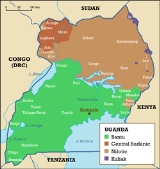
Languages of Uganda
Encyclopedia
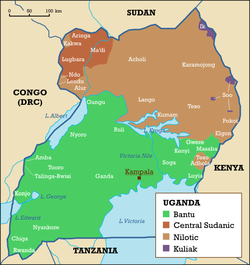
Uganda
Uganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
is a multilingual country. Forty of its living indigenous languages fall into three main families - Bantu
Bantu languages
The Bantu languages constitute a traditional sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages. There are about 250 Bantu languages by the criterion of mutual intelligibility, though the distinction between language and dialect is often unclear, and Ethnologue counts 535 languages...
, Nilotic
Nilotic languages
The Nilotic languages are a group of Eastern Sudanic languages spoken across a wide area between southern Sudan and Tanzania by the Nilotic peoples, particularly associated with cattle-herding...
, and Central Sudanic
Central Sudanic languages
Starostin notes that the poorly attested language Mimi of Decorse is suggestive of Central Sudanic, though he provisionally treats it as an isolate.-References:...
- with another 2 languages in the Kuliak family
Kuliak languages
-References:* Heine, Bernd The Kuliak Languages of Eastern Uganda. Nairobi: East African Publishing House.* Ehret, Christopher "The classification of Kuliak", in ed. Thilo Schadeberg & Lionel Bender, Nilo-Saharan: Proceedings of the First Nilo-Saharan Linguistics Colloquium, Leiden, September...
. English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, inherited from the colonial period, and Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
, which is regionally important, are official languages. There is also a Ugandan Sign Language
Ugandan Sign Language
Ugandan Sign Language is the deaf sign language of Uganda. Uganda was the second country in the world to recognize sign language in its constitution, in 1995. A Ugandan Sign Language Dictionary has been published. However, knowledge of USL is primarily urban, as access to education for the rural...
.
Languages indigenous to Uganda
In all of the Bantu speaking areas of Uganda, dialect continuaDialect continuum
A dialect continuum, or dialect area, was defined by Leonard Bloomfield as a range of dialects spoken across some geographical area that differ only slightly between neighboring areas, but as one travels in any direction, these differences accumulate such that speakers from opposite ends of the...
are very common. For example, people around Mbarara in Ankole District speak Nkole and people from Fort Portal in Toro District speak Tooro, but in the area between those towns one will find villages where most of the people speak a dialect which is best characterized as intermediate between Nkole and Tooro. In recognition of the closeness of four of these languages (Nkole, Tooro, Kiga, and Nyoro
Nyoro language
The Nyoro language is a local language of the Nyoro people of Uganda. It belongs to the Niger–Congo family, Benue–Congo subgroup, Bantu branch . Its Ethnologue code is NYR, ISO 639-2: nyo. It probably has two dialects: Orunyoro and Rutagwenda. A standardized orthography was established in 1947....
), and in order to facilitate work in them such as teaching, a standardized version called "Runyakitara"
Runyakitara language
The Kitara language, commonly known as Runyakitara, is a recent standardized form of four linguistically closely related languages of western Uganda:*Nyoro or Runyoro*Kiga or Rukiga...
was developed around 1990.
In south central Uganda
Uganda
Uganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by...
, the Bantu languages
Bantu languages
The Bantu languages constitute a traditional sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages. There are about 250 Bantu languages by the criterion of mutual intelligibility, though the distinction between language and dialect is often unclear, and Ethnologue counts 535 languages...
of Luganda and Soga are largely interintelligible
Mutual intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is recognized as a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related languages can readily understand each other without intentional study or extraordinary effort...
.
Of Nilo-Saharan, the Eastern Sudanic
Eastern Sudanic languages
Ehret 2001 [1984]Ehret, published in 2001 but circulating in manuscript form since at least 1984, calls the family "Eastern Sahelian", and idiosyncratically adds the Kuliak languages and Berta, which Bender assigns to higher-level branches of Nilo-Saharan, and reassigns Nyima to the southern branch...
branch is well represented by several Nilotic languages, eastern
Eastern Nilotic languages
The Eastern Nilotic languages are one of the three primary branches of the Nilotic languages, themselves belonging to the Eastern Sudanic subfamily of Nilo-Saharan; they are believed to have begun to diverge about 3,000 years ago, and have spread southwards from an original home in Equatoria in...
as well as western
Western Nilotic languages
The Western Nilotic languages are one of the three primary branches of the Nilotic languages, themselves belonging to the Eastern Sudanic subfamily of Nilo-Saharan...
. Eastern Nilotic languages include Karamojong
Karamojong language
The Karamojong Language is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken mainly in the Karamoja subregion of north-eastern Uganda....
of Eastern Uganda (370,000), the Bari languages in the extreme northwestern corner (about 150,000), and Teso south of Lake Kyoga (999,537). Alur
Alur language
Alur is spoken in northwestern Uganda and northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo by the Alur people.Dialects*Jokot*Jonam *Mambisa*Wanyoro- Phonetics :VowelsAlur has 9 vowels....
(459,000), Acholi
Acholi language
Acholi is a language primarily spoken by the Acholi people in the districts of Gulu, Kitgum and Pader, a region known as Acholiland in northern Uganda. Acholi is also spoken in the southern part of the Opari District of South Sudan...
, Lango, Adhola language and Kumam language of eastern Uganda are Western Nilotic Luo languages
Luo languages
The Nilotic Luo languages, or Lwoian, are a dozen languages spoken by the Luo peoples in an area ranging from southern Sudan via Uganda to southern Kenya, with Dholuo extending into northern Tanzania and Alur into the Democratic Republic of the Congo. They form one of the two branches of Western...
(Acholi and Lango are interintelligible, and sometimes the term "Luo" is used to cover them). Some southern Nilotic Kalenjin languages are spoken along the border with Kenya
Kenya
Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east...
, including Pokot and the Elgon languages
Elgon languages
The Elgon languages are languages of the Southern Nilotic Kalenjin family spoken in the Mount Elgon area in western Kenya and eastern Uganda. According to the Ethnologue, there are two main Elgon languages: Kupsabiny and Sabaot...
near Kupsabiny. The eastern Ugandan Kuliak languages
Kuliak languages
-References:* Heine, Bernd The Kuliak Languages of Eastern Uganda. Nairobi: East African Publishing House.* Ehret, Christopher "The classification of Kuliak", in ed. Thilo Schadeberg & Lionel Bender, Nilo-Saharan: Proceedings of the First Nilo-Saharan Linguistics Colloquium, Leiden, September...
Ik
Ik language
The Ik language, also known as Icetot, Icietot, Ngulak, or Teuso, Teuth, are one of the Kuliak languages of northeastern Uganda. The Ik people have a positive attitude toward their language, which is increasing; with Tepes being moribund, Ik may soon be the sole remaining language of its family....
and Soo are also members of the Eastern Sudanic branch. Lugbara
Lugbara language
Lugbara is the language of the Lugbara people. It is spoken in the West Nile region in northwestern Uganda, as well as the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Orientale Province. Lugbara was first written by Christian missionaries in 1918, based on the Ayivu dialect...
, Aringa
Aringa language
Aringa, also known as Low Lugbara, is a Central Sudanic language spoken by the Aringa people in the West Nile region of Uganda. It is related to the language spoken by the Lugbara and Madi peoples....
, Ma'di
Madi language (Sudan and Uganda)
The Ma'di language is a found in Uganda and South Sudan. . The Madi people refer to their language as Ma'di ti literally: Ma'di mouth....
and Ndo
Ndo language
Ndo, also Ke’bu or Membitu, is a Central Sudanic language of northeastern Congo and western Uganda spoken by a caste of blacksmiths....
of northwestern Uganda are languages of the Central Sudanic
Central Sudanic languages
Starostin notes that the poorly attested language Mimi of Decorse is suggestive of Central Sudanic, though he provisionally treats it as an isolate.-References:...
branch of Nilo-Saharan.
Language policy
In Uganda, like in many African countries, EnglishEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, the language of the colonizing power, was introduced in government and public life by way of missionary work and the educational system. During the first decades of the twentieth century, Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
gained influence as it was not only used in the army and the police, but was also taught in schools. The Ganda viewed the introduction of Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
as a threat to their political power and partly through their influence, English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
remained the only official language at that time. Upon Uganda's independence in 1962, English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
was maintained as the official language, as it was already rooted deeply in administration, media, and education. Also, Uganda's ethnolinguistic diversity made it difficult to choose another language as the official language
Official language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
of Uganda.
After independence there were efforts to choose an indigenous official language, with Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
and Luganda as the most considered candidates. Although Luganda was the most geographically spread language, people outside Buganda
Buganda
Buganda is a subnational kingdom within Uganda. The kingdom of the Ganda people, Buganda is the largest of the traditional kingdoms in present-day Uganda, comprising all of Uganda's Central Region, including the Ugandan capital Kampala, with the exception of the disputed eastern Kayunga District...
were opposed to having it as a national language
National language
A national language is a language which has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a people and perhaps by extension the territory they occupy. The term is used variously. A national language may for instance represent the national identity of a nation or country...
, as were those of the Buganda kingdom because they felt other tribes' mispronunciation and grammar errors would ruin their language. English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
remained the official language.
The native languages of the Ugandan people have had interesting effects on the English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
spoken in the country, leading to what many call Ugandan English
Ugandan English
Ugandan English,, the dialect of English spoken in Uganda, like those spoken elsewhere, has developed a strong local flavour. Though standard British English is widely considered to be the correct form of the language in Uganda, most Ugandans who speak English have had little contact with native...
.
During the regime of Idi Amin
Idi Amin
Idi Amin Dada was a military leader and President of Uganda from 1971 to 1979. Amin joined the British colonial regiment, the King's African Rifles in 1946. Eventually he held the rank of Major General in the post-colonial Ugandan Army and became its Commander before seizing power in the military...
, Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
, the East African lingua franca
Lingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
, became the second official national language, but it lost its official and national status in the 1995 Constitution. In September 2005, the Ugandan Parliament voted to once again make Swahili
Swahili language
Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia...
the second official national language. It is most widely spoken outside of Buganda.

