
Labiovelar consonant
Encyclopedia
A labialized velar is a velar consonant
which is labialized, that is, which has an /w/-like secondary articulation
. Common examples are [kʷ, ɡʷ, xʷ, ŋʷ], which are pronounced like a [k, ɡ, x, ŋ] with rounded lips. See for example the labialized voiceless velar plosive
[kʷ]. Such sounds occur across Africa, throughout the Americas, in the Caucasus, etc.
.) However, languages such as Japanese
and perhaps the Northern Iroquoian languages
have something closer to a true labial–velar approximant, where the lips come together. In close transcription, the symbol [w] may be avoided in such cases, or it may be used with an under-rounding diacritic, as [w̜].
[w] and its voiceless equivalent are the only labialized velars with dedicated IPA symbols:
1In dialects that distinguish between which and witch.
The voiceless approximant is traditionally called a "voiceless labial–velar fricative", but true doubly articulated
fricatives are not known to be used in any language, as they are quite difficult to pronounce and even more to aurally distinguish. (However, very occasionally the symbol [ʍ] is used for a labialized velar fricative, [xʷ]. This usage is not approved by the IPA
.)
Velar consonant
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum)....
which is labialized, that is, which has an /w/-like secondary articulation
Secondary articulation
Secondary articulation refers to co-articulated consonants where the two articulations are not of the same manner. The approximant-like secondary articulation is weaker than the primary, and colors it rather than obscuring it...
. Common examples are [kʷ, ɡʷ, xʷ, ŋʷ], which are pronounced like a [k, ɡ, x, ŋ] with rounded lips. See for example the labialized voiceless velar plosive
Labialized voiceless velar plosive
The labialized voiceless velar plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and it is a common sound cross-linguistically. It is effectively a and a sound pronounced simultaneously...
[kʷ]. Such sounds occur across Africa, throughout the Americas, in the Caucasus, etc.
Labialized velar approximants
The most common labiovelar consonant is the voiced approximant [w]. This is normally a labialized velar, as is its vocalic cousin [u]. (Labialization is called rounding in vowels, and a velar place is called backBack vowel
A back vowel is a type of vowel sound used in spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a back vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far back as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Back vowels are sometimes also called dark...
.) However, languages such as Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
and perhaps the Northern Iroquoian languages
Iroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a First Nation and Native American language family.-Family division:*Ruttenber, Edward Manning. 1992 [1872]. History of the Indian tribes of Hudson's River. Hope Farm Press....
have something closer to a true labial–velar approximant, where the lips come together. In close transcription, the symbol [w] may be avoided in such cases, or it may be used with an under-rounding diacritic, as [w̜].
[w] and its voiceless equivalent are the only labialized velars with dedicated IPA symbols:
| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
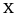 |
voiceless labialized velar approximant | English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
which | [ʍɪtʃ]1 | 'which' |
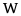 |
voiced labialized velar approximant | English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
witch | [wɪtʃ] | 'witch' |
1In dialects that distinguish between which and witch.
The voiceless approximant is traditionally called a "voiceless labial–velar fricative", but true doubly articulated
Doubly articulated consonant
Doubly articulated consonants are consonants with two simultaneous primary places of articulation of the same manner . They are a subset of co-articulated consonants. They are to be distinguished from co-articulated consonants with secondary articulation, that is, a second articulation not of the...
fricatives are not known to be used in any language, as they are quite difficult to pronounce and even more to aurally distinguish. (However, very occasionally the symbol [ʍ] is used for a labialized velar fricative, [xʷ]. This usage is not approved by the IPA
International Phonetic Association
The International Phonetic Association is an organization that promotes the scientific study of phonetics and the various practical applications of that science. The IPA’s major contribution to phonetics is the International Phonetic Alphabet—a notational standard for the phonetic...
.)
See also
- Labialization
- Doubly articulated consonantDoubly articulated consonantDoubly articulated consonants are consonants with two simultaneous primary places of articulation of the same manner . They are a subset of co-articulated consonants. They are to be distinguished from co-articulated consonants with secondary articulation, that is, a second articulation not of the...
- Co-articulated consonantCo-articulated consonantCo-articulated consonants or complex consonants are consonants produced with two simultaneous places of articulation. They may be divided into two classes, doubly articulated consonants with two primary places of articulation of the same manner , and consonants with secondary articulation, that is,...
- Proto-Indo-European languageProto-Indo-European languageThe Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...

