
Lagrangian and Eulerian coordinates
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
and finite-deformation plasticity
the Lagrangian specification of the flow field is a way of looking at fluid motion where the observer follows an individual fluid parcel as it moves through space and time. Plotting the position of an individual parcel through time gives the pathline of the parcel. This can be visualized as sitting in a boat and drifting down a river.
The Eulerian specification of the flow field is a way of looking at fluid motion that focuses on specific locations in the space through which the fluid flows as time passes. This can be visualized by sitting on the bank of a river and watching the water pass the fixed location.
The Lagrangian and Eulerian specifications of the flow field are sometimes loosely denoted as the Lagrangian and Eulerian frame of reference. However, in general both the Lagrangian and Eulerian specification of the flow field can be applied in any observer's frame of reference
, and in any coordinate system
used within the chosen frame of reference.
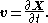
Consequently, u and v are related through
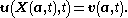
Within a chosen coordinate system, a and x are referred to as the Lagrangian coordinates and Eulerian coordinates of the flow.
The Lagrangian and Eulerian specifications of the kinematics
and dynamics of the flow field are related by the substantial derivative (also called the Lagrangian derivative, convective derivative, material derivative, or particle derivative):
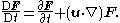
This tells us that the total rate of change of some vector function F as the fluid parcels moves through a flow field described by its Eulerian specification u is equal to the sum of the local rate of change and convective rate of change of F.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
and finite-deformation plasticity
Plasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, plasticity describes the deformation of a material undergoing non-reversible changes of shape in response to applied forces. For example, a solid piece of metal being bent or pounded into a new shape displays plasticity as permanent changes occur within the...
the Lagrangian specification of the flow field is a way of looking at fluid motion where the observer follows an individual fluid parcel as it moves through space and time. Plotting the position of an individual parcel through time gives the pathline of the parcel. This can be visualized as sitting in a boat and drifting down a river.
The Eulerian specification of the flow field is a way of looking at fluid motion that focuses on specific locations in the space through which the fluid flows as time passes. This can be visualized by sitting on the bank of a river and watching the water pass the fixed location.
The Lagrangian and Eulerian specifications of the flow field are sometimes loosely denoted as the Lagrangian and Eulerian frame of reference. However, in general both the Lagrangian and Eulerian specification of the flow field can be applied in any observer's frame of reference
Frame of reference
A frame of reference in physics, may refer to a coordinate system or set of axes within which to measure the position, orientation, and other properties of objects in it, or it may refer to an observational reference frame tied to the state of motion of an observer.It may also refer to both an...
, and in any coordinate system
Coordinate system
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system which uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of a point or other geometric element. The order of the coordinates is significant and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by...
used within the chosen frame of reference.
Description
In the Eulerian specification of the flow field, the flow quantities are depicted as a function of fixed position x and time t. Specifically, the flow velocity is described as u(x,t). On the other hand, in the Lagrangian specification, all fluid parcels are labelled by some vector field a, with a time-independent for each fluid parcel. Often, a is chosen to be the center of mass of the parcels at some initial time t0. It is chosen in this particular manner to account for the possible changes of the shape over time. Therefore the center of mass is a good parametrization of the velocity v of the parcel. In the Lagrangian description, the flow velocity v(a,t) is related to the position X(a,t) of the fluid parcels by: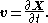
Consequently, u and v are related through
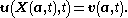
Within a chosen coordinate system, a and x are referred to as the Lagrangian coordinates and Eulerian coordinates of the flow.
The Lagrangian and Eulerian specifications of the kinematics
Kinematics
Kinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
and dynamics of the flow field are related by the substantial derivative (also called the Lagrangian derivative, convective derivative, material derivative, or particle derivative):
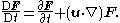
This tells us that the total rate of change of some vector function F as the fluid parcels moves through a flow field described by its Eulerian specification u is equal to the sum of the local rate of change and convective rate of change of F.
See also
- Streamlines, streaklines, and pathlines
- Fluid dynamicsFluid dynamicsIn physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
- Frame of referenceFrame of referenceA frame of reference in physics, may refer to a coordinate system or set of axes within which to measure the position, orientation, and other properties of objects in it, or it may refer to an observational reference frame tied to the state of motion of an observer.It may also refer to both an...
- Coordinate systemCoordinate systemIn geometry, a coordinate system is a system which uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of a point or other geometric element. The order of the coordinates is significant and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by...
- Equivalent latitudeEquivalent latitudeEquivalent latitude is a Lagrangian coordinateused in atmospheric science,particularly in the study of stratospheric dynamics.Each isoline in a map of equivalent latitude follows that of an atmospherictracer and encloses the same area as the latitude line...

