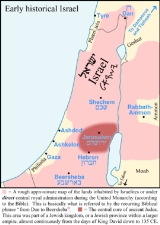
Kingdom of Israel
Encyclopedia
- This article is about the northern kingdom of Israel during the period of divided monarchy, For the original kingdom during the period of the united monarchy see Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy). For other uses see Kingdom of Israel (disambiguation)Kingdom of Israel (disambiguation)The Kingdom of Israel may mean :*Kingdom of Israel , the kingdom established by the Israelites and uniting them under a single king*Kingdom of Israel , the kingdom of northern Israelites...
.
The Kingdom of Israel was, according to the Bible
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible is a term used by biblical scholars outside of Judaism to refer to the Tanakh , a canonical collection of Jewish texts, and the common textual antecedent of the several canonical editions of the Christian Old Testament...
, one of the successor states to the older United Monarchy
United Monarchy
According to Biblical tradition, the united Kingdom of Israel was a kingdom that existed in the Land of Israel, a period referred to by scholars as the United Monarchy. Biblical historians date the kingdom from c. 1020 BCE to c...
(also often called the 'Kingdom of Israel'). It was thought to exist roughly from the 930s BCE until about the 720s BCE, when the kingdom was conquered by the Assyrian Empire
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
. The major cities of the kingdom were Shechem
Shechem
Shechem was a Canaanite city mentioned in the Amarna letters, and is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as an Israelite city of the tribe of Manasseh and the first capital of the Kingdom of Israel...
, Tirzah
Tirzah (ancient city)
Tirzah was a town in the Samarian highlands northeast of Shechem; it is generally identified with Tell el-Farah , NE of modern Nablus.-In the Bible:...
, and Shomron (Samaria
Samaria
Samaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
).
Historians often refer to ancient Israel as the Northern Kingdom to differentiate it from the Southern Kingdom of Judah
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was a Jewish state established in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. It is often referred to as the "Southern Kingdom" to distinguish it from the northern Kingdom of Israel....
.
Name
In the Hebrew BibleHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible is a term used by biblical scholars outside of Judaism to refer to the Tanakh , a canonical collection of Jewish texts, and the common textual antecedent of the several canonical editions of the Christian Old Testament...
, the Kingdom of Israel has been referred to as "House of Joseph". It has also been referred to as "Israel in Samaria".
Territory
The territory of the Kingdom of Israel comprised the territories of the tribes of ZebulunTribe of Zebulun
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Zebulun was one of the Tribes of Israel....
, Issachar
Tribe of Issachar
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Issachar was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
, Asher
Tribe of Asher
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Asher! was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
, Naphtali
Tribe of Naphtali
The Tribe of Naphtali was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
, Dan
Tribe of Dan
The Tribe of Dan, also sometimes spelled as "Dann", was one of the Tribes of Israel. Though known mostly from biblical sources, they were possibly descendants of the Denyen Sea Peoples who joined with Hebrews...
, Manasseh
Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh was one of the Tribes of Israel. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the House of Joseph....
, Ephraim
Tribe of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim was one of the Tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim also formed the House of Joseph....
, Reuben
Tribe of Reuben
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Reuben was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Reuben was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government...
and Gad
Tribe of Gad
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Gad was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Gad was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government existed,...
.
Its capital was Samaria
Samaria
Samaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
.
United Monarchy
The united Kingdom of Israel is said to have existed from about 1030 to about 930 BCE. It was a union of all the twelve IsraeliteIsraelite
According to the Bible the Israelites were a Hebrew-speaking people of the Ancient Near East who inhabited the Land of Canaan during the monarchic period .The word "Israelite" derives from the Biblical Hebrew ישראל...
tribes living in the area that presently approximates modern Israel and the Palestinian territories
Palestinian territories
The Palestinian territories comprise the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. Since the Palestinian Declaration of Independence in 1988, the region is today recognized by three-quarters of the world's countries as the State of Palestine or simply Palestine, although this status is not recognized by the...
.
Division

Solomon
Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before...
in about 931 BCE, all the Israelite tribes except for Judah
Tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Judah was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes....
and Benjamin
Tribe of Benjamin
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Benjamin בִּנְיָמִין was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BCE, the Tribe of Benjamin was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes...
(called the ten northern tribes) refused to accept Rehoboam
Rehoboam
Rehoboam was initially king of the United Monarchy of Israel but after the ten northern tribes of Israel rebelled in 932/931 BC to form the independent Kingdom of Israel he was king of the Kingdom of Judah, or southern kingdom. He was a son of Solomon and a grandson of David...
, the son and successor of Solomon, as their king. The rebellion against Rehoboam arose after he refused to lighten the burden of tax
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
ation and services that his father had imposed on his subjects.
Jeroboam
Jeroboam
Jeroboam was the first king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel after the revolt of the ten northern Israelite tribes against Rehoboam that put an end to the United Monarchy....
, who was not of the Davidic line, was sent for from Egypt
History of Ancient Egypt
The History of Ancient Egypt spans the period from the early predynastic settlements of the northern Nile Valley to the Roman conquest in 30 BC...
by the malcontents. The Tribe of Ephraim
Tribe of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim was one of the Tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim also formed the House of Joseph....
and all Israel raised the old cry, "Every man to his tents, O Israel". Rehoboam fled to Jerusalem, and in 930 BCE (some date it in 920 BCE), Jeroboam was proclaimed king over all Israel at Shechem
Shechem
Shechem was a Canaanite city mentioned in the Amarna letters, and is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as an Israelite city of the tribe of Manasseh and the first capital of the Kingdom of Israel...
. After the revolt at Shechem
Shechem
Shechem was a Canaanite city mentioned in the Amarna letters, and is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as an Israelite city of the tribe of Manasseh and the first capital of the Kingdom of Israel...
at first only the tribe of Judah
Tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Judah was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes....
remained loyal to the house of David
Davidic line
The Davidic line refers to the tracing of lineage to the King David referred to in the Hebrew Bible, as well as the New Testament...
. But very soon after the tribe of Benjamin
Tribe of Benjamin
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Benjamin בִּנְיָמִין was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BCE, the Tribe of Benjamin was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes...
joined Judah. The northern kingdom continued to be called the Kingdom of Israel or Israel, while the southern kingdom was called the kingdom of Judah. 2 Chronicles 15:9 also says that members of the tribes of Ephraim
Tribe of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim was one of the Tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim also formed the House of Joseph....
, Manasseh
Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh was one of the Tribes of Israel. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the House of Joseph....
and Simeon
Tribe of Simeon
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Simeon was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BC, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
fled to Judah during the reign of Asa of Judah
Asa of Judah
Asa was the third king of the Kingdom of Judah and the fifth king of the House of David. He was the son of Abijam, grandson of Rehoboam, and great-grandson of Solomon. The Hebrew Bible gives the period of his reign as 41 years. His reign is dated between 913-910 BCE to 873-869 BCE. He was...
.
Both Eusebius and Josephus
Josephus
Titus Flavius Josephus , also called Joseph ben Matityahu , was a 1st-century Romano-Jewish historian and hagiographer of priestly and royal ancestry who recorded Jewish history, with special emphasis on the 1st century AD and the First Jewish–Roman War, which resulted in the Destruction of...
place the division in 997 BCE - lunar dates of Venus can be mistaken as 64 years earlier. (Crossing of sun over Mars as Tamuz would be 10 July 997 BCE.)
Shechem
Shechem
Shechem was a Canaanite city mentioned in the Amarna letters, and is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as an Israelite city of the tribe of Manasseh and the first capital of the Kingdom of Israel...
was the first capital of the Kingdom of Israel. Afterwards it was Tirzah
Tirzah (ancient city)
Tirzah was a town in the Samarian highlands northeast of Shechem; it is generally identified with Tell el-Farah , NE of modern Nablus.-In the Bible:...
. King Omri
Omri
Omri was a king of Israel, successful military campaigner and first in the line of Omride kings that included Ahab, Ahaziah and Joram.He was "commander of the army" of king Elah when Zimri murdered Elah and made himself king. Instead, the troops at Gibbethon chose Omri as king, and he led them to...
built his capital in Samaria
Samaria
Samaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
(16:24), which continued as such until the destruction of the Kingdom by the Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
ns . During the three-year siege of Samaria by the Assyrians, Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V was king of Assyria from 727 to 722 BC. He first appears as governor of Zimirra in Phoenicia in the reign of his father, Tiglath-Pileser III....
died and was succeeded by Sargon II of Assyria, who himself records the capture of that city thus: "Samaria I looked at, I captured; 27,280 men who dwelt in it I carried away" into Assyria. Thus, around 720 BCE, after two centuries, the kingdom of the ten tribes came to an end.
Today, among archaeologists, Samaria is one of the most universally accepted archaeological sites from the biblical period At around 850 BCE, the Mesha Stele
Mesha Stele
The Mesha Stele is a black basalt stone bearing an inscription by the 9th century BC ruler Mesha of Moab in Jordan....
, written in Old Hebrew alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, records a victory of King Mesha
Mesha
King Mesha of Moab was a king of Moabites around the 9th century BC, known most famous for writing the Mesha stela.The books of Samuel record that Moab was conquered by David and retained in the territories of his son Solomon . Later, King Omri of Israel reconquered Moab after Moab was lost...
of Moab against king Omri
Omri
Omri was a king of Israel, successful military campaigner and first in the line of Omride kings that included Ahab, Ahaziah and Joram.He was "commander of the army" of king Elah when Zimri murdered Elah and made himself king. Instead, the troops at Gibbethon chose Omri as king, and he led them to...
of Israel and his son Ahab
Ahab
Ahab or Ach'av or Achab in Douay-Rheims was king of Israel and the son and successor of Omri according to the Hebrew Bible. His wife was Jezebel....
.
Relations between the kingdoms
For the first sixty years, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over the northern kingdom, and there was perpetual war between them. For the following eighty years, there was no open war between them, and, for the most part, they were in friendly alliance, co-operating against their common enemies, especially against DamascusDamascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
.
The conflict between Israel and Judah was resolved when Jehoshaphat
Jehoshaphat
Jehoshaphat was the fourth king of the The Kingdom of Judah, and successor of his father Asa. His children included Jehoram, who succeeded him as king...
, King of Judah, allied himself with the house of Ahab
Ahab
Ahab or Ach'av or Achab in Douay-Rheims was king of Israel and the son and successor of Omri according to the Hebrew Bible. His wife was Jezebel....
through marriage. Later, Jehosophat's son and successor, Jehoram of Judah
Jehoram of Judah
Jehoram of Judah was the king of the southern Kingdom of Judah, and the son of Jehoshaphat .According to , Jehoram became king of Judah in the fifth year of Jehoram of Israel, when his father Jehoshaphat was king of Judah, indicating a co-regency. The author of Kings also speaks of both Jehoram...
, married Ahab's daughter Athaliah
Athaliah
Athaliah was the queen of Judah during the reign of King Jehoram, and later became sole ruler of Judah for six years. William F. Albright has dated her reign to 842–837 BC, while Edwin R. Thiele's dates, as taken from the third edition of his magnum opus, were 842/841 to 836/835 BC...
, cementing the alliance. However, the sons of Ahab were slaughtered by Jehu
Jehu
Jehu was a king of Israel. He was the son of Jehoshaphat, and grandson of Nimshi.William F. Albright has dated his reign to 842-815 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 841-814 BC...
following his coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
around 840 BCE.
Destruction of the kingdom
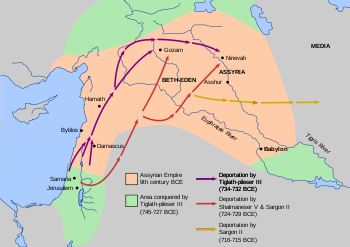
Pekah
Pekah was king of Israel. He was a captain in the army of king Pekahiah of Israel, whom he killed to become king. Pekah was the son of Remaliah ....
of Israel allied with Rezin
Rezin
King Rezin of Aram or Rasin of Syria in DRB ruled from Damascus during the 8th century BC. During his reign he was a tributary of King Tiglath-pileser III of Assyria....
, king of Aram
Aram (Biblical region)
Aram is the name of a region mentioned in the Bible located in central Syria, including where the city of Aleppo now stands.-Etymology:The etymology is uncertain. One standard explanation is an original meaning of "highlands"...
, threatened Jerusalem, and Ahaz
Ahaz
Ahaz was king of Judah, and the son and successor of Jotham. He is one of the kings mentioned in the genealogy of Jesus in the Gospel of Matthew....
, king of Judah, appealed to Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III was a prominent king of Assyria in the eighth century BC and is widely regarded as the founder of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Tiglath-Pileser III seized the Assyrian throne during a civil war and killed the royal family...
, the king of Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
, for help. After Ahaz paid tribute to Tiglath-Pileser Tiglath-Pileser sacked Damascus and Israel, annexing Aram and territory of the tribes of Reuben
Tribe of Reuben
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Reuben was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Reuben was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government...
, Gad
Tribe of Gad
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Gad was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Gad was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government existed,...
and Manasseh
Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh was one of the Tribes of Israel. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the House of Joseph....
in Gilead including the desert outposts of Jetur, Naphish and Nodab. People from these tribes including the Reubenite leader, were taken captive and resettled in the region of the Khabur River
Khabur River
The Khabur River , , , ) is the largest perennial tributary to the Euphrates in Syrian territory. Although the Khabur originates in Turkey, the karstic springs around Ra's al-'Ayn are the river's main source of water. Several important wadis join the Khabur north of Al-Hasakah, together creating...
system. Tiglath-Pilesar also captured the territory of Naphtali
Tribe of Naphtali
The Tribe of Naphtali was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
and the city of Janoah in Ephraim
Tribe of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim was one of the Tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim also formed the House of Joseph....
and an Assyrian governor was placed over the region of Naphtali. According to and , the population of Aram and the annexed part of Israel was deported to Assyria.
Israel continued to exist within the reduced territory as an independent kingdom until around 720 BCE, when it was again invaded by Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
and the rest of the population deported. The Bible relates that the population of Israel was exiled, becoming known as The Ten Lost Tribes, leaving only the Tribe of Judah
Tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Judah was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes....
, the Tribe of Simeon
Tribe of Simeon
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Simeon was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BC, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
(that was "absorbed" into Judah), the Tribe of Benjamin
Tribe of Benjamin
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Benjamin בִּנְיָמִין was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BCE, the Tribe of Benjamin was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes...
and the people of the Tribe of Levi who lived among them of the original Israelites nation in the southern Kingdom of Judah. However, other writers estimate that only a fifth of the population (about 40,000) were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III was a prominent king of Assyria in the eighth century BC and is widely regarded as the founder of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Tiglath-Pileser III seized the Assyrian throne during a civil war and killed the royal family...
and Sargon II
Sargon II
Sargon II was an Assyrian king. Sargon II became co-regent with Shalmaneser V in 722 BC, and became the sole ruler of the kingdom of Assyria in 722 BC after the death of Shalmaneser V. It is not clear whether he was the son of Tiglath-Pileser III or a usurper unrelated to the royal family...
. Many also fled south to Jerusalem, which appears to have expanded in size fivefold during this period, requiring a new wall to be built, and a new source of water (Siloam
Siloam
Siloam is an ancient Greek name derived from the more ancient Hebrew Shiloah. The Arabic, Silwan, was derived form the Greek, Siloam. It is an ancient site in Jerusalem, south of the Old City.-Antiquity:...
) to be provided by King Hezekiah
Hezekiah
Hezekiah was the son of Ahaz and the 14th king of Judah. Edwin Thiele has concluded that his reign was between c. 715 and 686 BC. He is also one of the most prominent kings of Judah mentioned in the Hebrew Bible....
.
The remainder of the northern kingdom was conquered by Sargon II
Sargon II
Sargon II was an Assyrian king. Sargon II became co-regent with Shalmaneser V in 722 BC, and became the sole ruler of the kingdom of Assyria in 722 BC after the death of Shalmaneser V. It is not clear whether he was the son of Tiglath-Pileser III or a usurper unrelated to the royal family...
, who captured the capital city Samaria
Samaria
Samaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
in the territory of Ephraim. He took 27,290 people captive from the city of Samaria resettling some with the Israelites in the Khabur region and the rest in the land of the Medes
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
thus establishing Jewish communities in Ecbatana
Ecbatana
Ecbatana is supposed to be the capital of Astyages , which was taken by the Persian emperor Cyrus the Great in the sixth year of Nabonidus...
and Rages.
The Book of Tobit
Book of Tobit
The Book of Tobit is a book of scripture that is part of the Catholic and Orthodox biblical canon, pronounced canonical by the Council of Carthage of 397 and confirmed for Roman Catholics by the Council of Trent...
additionally records that Sargon had taken other captives from the northern kingdom to the Assyrian capital of Nineveh, in particular Tobit from the town of Thisbe in Naphtali.
In medieval Rabbinic fable the concept of the ten tribes who were taken away from the House of David (who continued the rule of the southern kingdom of Judah) becomes confounded with accounts of the Assyrian deportations leading to the myth of the "Ten Lost Tribes". The recorded history differs from this fable: No record exists of the Assyrians having exiled people from Dan, Asher, Issachar, Zebulun or western Manasseh. Descriptions of the deportation of people from Reuben
Tribe of Reuben
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Reuben was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Reuben was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government...
, Gad
Tribe of Gad
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Gad was one of the Tribes of Israel.From after the conquest of the land by Joshua until the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel in c. 1050 BC, the Tribe of Gad was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government existed,...
, Manasseh
Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh was one of the Tribes of Israel. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the House of Joseph....
in Gilead
Gilead
In the Bible "Gilead" means hill of testimony or mound of witness, , a mountainous region east of the Jordan River, situated in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. It is also referred to by the Aramaic name Yegar-Sahadutha, which carries the same meaning as the Hebrew . From its mountainous character...
, Ephraim
Ephraim
Ephraim ; was, according to the Book of Genesis, the second son of Joseph and Asenath. Asenath was an Egyptian woman whom Pharaoh gave to Joseph as wife, and the daughter of Potipherah, a priest of On. Ephraim was born in Egypt before the arrival of the children of Israel from Canaan...
and Naphtali indicate that only a portion of these tribes were deported and the places to which they were deported are known locations given in the accounts. The deported communities are mentioned as still existing at the time of the composition of the books of Kings and Chronicles and did not disappear by assimilation. 2 Chronicles 30:1-11 explicitly mentions northern Israelites who had been spared by the Assyrians in particular people of Ephraim
Tribe of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim was one of the Tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim also formed the House of Joseph....
, Manasseh
Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh was one of the Tribes of Israel. Together with the Tribe of Ephraim, Manasseh also formed the House of Joseph....
, Asher
Tribe of Asher
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Asher! was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
, Issachar
Tribe of Issachar
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Issachar was one of the Tribes of Israel.Following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelite tribes after about 1200 BCE, Joshua allocated the land among the twelve tribes...
and Zebulun
Tribe of Zebulun
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Zebulun was one of the Tribes of Israel....
and how members of the latter three returned to worship at the Temple in Jerusalem during the reign of Hezekiah
Hezekiah
Hezekiah was the son of Ahaz and the 14th king of Judah. Edwin Thiele has concluded that his reign was between c. 715 and 686 BC. He is also one of the most prominent kings of Judah mentioned in the Hebrew Bible....
.
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah continued to exist as an independent state until 586 BCE, when it was conquered by the Neo-Babylonian EmpireNeo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire was a period of Mesopotamian history which began in 626 BC and ended in 539 BC. During the preceding three centuries, Babylonia had been ruled by their fellow Akkadian speakers and northern neighbours, Assyria. Throughout that time Babylonia...
.
Religion in the Kingdom of Israel
The religious climate of the Kingdom of Israel appears to have followed two major trends. The first, that of YHWH, and the second the cult of BaalBaal
Baʿal is a Northwest Semitic title and honorific meaning "master" or "lord" that is used for various gods who were patrons of cities in the Levant and Asia Minor, cognate to Akkadian Bēlu...
as detailed in the Hebrew Bible
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible is a term used by biblical scholars outside of Judaism to refer to the Tanakh , a canonical collection of Jewish texts, and the common textual antecedent of the several canonical editions of the Christian Old Testament...
, and in the so-called "Baal cycle
Baal cycle
The Baal cycle is a Ugaritic cycle of stories about the Canaanite god Baal, also known as Hadad the god of storm and fertility. They are written in Ugaritic, a language written in a cuneiform alphabet, on a series of clay tablets found in the 1920s in the Tell of Ugarit , situated on the...
" discovered at Ugarit
Ugarit
Ugarit was an ancient port city in the eastern Mediterranean at the Ras Shamra headland near Latakia, Syria. It is located near Minet el-Beida in northern Syria. It is some seven miles north of Laodicea ad Mare and approximately fifty miles east of Cyprus...
.
It is recorded in the Hebrew Bible
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible is a term used by biblical scholars outside of Judaism to refer to the Tanakh , a canonical collection of Jewish texts, and the common textual antecedent of the several canonical editions of the Christian Old Testament...
that Jeroboam
Jeroboam
Jeroboam was the first king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel after the revolt of the ten northern Israelite tribes against Rehoboam that put an end to the United Monarchy....
built two places of worship, one at Bethel and one at far northern Dan, to be an alternative to the Temple in Jerusalem
Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem or Holy Temple , refers to one of a series of structures which were historically located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, the current site of the Dome of the Rock. Historically, these successive temples stood at this location and functioned as the centre of...
. He did not want the people of his kingdom to have religious ties to Jerusalem, the capital city of the rival Kingdom of Judah
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was a Jewish state established in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. It is often referred to as the "Southern Kingdom" to distinguish it from the northern Kingdom of Israel....
. He erected golden bulls at the entrance to the Temples to represent the national god. These acts became known as the way of Jeroboam or the errors of Jeroboam.
Ahab allowed the cult worship of Baal
Baal
Baʿal is a Northwest Semitic title and honorific meaning "master" or "lord" that is used for various gods who were patrons of cities in the Levant and Asia Minor, cognate to Akkadian Bēlu...
to become an acceptable religion of the kingdom. His wife Jezebel
Jezebel
Jezebel may refer to:* Jezebel, wife of King Ahab*Jezebel, in the Book of Revelation 2:20 a prophetess in the church of Thyatira* Jezebel , starring Bette Davis and Henry Fonda* Jezebel , a blog aimed at women...
was a devotee to Baal worship.
Prophets active in the Kingdom of Israel
- Elijah, opponent of religious inventions under Ahab and Jezebel
- ElishaElishaElisha is a prophet mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and the Qur'an. His name is commonly transliterated into English as Elisha via Hebrew, Eliseus via Greek and Latin, or Alyasa via Arabic.-Biblical biography:...
, chosen successor of Elijah - AmosAmos (prophet)Amos is a minor prophet in the Old Testament, and the author of the Book of Amos. Before becoming a prophet, Amos was a sheep herder and a sycamore fig farmer. Amos' prior professions and his claim "I am not a prophet nor a son of a prophet" indicate that Amos was not from the school of prophets,...
- HoseaHoseaHosea was the son of Beeri and a prophet in Israel in the 8th century BC. He is one of the Twelve Prophets of the Jewish Hebrew Bible, also known as the Minor Prophets of the Christian Old Testament. Hosea is often seen as a "prophet of doom", but underneath his message of destruction is a promise...
- JonahJonahJonah is the name given in the Hebrew Bible to a prophet of the northern kingdom of Israel in about the 8th century BC, the eponymous central character in the Book of Jonah, famous for being swallowed by a fish or a whale, depending on translation...
- NahumNahumNahum was a minor prophet whose prophecy is recorded in the Hebrew Bible. His book comes in chronological order between Micah and Habakkuk in the Bible. He wrote about the end of the Assyrian Empire, and its capital city, Nineveh, in a vivid poetic style....
Royal Houses of Israel
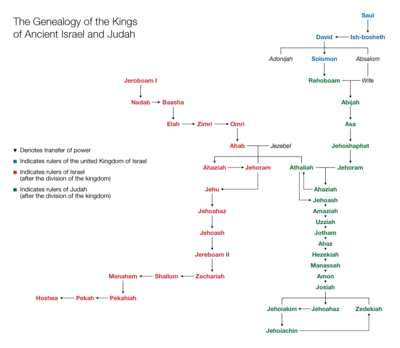
William F. Albright
William Foxwell Albright was an American archaeologist, biblical scholar, philologist and expert on ceramics. From the early twentieth century until his death, he was the dean of biblical archaeologists and the universally acknowledged founder of the Biblical archaeology movement...
or Edwin R. Thiele
Edwin R. Thiele
Edwin R. Thiele was an American missionary in China, an editor, archaeologist, writer, and Old Testament professor. He is best known for his chronological studies of the Hebrew kingdom period.- Biography :...
, or the newer chronologies of Gershon Galil
Gershon Galil
Gershon Galil is Professor of Biblical Studies and Ancient History and former chair of the Department of Jewish History at the University of Haifa, Mount Carmel, Haifa, Israel. He received his doctorate at Hebrew University in Jerusalem. His work, The Chronology of the Kings of Israel and Judah,...
and Kenneth Kitchen
Kenneth Kitchen
Kenneth Anderson Kitchen is Personal and Brunner Professor Emeritus of Egyptology and Honorary Research Fellow at the School of Archaeology, Classics and Egyptology, University of Liverpool, England...
, all of which are shown below. All dates are BC/BCE
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
.
| Albright | Thiele | Galil | Kitchen | Common/Biblical name | Regnal Name and style | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The House of Saul |
||||||
| 1051–1010 | 1050–1010 | 1050–1010 | 1042–1010 | Saul Saul the King According to the Bible, Saul was the first king of the united Kingdom of Israel. He was anointed by the prophet Samuel and reigned from Gibeah. He commited suicide to avoid arrest in the battle against the Philistines at Mount Gilboa, during which three of his sons were also killed... |
'שאול המלך or Sha'ul | Reigned in Israel & Judah for 40 years: He killed himself during the war with the Philistines in Mount Gilboa. |
| 1010–1008 | 1000–998 | 1010–1008 | 1006–1004 | Ish-bosheth Ish-bosheth According to the Hebrew Bible, Ish-bosheth also called Eshbaal , Ashbaal or Ishbaal, was one of the four sons of King Saul, born c. 1047 BC... |
(also called Eshba'al or Ashba'al or Ishbaal) | Reigned in Israel for 2 years: |
The House of David |
||||||
| 1000–962 | 1010–970 | 1010–970 | David | דוד בן-ישי מלך ישראל David ben Yeshay, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Judah in Hebron 7 years and then over both Israel & Judah for 33 years in Jerusalem, 40 years in total. Death: Natural causes | |
| 962–922 | 970–931 | 971–931 | Solomon Solomon Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before... |
שלמה בן-דוד מלך ישראל Shelomoh ben David Solomon Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over United Kingdom of Israel (& Judah) in Jerusalem for 40 years. Death: Natural Causes | |
The House of Jeroboam |
||||||
| 922–901 | 931–910 | 931–909 | 931–911 | Jeroboam I Jeroboam Jeroboam was the first king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel after the revolt of the ten northern Israelite tribes against Rehoboam that put an end to the United Monarchy.... |
ירבעם בן-נבט מלך ישראל Yerav’am ben Nevat Jeroboam Jeroboam was the first king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel after the revolt of the ten northern Israelite tribes against Rehoboam that put an end to the United Monarchy.... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Led the rebellion and divided the kingdoms. Reigned in Israel (Northern Kingdom) for 22 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 901–900 | 910–909 | 909–908 | 911–910 | Nadab Nadab of Israel Nadab was the second king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel. He was the son and successor of Jeroboam. Nadab became king of Israel in the second year of Asa, king of Judah, and reigned for two years. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 901 - 900 BCE, while E. R... |
נדב בן-ירבעם מלך ישראל Nadav ben Yerav’am Nadab of Israel Nadab was the second king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel. He was the son and successor of Jeroboam. Nadab became king of Israel in the second year of Asa, king of Judah, and reigned for two years. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 901 - 900 BCE, while E. R... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned in Israel for 2 years. Death: Killed by Baasha, son of Ahijah of the house of Issachar, along with his whole family. |
The House of Baasha |
||||||
| 900–877 | 909–886 | 908–885 | 910–887 | Baasha | בעשא בן-אחיה מלך ישראל Ba’asha ben Achiyah, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Tirzah for 24 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 877–876 | 886–885 | 885–884 | 887–886 | Elah King Elah Elah was a son of Baasha, who succeeded him as the 4th king of Israel. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 877 BC - 876 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 886 BC - 885 BC.... |
אלה בן-בעשא מלך ישראל ’Elah ben Ba’asha King Elah Elah was a son of Baasha, who succeeded him as the 4th king of Israel. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 877 BC - 876 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 886 BC - 885 BC.... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Tirzah for 2 years. Death: Zimri, one of his officials, got him drunk and killed him at his house in Azra. |
The House of Zimri |
||||||
| 876 | 885 | 884 | 886 | Zimri Zimri (king) Zimri or Zambri was a king of Israel for seven days. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 876 BCE, while E. R. Thiele offers the date 885 BCE. His story is told in 1 Kings, Chapter 16.... |
זמרי מלך ישראל Zimri Zimri (king) Zimri or Zambri was a king of Israel for seven days. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 876 BCE, while E. R. Thiele offers the date 885 BCE. His story is told in 1 Kings, Chapter 16.... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Tirzah for 7 days. Death: He set his palace on fire when Omri and all the Israelites with him withdrew from Gibbethon and laid siege to Tirzah. |
The House of Omri |
||||||
| 876–869 | 885–874 | 884–873 | 886–875 | Omri Omri Omri was a king of Israel, successful military campaigner and first in the line of Omride kings that included Ahab, Ahaziah and Joram.He was "commander of the army" of king Elah when Zimri murdered Elah and made himself king. Instead, the troops at Gibbethon chose Omri as king, and he led them to... |
עמרי מלך ישראל ’Omri Omri Omri was a king of Israel, successful military campaigner and first in the line of Omride kings that included Ahab, Ahaziah and Joram.He was "commander of the army" of king Elah when Zimri murdered Elah and made himself king. Instead, the troops at Gibbethon chose Omri as king, and he led them to... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 12 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 869–850 | 874–853 | 873–852 | 875–853 | Ahab Ahab Ahab or Ach'av or Achab in Douay-Rheims was king of Israel and the son and successor of Omri according to the Hebrew Bible. His wife was Jezebel.... |
אחאב בן-עמרי מלך ישראל Ah’av ben ’Omri Ahab Ahab or Ach'av or Achab in Douay-Rheims was king of Israel and the son and successor of Omri according to the Hebrew Bible. His wife was Jezebel.... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 22 years. Death: Shot by an archer during the battle at Ramoth Gilead. He died upon his arrival on Samaria. |
| 850–849 | 853–852 | 852–851 | 853–852 | Ahaziah Ahaziah of Israel Ahaziah or Ochozias was king of Israel and the son of Ahab and Jezebel.William F. Albright has dated his reign to 850-849 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 853-852 BC... |
אחזיהו בן-אחאב מלך ישראל ’Ahazyahu ben 'Ah’av Ahaziah of Israel Ahaziah or Ochozias was king of Israel and the son of Ahab and Jezebel.William F. Albright has dated his reign to 850-849 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 853-852 BC... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 2 years. Death: He fell through the lattice of his upper room and injured himself. Elijah the prophet told him he would never leave his bed and would die on it. |
| 849–842 | 852–841 | 851–842 | 852–841 | Joram Jehoram of Israel Jehoram was a king of the northern Kingdom of Israel. He was the son of Ahab and Jezebel.According to , in the fifth year of Joram of Israel, Jehoram became king of Judah, when his father Jehoshaphat was king of Judah, indicating a co-regency... |
יורם בן-אחאב מלך ישראל Yehoram ben ’Ah’av Jehoram of Israel Jehoram was a king of the northern Kingdom of Israel. He was the son of Ahab and Jezebel.According to , in the fifth year of Joram of Israel, Jehoram became king of Judah, when his father Jehoshaphat was king of Judah, indicating a co-regency... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 11 years. Death: Killed by Jehu, the next king of Israel, |
The House of Jehu |
||||||
| 842–815 | 841–814 | 842–815 | 841–814 | Jehu Jehu Jehu was a king of Israel. He was the son of Jehoshaphat, and grandson of Nimshi.William F. Albright has dated his reign to 842-815 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 841-814 BC... |
יהוא בן-נמשי מלך ישראל Yehu ben Nimshi Jehu Jehu was a king of Israel. He was the son of Jehoshaphat, and grandson of Nimshi.William F. Albright has dated his reign to 842-815 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 841-814 BC... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 28 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 815–801 | 814–798 | 819–804 | 814–806 | Jehoahaz Jehoahaz of Israel Jehoahaz of Israel was king of Israel and the son of Jehu . William F. Albright has dated his reign to 815 BC – 801 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 814 BC – 798 BC. A stamp seal dated to the end of the 7th century BC has been found with the inscription "[belonging] to Jehoahaz, son of the... |
יהואחז בן-יהוא מלך ישראל Yeho’ahaz ben Yehu Jehoahaz of Israel Jehoahaz of Israel was king of Israel and the son of Jehu . William F. Albright has dated his reign to 815 BC – 801 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 814 BC – 798 BC. A stamp seal dated to the end of the 7th century BC has been found with the inscription "[belonging] to Jehoahaz, son of the... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 17 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 801–786 | 798–782 | 805–790 | 806–791 | Jehoash Jehoash of Israel Jehoash , whose name means “Yahweh has given,” was a king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel and the son of Jehoahaz. He was the 12th king of Israel and reigned for 16 years. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 801 BC – 786 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 798 BC – 782 BC... (Joash Jehoash of Israel Jehoash , whose name means “Yahweh has given,” was a king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel and the son of Jehoahaz. He was the 12th king of Israel and reigned for 16 years. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 801 BC – 786 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 798 BC – 782 BC... ) |
יואש בן-יואחז מלך ישראל Yeho’ash ben Yeho’ahaz Jehoash of Israel Jehoash , whose name means “Yahweh has given,” was a king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel and the son of Jehoahaz. He was the 12th king of Israel and reigned for 16 years. William F. Albright has dated his reign to 801 BC – 786 BC, while E. R. Thiele offers the dates 798 BC – 782 BC... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 16 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 786–746 | 782–753 | 790–750 | 791–750 | Jeroboam II Jeroboam II Jeroboam II was the son and successor of Jehoash, , and the fourteenth king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel, over which he ruled for forty-one years according to 2 Kings . His reign was contemporary with those of Amaziah and Uzziah , kings of Judah... |
ירבעם בן-יואש מלך ישראל Yerav’am ben Yeho’ash Jeroboam II Jeroboam II was the son and successor of Jehoash, , and the fourteenth king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel, over which he ruled for forty-one years according to 2 Kings . His reign was contemporary with those of Amaziah and Uzziah , kings of Judah... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 41 years. Death: Natural Causes. The Book of Jonah Jonah Jonah is the name given in the Hebrew Bible to a prophet of the northern kingdom of Israel in about the 8th century BC, the eponymous central character in the Book of Jonah, famous for being swallowed by a fish or a whale, depending on translation... or Jonah's journey to Nineveh Nineveh Nineveh was an ancient Assyrian city on the eastern bank of the Tigris River, and capital of the Neo Assyrian Empire. Its ruins are across the river from the modern-day major city of Mosul, in the Ninawa Governorate of Iraq.... (when he was swallowed by a whale or fish) happened at that time. |
| 746 | 753 | 750–749 | 750 | Zachariah | זכריה בן-ירבעם מלך ישראל Zekharyah ben Yerav’am, Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 6 months. Death: Shallum son of Jabesh killed him in front of the people and succeeded as king. |
The House of Shallum |
||||||
| 745 | 752 | 749 | 749 | Shallum Shallum of Israel Shallum of Israel was the king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel, and the son of Jabesh. He "conspired against Zachariah, and smote him before the people, and slew him, and reigned in his stead" . He reigned only "a month of days in Samaria" before Menahem rose up, put him to death , and became... |
שלם בן-יבש מלך ישראל Shallum ben Yavesh Shallum of Israel Shallum of Israel was the king of the ancient Kingdom of Israel, and the son of Jabesh. He "conspired against Zachariah, and smote him before the people, and slew him, and reigned in his stead" . He reigned only "a month of days in Samaria" before Menahem rose up, put him to death , and became... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 1 month. Death: Menahem son of Gadi attacked Shallum and assassinated him. |
The House of Menahem |
||||||
| 745–738 | 752–742 | 749–738 | 749–739 | Menahem Menahem Menahem, was a king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel. He was the son of Gadi, and the founder of the dynasty known as the House of Gadi or House of Menahem.... |
מנחם בן-גדי מלך ישראל Menahem ben Gadi Menahem Menahem, was a king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel. He was the son of Gadi, and the founder of the dynasty known as the House of Gadi or House of Menahem.... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 10 years. Death: Natural Causes |
| 738–737 | 742–740 | 738–736 | 739–737 | Pekahiah Pekahiah Pekahiah was a king of Israel and the son of Menahem, whom he succeeded, and the second and last king of Israel from the House of Gadi. He ruled from the capital of Samaria.... |
פקחיה בן-מנחם מלך ישראל Pekahyah ben Menahem Pekahiah Pekahiah was a king of Israel and the son of Menahem, whom he succeeded, and the second and last king of Israel from the House of Gadi. He ruled from the capital of Samaria.... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 2 years. Death: Pekah son of Remaliah, one of the chief officers, took 50 men with him and assassinated the king in his palace at Samaria. |
The House of Pekah |
||||||
| 737–732 | 740–732 | 736–732 | 737–732 | Pekah Pekah Pekah was king of Israel. He was a captain in the army of king Pekahiah of Israel, whom he killed to become king. Pekah was the son of Remaliah .... |
פקח בן-רמליהו מלך ישראל Pekah ben Remalyahu Pekah Pekah was king of Israel. He was a captain in the army of king Pekahiah of Israel, whom he killed to become king. Pekah was the son of Remaliah .... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 5 years. Death: Hoshea son of Elah conspired against him and assassinated him. |
The House of Hoshea |
||||||
| 732–722 | 732–722 | 732–722 | 732–722 | Hoshea Hoshea See also Hosea, who has the same name in Biblical Hebrew.Hoshea was the last king of the Israelite Kingdom of Israel and son of Elah . William F. Albright dated reign to 732 – 721 BC, while E. R. Thiele offered the dates 732 – 723 BC.Assyrian records basically confirm the Biblical... |
הושע בן-אלה מלך ישראל Hoshe’a ben ’Elah Hoshea See also Hosea, who has the same name in Biblical Hebrew.Hoshea was the last king of the Israelite Kingdom of Israel and son of Elah . William F. Albright dated reign to 732 – 721 BC, while E. R. Thiele offered the dates 732 – 723 BC.Assyrian records basically confirm the Biblical... , Melekh Yisra’el |
Reigned over Israel in Samaria for 9 years. Death: King Shalmanser attacked and captured Samaria. He charged Hoshea of treason and he put him in prison, then, he deported the Israelites to Assyria. |
See also
- Assyrian captivity of IsraelAssyrian captivity of IsraelThe Northern Kingdom of Israel was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian monarchs, Tiglath-Pileser III and Shalmaneser V. The later Assyrian rulers Sargon II and his son and successor, Sennacherib, were responsible for finishing the twenty year demise of Israel's northern ten tribe kingdom. Sennacherib...
- Government of ancient Israel
- History of ancient Israel and JudahHistory of ancient Israel and JudahIsrael and Judah were related Iron Age kingdoms of ancient Palestine. The earliest known reference to the name Israel in archaeological records is in the Merneptah stele, an Egyptian record of c. 1209 BCE. By the 9th century BCE the Kingdom of Israel had emerged as an important local power before...
- Ten Lost TribesTen Lost TribesThe Ten Lost Tribes of Israel refers to those tribes of ancient Israel that formed the Kingdom of Israel and which disappeared from Biblical and all other historical accounts after the kingdom was destroyed in about 720 BC by ancient Assyria...
- IsraelIsraelThe State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
- The Bible UnearthedThe Bible UnearthedThe Bible Unearthed: Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts is a 2001 book about the archaeology of Israel and its relationship to the origins of the Hebrew Bible...
External links
- About Israel - The Information Center About Israel
- Biblical History The Jewish History Resource Center - Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- Complete Bible Genealogy A synchronized chart of the kings of Israel and Judah

