
Languages of Norway
Encyclopedia
There are a large number of languages spoken in Norway. Of these, the Norwegian language
is the most widely spoken and the main official language of the country.
is Norwegian. It is a North Germanic language, closely related to Swedish
and Danish
, all linguistic descendants of Old Norse
. Norwegian is used by some 95% of the population as a first language. The language has two separate written standards
: Nynorsk
("New Norwegian", "new" in the sense of contemporary or modern) and Bokmål
("Book Language"), both of which are official.
is a movement rooted in both Norwegian nationalism and the 400 years of Danish
rule in Norway (see Denmark-Norway). The koiné (mixed language) known as Dano-Norwegian
(Dansk-Norsk) which developed in Norwegian cities was the result of Danish replacing Norwegian as the language of the elite in that country (Danish was used in courts of law, by the cultured, and, after the Lutheran Reformation of 1536, replaced Latin as a liturgical language). An adoption of Norwegian orthography into the Danish language gave rise to the written standard of Riksmål, which later became Bokmål. Nynorsk, a new standard of Norwegian based upon the spoken language, was acknowledged by the parliament in 1885, and in 1892 it was first possible to use Nynorsk as a language of primary instruction. By 1920, Nynorsk was being used widely in western Norway and the mountain valleys, where it still has its stronghold, and Bokmål was used in the more populous areas of the country. Later, attempts were made to reconcile the two standards into Samnorsk, or "Common Norwegian", although this never came to fruition.
in the 1850s, based on rural, spoken Norwegian, rather than the cultured, Danish-influenced Norwegian spoken in cities. Its first official codification was in 1901, was given the name Nynorsk in 1929, and has been used officially (alongside Bokmål) since 1938. Its usage, however has declined: in 1944 it was used by 34,1% (highest recorded number), in 1971 by 17,5% of the population, today, some 15% of schoolchildren are taught Nynorsk as their written language, and nynorsk is reportedly used as main form of Norwegian by around 7,4% of the total population, whereas an additional 5% switch between bokmål and nynorsk.
. It has few active users, but is supported by the Ivar Aasen-sambandet
organization, founded in 1965 in response to the samnorsk policy of the government at the time.
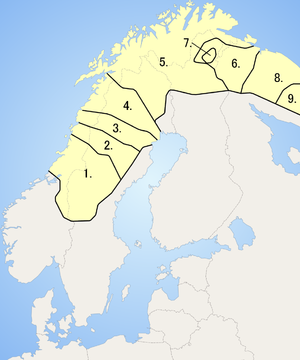 The Sami people
The Sami people
were the original inhabitants of Northern Scandinavia, and though they mostly adopted Norwegian, Swedish, Finnish, or Russian
, due in no small part to official assimilation policies, some still speak Sami languages
. Sami languages, like Kven and Finnish, belong to the Uralic
language family. The Sami languages spoken in Norway include Lule Sami
(spoken by around 500 in Norway), North Sami (spoken by around 15,000 Norwegian Sami), Pite Sami
(which is nearly extinct
) and South Sami (which has around 300 speakers in Norway). Sami languages are official in seven Norwegian municipalities.
 Spoken by the Kven people, the Kven language
Spoken by the Kven people, the Kven language
is a Finnic language, closely related to Finnish
, and spoken by some five to eight thousand people in northeastern Norway, particularly in Tromsø
(in the county of Troms
) and Finnmark
. Mirroring the situation of Meänkieli
in Sweden
, Kven is sometimes considered to be a dialect of Finnish, and has a large degree of mutual intelligibility
with the language.
, and today are spread across all of Europe
. The Romani language
, an Indo-European
, Indo-Aryan language (related to other languages spoken in India today), is split into a great number of dialects. Two of these, Tavringer Romani and Vlax Romani, are spoken in Norway, by populations of 6,000 and 500, respectively. Scandoromani
is another Romani dialect indigenous to Norway, as well as Sweden. Because of the wandering nature of the Roma people, there is no geographic stronghold of the Romani language in Norway.
, a gypsy population in Norway which intermarried with Romani and Yeniche (German Traveller) populations, the Norwegian Traveller language, also known as Rodi
, is based on Norwegian, but has heavy borrowing from Northern Romani and Rotwelsch
. There is no estimate on how many Norwegian Traveller speakers there are in Norway, but it is known that the language is alive.
Norwegian language
Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Norway, where it is the official language. Together with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants .These Scandinavian languages together with the Faroese language...
is the most widely spoken and the main official language of the country.
Norwegian
The most widely spoken language in NorwayNorway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
is Norwegian. It is a North Germanic language, closely related to Swedish
Swedish language
Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish...
and Danish
Danish language
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language...
, all linguistic descendants of Old Norse
Old Norse
Old Norse is a North Germanic language that was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and inhabitants of their overseas settlements during the Viking Age, until about 1300....
. Norwegian is used by some 95% of the population as a first language. The language has two separate written standards
Standard language
A standard language is a language variety used by a group of people in their public discourse. Alternatively, varieties become standard by undergoing a process of standardization, during which it is organized for description in grammars and dictionaries and encoded in such reference works...
: Nynorsk
Nynorsk
Nynorsk or New Norwegian is one of two official written standards for the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. The standard language was created by Ivar Aasen during the mid-19th century, to provide a Norwegian alternative to the Danish language which was commonly written in Norway at the...
("New Norwegian", "new" in the sense of contemporary or modern) and Bokmål
Bokmål
Bokmål is one of two official Norwegian written standard languages, the other being Nynorsk. Bokmål is used by 85–90% of the population in Norway, and is the standard most commonly taught to foreign students of the Norwegian language....
("Book Language"), both of which are official.
Norwegian language struggle
Known as Språkstriden in Norwegian, the Norwegian language struggleNorwegian language struggle
The Norwegian language struggle is an ongoing controversy within Norwegian culture and politics related to spoken and written Norwegian. From the 16th to the 19th centuries, Danish was the standard written language of Norway due to Danish rule...
is a movement rooted in both Norwegian nationalism and the 400 years of Danish
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
rule in Norway (see Denmark-Norway). The koiné (mixed language) known as Dano-Norwegian
Dano-Norwegian
Dano-Norwegian is a linguistic term for a koiné that evolved among the urban elite in Norwegian cities during the later years of the union between the Kingdoms of Denmark and Norway . It is from this koiné that Riksmål and Bokmål developed...
(Dansk-Norsk) which developed in Norwegian cities was the result of Danish replacing Norwegian as the language of the elite in that country (Danish was used in courts of law, by the cultured, and, after the Lutheran Reformation of 1536, replaced Latin as a liturgical language). An adoption of Norwegian orthography into the Danish language gave rise to the written standard of Riksmål, which later became Bokmål. Nynorsk, a new standard of Norwegian based upon the spoken language, was acknowledged by the parliament in 1885, and in 1892 it was first possible to use Nynorsk as a language of primary instruction. By 1920, Nynorsk was being used widely in western Norway and the mountain valleys, where it still has its stronghold, and Bokmål was used in the more populous areas of the country. Later, attempts were made to reconcile the two standards into Samnorsk, or "Common Norwegian", although this never came to fruition.
Bokmål
Bokmål, the written language of 80-90% of the Norwegian population, is based on Riksmål, although it differs in terms of genders, lexicon, counting system, a tendency to permit concrete noun endings in abstract situations and diphthongs versus single vowels. Riksmål was officially changed to Bokmål in 1929.Nynorsk
Nynorsk was developed by the linguist Ivar AasenIvar Aasen
Ivar Andreas Aasen was a Norwegian philologist, lexicographer, playwright and poet.-Background:...
in the 1850s, based on rural, spoken Norwegian, rather than the cultured, Danish-influenced Norwegian spoken in cities. Its first official codification was in 1901, was given the name Nynorsk in 1929, and has been used officially (alongside Bokmål) since 1938. Its usage, however has declined: in 1944 it was used by 34,1% (highest recorded number), in 1971 by 17,5% of the population, today, some 15% of schoolchildren are taught Nynorsk as their written language, and nynorsk is reportedly used as main form of Norwegian by around 7,4% of the total population, whereas an additional 5% switch between bokmål and nynorsk.
Høgnorsk
A more conservative variation of Nynorsk exists, called HøgnorskHøgnorsk
Høgnorsk, meaning "High Norwegian", is a term for varieties of the Norwegian language form Nynorsk that reject most of the official reforms that have been introduced since the creation of Landsmål...
. It has few active users, but is supported by the Ivar Aasen-sambandet
Ivar Aasen-sambandet
Ivar Aasen-sambandet is an umbrella organization of associations and individuals promoting the use of the Høgnorsk variant of the Norwegian language.- History :...
organization, founded in 1965 in response to the samnorsk policy of the government at the time.
Sami languages

Sami people
The Sami people, also spelled Sámi, or Saami, are the arctic indigenous people inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses parts of far northern Sweden, Norway, Finland, the Kola Peninsula of Russia, and the border area between south and middle Sweden and Norway. The Sámi are Europe’s northernmost...
were the original inhabitants of Northern Scandinavia, and though they mostly adopted Norwegian, Swedish, Finnish, or Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
, due in no small part to official assimilation policies, some still speak Sami languages
Sami languages
Sami or Saami is a general name for a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sami people in parts of northern Finland, Norway, Sweden and extreme northwestern Russia, in Northern Europe. Sami is frequently and erroneously believed to be a single language. Several names are used for the Sami...
. Sami languages, like Kven and Finnish, belong to the Uralic
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
language family. The Sami languages spoken in Norway include Lule Sami
Lule Sami
Lule Sami is a Uralic, Sami language spoken in Lule Lappmark, i.e., around Luleå, Sweden and in the northern parts of Nordland county in Norway, especially Tysfjord municipality, where Lule Sami is an official language...
(spoken by around 500 in Norway), North Sami (spoken by around 15,000 Norwegian Sami), Pite Sami
Pite Sami
Pite Sami, also known as Arjeplog Sami, is a Sami language traditionally spoken in Sweden and Norway. It is a critically endangered language that has only about 25–50 native speakers left and is now only spoken on the Swedish side of the border along the Pite River in the north of Arjeplog...
(which is nearly extinct
Endangered language
An endangered language is a language that is at risk of falling out of use. If it loses all its native speakers, it becomes a dead language. If eventually no one speaks the language at all it becomes an "extinct language"....
) and South Sami (which has around 300 speakers in Norway). Sami languages are official in seven Norwegian municipalities.
Kven


Kven language
The Kven language is a Finnic language spoken in Northern Norway by the Kven people. For political and historical reasons it received the status of a minority language in 2005 within the framework of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
is a Finnic language, closely related to Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
, and spoken by some five to eight thousand people in northeastern Norway, particularly in Tromsø
Tromsø
Tromsø is a city and municipality in Troms county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.Tromsø city is the ninth largest urban area in Norway by population, and the seventh largest city in Norway by population...
(in the county of Troms
Troms
or Romsa is a county in North Norway, bordering Finnmark to the northeast and Nordland in the southwest. To the south is Norrbotten Län in Sweden and further southeast is a shorter border with Lapland Province in Finland. To the west is the Norwegian Sea...
) and Finnmark
Finnmark
or Finnmárku is a county in the extreme northeast of Norway. By land it borders Troms county to the west, Finland to the south and Russia to the east, and by water, the Norwegian Sea to the northwest, and the Barents Sea to the north and northeast.The county was formerly known as Finmarkens...
. Mirroring the situation of Meänkieli
Meänkieli
Meänkieli is the name used in Sweden for Finnish dialects spoken in the northernmost parts of the country, around the valley of the Torne River....
in Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, Kven is sometimes considered to be a dialect of Finnish, and has a large degree of mutual intelligibility
Mutual intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is recognized as a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related languages can readily understand each other without intentional study or extraordinary effort...
with the language.
Romani
The Roma people, commonly called gypsies, are a diaspora population originating in IndiaIndia
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, and today are spread across all of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. The Romani language
Romani language
Romani or Romany, Gypsy or Gipsy is any of several languages of the Romani people. They are Indic, sometimes classified in the "Central" or "Northwestern" zone, and sometimes treated as a branch of their own....
, an Indo-European
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
, Indo-Aryan language (related to other languages spoken in India today), is split into a great number of dialects. Two of these, Tavringer Romani and Vlax Romani, are spoken in Norway, by populations of 6,000 and 500, respectively. Scandoromani
Scandoromani
Scandoromani , also known as Tavringer Romani and the Tattare language, is a North Germanic based Para-Romani. It is currently spoken by the Norwegian and Swedish Travellers, a Romani minority community, in Sweden and Norway ."Scandoromani" is a term coined by academics...
is another Romani dialect indigenous to Norway, as well as Sweden. Because of the wandering nature of the Roma people, there is no geographic stronghold of the Romani language in Norway.
Norwegian Traveller
Spoken by the Norwegian TravellersIndigenous Norwegian Travellers
The indigenous Norwegian Travellers are an ethnic minority group in Norway. They are a wandering people who once travelled by foot, with horse-drawn carts and with boats along the southern and southwestern coastline of Norway.-Names for the group:...
, a gypsy population in Norway which intermarried with Romani and Yeniche (German Traveller) populations, the Norwegian Traveller language, also known as Rodi
Rodi language
Rodi, also known by the ambiguous term Traveller Norwegian, is a language spoken by the indigenous Norwegian Travellers in Norway. It is an offshoot of Norwegian with significant influence of Sinti, Rotwelsch and, especially in recent decades, Scandoromani...
, is based on Norwegian, but has heavy borrowing from Northern Romani and Rotwelsch
Rotwelsch
Rotwelsch or Gaunersprache is a secret language, a cant or thieves' argot, spoken by covert groups primarily in southern Germany and Switzerland.-Origin and development:...
. There is no estimate on how many Norwegian Traveller speakers there are in Norway, but it is known that the language is alive.

