
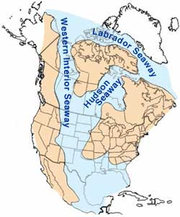
Laramidia
Encyclopedia
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous period is divided in the geologic timescale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous series...
period, when the Western Interior Seaway
Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway, also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, and the North American Inland Sea, was a huge inland sea that split the continent of North America into two halves, Laramidia and Appalachia, during most of the mid- and late-Cretaceous Period...
split the continent of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
in two. Two landmasses existed: the eastern one is called Appalachia
Appalachia (Mesozoic)
In the Mesozoic Era, Appalachia was a land area which is now an eastern part of the USA and Canada, separated from Laramidia by the Western Interior Seaway, which shrank, divided across the Dakotas, retreated south towards the Gulf of Mexico and finally dried up.-Fauna:From the Turonian age of the...
; Laramidia is the name given to the western landmass. Since the two landmasses were separated geographically, the fauna on each of them was quite different. For example, the armor-plated nodosaurs were relatively abundant in Appalachia. However, in Laramidia, only rare and specialized forms, such as Edmontonia
Edmontonia
Edmontonia was an armoured dinosaur, a part of the nodosaur family from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is named after the Edmonton Formation , the unit of rock it was found in.-Description:...
and Panoplosaurus
Panoplosaurus
Panoplosaurus is a genus of nodosaurid dinosaur. It was one of the last known nodosaurids, living during the Late Cretaceous in what is now North America; fossils have been located in Alberta, Canada....
, have been found.
Laramidia stretches from modern-day Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
to Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
. It is very rich in dinosaur fossils, suggesting that the American West was home to one of the most diverse dinosaur faunas anywhere in the world. Tyrannosaurs
Tyrannosauridae
Tyrannosauridae is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs which comprises two subfamilies containing up to six genera, including the eponymous Tyrannosaurus. The exact number of genera is controversial, with some experts recognizing as few as three...
, dromaeosaurids
Dromaeosauridae
Dromaeosauridae is a family of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. They were small- to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek dromeus meaning 'runner' and sauros meaning 'lizard'...
, troodontids
Troodontidae
Troodontidae is a family of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and scrappy and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages...
, hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids or duck-billed dinosaurs are members of the family Hadrosauridae, and include ornithopods such as Edmontosaurus and Parasaurolophus. They were common herbivores in the Upper Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia, Europe and North America. They are descendants of the Upper...
, ceratopsia
Ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs which thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. The earliest known ceratopsian, Yinlong downsi, lived between 161.2 and 155.7...
ns (including Kosmoceratops
Kosmoceratops
Kosmoceratops is a genus of herbivorous chasmosaurine ceratopsian dinosaur, which lived during the Late Cretaceous period in the part of the island continent Laramidia that is now Utah, United States...
and Utahceratops
Utahceratops
Utahceratops is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a chasmosaurine ceratopsian which lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now Utah. Its fossils have been recovered from the Kaiparowits Formation. It was first named by Scott D. Sampson, Mark A. Loewen, Andrew A....
), pachycephalosaurs
Pachycephalosauria
Pachycephalosauria is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Well-known genera include Pachycephalosaurus, Stegoceras, Stygimoloch, and Dracorex. Most lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, in what is now North America and Asia. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/omnivorous animals with thick skulls...
, and titanosaur sauropods
Sauropoda
Sauropoda , or the sauropods , are an infraorder of saurischian dinosaurs. They had long necks, long tails, small heads , and thick, pillar-like legs. They are notable for the enormous sizes attained by some species, and the group includes the largest animals to have ever lived on land...
are some of the dinosaur groups that lived on this landmass. Dinosaur fossils have been found in the region from Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
to New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
.

