
Laboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery
Encyclopedia

Surgical planning
The surgical planning is the preoperative method of pre-visualising a surgical intervention, in order to predefine the surgical steps and furthermore the bone segment navigation in the context of computer assisted surgery....
. Starting with 1998, LUCAS was developed at the University of Regensburg, Germany
University of Regensburg
The University of Regensburg is a public research university located in the medieval city of Regensburg, Bavaria, a city that is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university was founded on July 18, 1962 by the Landtag of Bavaria as the fourth full-fledged university in Bavaria...
, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company. The resulting surgical planning is then reproduced
Bone segment navigation
Bone segment navigation is a surgical method used in the field to find the anatomical position of displaced bone fragments in fractures, allowing a good fixation by osteosynthesis. It has been developed for the first time in oral and maxillofacial surgery....
onto the patient by using a navigation system
Surgical Segment Navigator
The Surgical Segment Navigator is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the Surgical Tool Navigator , the Surgical Microscope Navigator and the 6DOF Manipulator , developed by Carl Zeiss.- SSN :The SSN has been developed as...
. In fact, LUCAS is integrated into the same platform
Platform (computing)
A computing platform includes some sort of hardware architecture and a software framework , where the combination allows software, particularly application software, to run...
together with the Surgical Segment Navigator (SSN)
Surgical Segment Navigator
The Surgical Segment Navigator is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the Surgical Tool Navigator , the Surgical Microscope Navigator and the 6DOF Manipulator , developed by Carl Zeiss.- SSN :The SSN has been developed as...
, the Surgical Tool Navigator (STN), the Surgical Microscope Navigator (SMN) and the 6DOF
Degrees of freedom (engineering)
In mechanics, degrees of freedom are the set of independent displacements and/or rotations that specify completely the displaced or deformed position and orientation of the body or system...
Manipulator (or, in German, "Mehrkoordinatenmanipulator" - MKM), also from the Carl Zeiss Company.
Workflow
Data from separate bidimensional2D geometric model
A 2D geometric model is a geometric model of an object as two-dimensional figure, usually on the Euclidean or Cartesian plane.Even though all material objects are three-dimensional, a 2D geometric model is often adequate for certain flat objects, such as paper cut-outs and machine parts made of...
slices generated by a CT
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
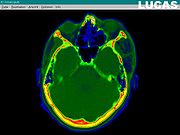
or MRI scan are uploaded into the LUCAS system. The resulting dataset is then processed, in order to eliminate image noise
Image noise
Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images, and is usually an aspect of electronic noise. It can be produced by the sensor and circuitry of a scanner or digital camera...
, and to enhance the anatomical contours and also the general contrast of the images. The next step is to create a virtual 3D
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
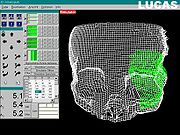
model from the gathered collection of 2D
2D geometric model
A 2D geometric model is a geometric model of an object as two-dimensional figure, usually on the Euclidean or Cartesian plane.Even though all material objects are three-dimensional, a 2D geometric model is often adequate for certain flat objects, such as paper cut-outs and machine parts made of...
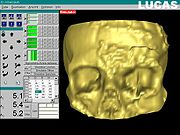
images. The bone segment that is to be repositioned is marked, on the 3D grid reconstructed model; then, the actual repositioning of that bone segment is done on the virtual model, until the optimal anatomical position is obtained. The criteria for the optimal position of the bone segment are: symmetry with the opposite side, the continuity of the normal bone contours, or the normal volume of an anatomical region (such as the Orbit
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
. Afterwards, a textured final image is rendered. The calculated vectors for the bone segment repositioning, together with the whole virtual model are finally transferred to the Surgical Segment Navigator
Surgical Segment Navigator
The Surgical Segment Navigator is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the Surgical Tool Navigator , the Surgical Microscope Navigator and the 6DOF Manipulator , developed by Carl Zeiss.- SSN :The SSN has been developed as...
.

