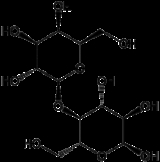
Lactose
Overview
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
that is found most notably in milk
Milk
Milk is a white liquid produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals before they are able to digest other types of food. Early-lactation milk contains colostrum, which carries the mother's antibodies to the baby and can reduce the risk of many...
and is formed from galactose
Galactose
Galactose , sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a type of sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose....
and glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
. Lactose makes up around 2~8% of milk (by weight), although the amount varies among species and individuals. It is extracted from sweet or sour whey
Whey
Whey or Milk Serum is the liquid remaining after milk has been curdled and strained. It is a by-product of the manufacture of cheese or casein and has several commercial uses. Sweet whey is manufactured during the making of rennet types of hard cheese like cheddar or Swiss cheese...
. The name comes from or , the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
word for milk, plus the -ose ending used to name sugars. It has a formula of C12H22O11.
Lactose was discovered in milk in 1619 by Fabriccio Bartoletti, and identified as a sugar in 1780 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele was a German-Swedish pharmaceutical chemist. Isaac Asimov called him "hard-luck Scheele" because he made a number of chemical discoveries before others who are generally given the credit...
.
Lactose is a disaccharide
Disaccharide
A disaccharide or biose is the carbohydrate formed when two monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction which involves the elimination of a small molecule, such as water, from the functional groups only. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides form an aqueous solution when dissolved in water...
derived from the condensation
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
of galactose
Galactose
Galactose , sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a type of sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose....
and glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
, which form a β-1→4 glycosidic linkage.
Unanswered Questions

