
Kelvin water dropper
Encyclopedia
Electrostatic generator
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is a mechanical device that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current...
Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin OM, GCVO, PC, PRS, PRSE, was a mathematical physicist and engineer. At the University of Glasgow he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging...
(1867), is a type of electrostatic generator
Electrostatic generator
An electrostatic generator, or electrostatic machine, is a mechanical device that produces static electricity, or electricity at high voltage and low continuous current...
. Kelvin referred to the device as his water-dropping condenser. The device uses falling water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
drops
Drop (liquid)
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant drop...
to generate voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
differences by using positive feedback
Positive feedback
Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small disturbance on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system that responds to a perturbation in a way that reduces its effect is...
and the electrostatic induction
Electrostatic induction
Electrostatic induction is a redistribution of electrical charge in an object, caused by the influence of nearby charges. Induction was discovered by British scientist John Canton in 1753 and Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke in 1762. Electrostatic generators, such as the Wimshurst machine, the...
occurring between interconnected, oppositely charged
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
systems.
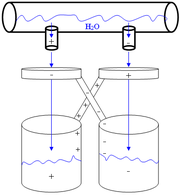
The setup
The simplest setup for this is getting it on as pictured at right. A reservoirReservoir
A reservoir , artificial lake or dam is used to store water.Reservoirs may be created in river valleys by the construction of a dam or may be built by excavation in the ground or by conventional construction techniques such as brickwork or cast concrete.The term reservoir may also be used to...
has two holes that drip water (or other liquid). The streams of dripping water each pass through a conducting ring, and land in a bucket. The buckets must be electrically isolated from each other and from their environment. Similarly, the rings must be electrically isolated from each other and their environment. The left ring is electrically connected with (wired to) the right bucket. And the right ring is wired to the left bucket. It is essential that each ring be placed around the point at which the stream of water passing through it first breaks into drops.
If the buckets are metal (conducting) the wires may be attached to the buckets. Otherwise, the bucket-end of each wire can just sit in its bucket, as long as it is contacting the water in the bucket.
Principle of operation
Any small charge on either of the two buckets suffices to begin the charging process. Suppose, therefore, that the left bucket has a small positive charge. Now the right ring also has some positive charge since it is connected to the bucket. The charge on the right ring will attract negative charge into the right-hand stream by electrostatic attraction. When a drop breaks off the end of the right-hand stream, the drop carries negative charge with it. When the negatively charged water drop falls into its bucket (the right one), it gives that bucket and the attached ring (the left one) a negative charge.Once the left ring has a negative charge, it attracts positive charge into the left-hand stream. When drops break off the end of that stream, they carry positive charge to the positively charged bucket, making that bucket even more positively charged.
So positive charges are attracted to the left-hand stream by the ring, and positive charge drips into the positively charged left bucket. Negative charges are attracted to the right-hand stream and negative charge drips into the negatively charged right bucket. The positive feedback of this process makes each bucket and ring more and more charged. The higher the charge, the more effective the electrostatic induction
Electrostatic induction
Electrostatic induction is a redistribution of electrical charge in an object, caused by the influence of nearby charges. Induction was discovered by British scientist John Canton in 1753 and Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke in 1762. Electrostatic generators, such as the Wimshurst machine, the...
is, so the charges grow exponentially with time.
Eventually, when both buckets have become highly charged, a few effects may be seen. An electric spark
Electric spark
An electric spark is a type of electrostatic discharge that occurs when an electric field creates an ionized electrically conductive channel in air producing a brief emission of light and sound. A spark is formed when the electric field strength exceeds the dielectric field strength of air...
may briefly arc between the two buckets or rings, decreasing the charge on each bucket. Or if this isn't allowed to happen, the buckets will start to electro-statically repel
Coulomb's law
Coulomb's law or Coulomb's inverse-square law, is a law of physics describing the electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles. It was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb and was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism...
the droplets falling towards them, and may fling the droplets away from the buckets. The water drops might also be attracted to the rings enough to touch the rings and deposit their charge on the oppositely charged rings, which decreases the charge on that ring. Each of these effects will limit the voltage that can be reached by the device.
As with other forms of hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
power, the energy here ultimately comes from the gravitational energy released by letting the water drops fall. Most of the energy is wasted as heat when the water drops land in the buckets.
The apparatus can be extended to more than two streams of droplets.
Other names
This water dropper apparatus is sometimes called the Kelvin hydroelectric generator, the Kelvin electrostatic generator, or Lord Kelvin's thunderstorm.External links
- Video demonstrating Kelvin water dropper in operation: "10, M.I.T. 8.02 Electricity & Magnetism, Spring [term] 2002". See the last 6 minutes of this video for operation of Kelvin water dropper. Printed material related to this video: See "MIT Open Courseware" website; specifically, assignment 4 of course 8.02, which is available here: http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/Physics/8-02Electricity-and-MagnetismSpring2002/DownloadthisCourse/index.htm . As is seen in the video, the water must be charged as the stream breaks into droplets. If one attempts to charge the stream before it breaks into droplets — and the outlet can have several streams, as in a shower head — any charge that's induced in the stream can flow backwards through the stream and into the reservoir instead of flowing onto the droplets, so that in effect, the system is short-circuited. Properly operated Kelvin devices can generate high voltages, resulting in large, long, frequent, and bright sparks.
- Detailed description of device and how to build your own Kelvin water dropper.

