
Karyolysis
Encyclopedia
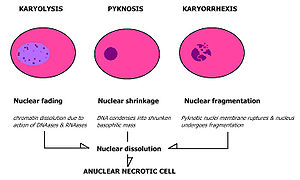
Chromatin
Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The primary functions of chromatin are; to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage, and to control gene...
matter of a dying cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
due to the activity of DNase. The whole cell will eventually stain uniformly with eosin
Eosin
Eosin is a fluorescent red dye resulting from the action of bromine on fluorescein. It can be used to stain cytoplasm, collagen and muscle fibers for examination under the microscope. Structures that stain readily with eosin are termed eosinophilic....
after karyolysis. It is usually preceded by karyorrhexis
Karyorrhexis
Karyorrhexis is the destructive fragmentation of the nucleus of a dying cell whereby its chromatin is distributed irregularly throughout the cytoplasm. It is usually preceded by pyknosis and is followed by karyolysis and can occur as a result of either programmed cell death or necrosis....
and occurs mainly as a result of necrosis
Necrosis
Necrosis is the premature death of cells in living tissue. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma. This is in contrast to apoptosis, which is a naturally occurring cause of cellular death...
, while in apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
after karyorrhexis the nucleus usually dissolves into apoptotic bodies.

