
Kagome lattice
Encyclopedia
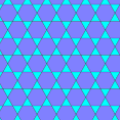
Arrangement of lines
In geometry an arrangement of lines is the partition of the plane formed by a collection of lines. Bounds on the complexity of arrangements have been studied in discrete geometry, and computational geometers have found algorithms for the efficient construction of arrangements.-Definition:For any...
of lath
Lath
A lath is a thin, narrow strip of some straight-grained wood or other material, including metal or gypsum. A lattice, or lattice-work, is a criss-crossed or interlaced arrangement of laths, or the pattern made by such an arrangement...
s composed of interlaced triangles such that each point where two laths cross has four neighboring points. Although called a lattice, it is more closely related to the trihexagonal tiling
Trihexagonal tiling
In geometry, the trihexagonal tiling is a semiregular tiling of the Euclidean plane. There are two triangles and two hexagons alternating on each vertex...
than to a mathematical lattice
Lattice (group)
In mathematics, especially in geometry and group theory, a lattice in Rn is a discrete subgroup of Rn which spans the real vector space Rn. Every lattice in Rn can be generated from a basis for the vector space by forming all linear combinations with integer coefficients...
.
Its name derives from two separate Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
words, meaning the pattern of holes ("me", literally "eyes") in a basket ("kago"). There has been some debate about the proper way to write this term. Lately, it is understood that it is not strictly a Japanese word in itself and it is not the name of a person. Hence, it is proper for kagome to be written in roman font, not italic (foreign words), with a lower-case k, and without an unnecessary (pronunciation) acute accent on the last e.
Some minerals
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
, namely jarosites
Jarosite
Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and iron with a chemical formula of KFe3+362. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides...
and herbertsmithite, contain layers with kagome lattice arrangement of atoms
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
in their crystal structure
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
. These minerals display novel physical properties connected with geometrically frustrated magnetism. The term is much in use nowadays in the scientific literature, especially by theorists studying the magnetic properties of a theoretical kagome lattice in two or three dimensions.
The term was first coined by Japanese physicist Kōji Fushimi, who was working with Ichirō Shōji. The first paper on the subject appeared in 1951. There is an article in Physics Today
Physics Today
Physics Today, created in 1948, is the membership journal of the American Institute of Physics. It is provided to 130,000 members of twelve physics societies, including the American Physical Society...
about all this.

