in March 2000.The organisation focuses on the user....
, an effort to standardize Unix desktop interoperability.
Since 2009, GNOME
GNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
and KDE co-host their conferences Akademy and GUADEC every two years under the Desktop Summit label.
In December 2010 KDE e.V. became a licensee of the Open Invention Network
Open Invention Network
The Open Invention Network is a company that acquires patents and licenses them royalty free to entities which, in turn, agree not to assert their own patents against Linux and Linux-related systems and applications.-History:...
.
Many Linux distribution
Linux distribution
A Linux distribution is a member of the family of Unix-like operating systems built on top of the Linux kernel. Such distributions are operating systems including a large collection of software applications such as word processors, spreadsheets, media players, and database applications...
s and other free operating systems are involved in the development and distribution of the software, and are therefore also active in the KDE community. These include commercial distributors such as Novell, Mandriva, Red Hat, or Canonical, but also government-funded non-commercial organizations such as the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey with its Linux distribution Pardus.
Notable uses
Brazil’s primary school education system operates computers running KDE software, includes more than 42,000 schools in 4,000 cities, serving nearly 52 million children. The base distribution is called Educational Linux, which is based on Kubuntu. Besides this, a thousand more students in Brazil use KDE products in their universities. KDE software is also running on computers in Portuguese and Venezuelan schools, with respectively 700 thousand and one million systems reached.Germany uses KDE software in its embassies around the world, representing around 11,000 systems. Through use of Pardus, a local Linux distribution, many sections of the Turkish government make use of KDE software, including the Turkish Armed Forces
Turkish Armed Forces
The Turkish Armed Forces are the military forces of the Republic of Turkey. They consist of the Army, the Navy , and the Air Force...
, Ministry of Foreign Affairs
Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Turkey)
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is a government ministry office of the Republic of Turkey, responsible for foreign affairs in Turkey. Professor Ahmet Davutoğlu is current Minister of Foreign Affairs of Turkey, appointed on May 1, 2009....
, Ministry of National Defence
Ministry of National Defence (Turkey)
The Ministry of National Defense is a government ministry office of the Republic of Turkey, responsible for defense affairs in Turkey.- Central :Following departments and plants are subordinated to the Ministry of National Defense:...
, Turkish Police, and the SGK (Social Security Institution of Turkey), although these departments often do not exclusively use Pardus as their operating system. The CERN
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research , known as CERN , is an international organization whose purpose is to operate the world's largest particle physics laboratory, which is situated in the northwest suburbs of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border...
(European Organization for Nuclear Research) built the Large Hadron Collider
Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider is the world's largest and highest-energy particle accelerator. It is expected to address some of the most fundamental questions of physics, advancing the understanding of the deepest laws of nature....
in Switzerland, one of the world’s largest science experiments, using KDE software.
External links
- The KDE website
- KDE.News, news announcements
- KDE TechBase

