
Larson-Miller relation
Encyclopedia
The Larson-Miller relation, also widely known as the Larson-Miller Parameter and often abbreviated LMP, is a parametric relation used to extrapolate experimental data on creep
and rupture life of engineering materials.
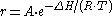
Where r is the creep process rate, A is a constant, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and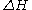 is the activation energy
is the activation energy
for the creep process. Taking the natural log of both sides:
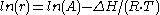
With some rearrangement:
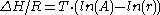
Using the fact that creep rate is inversely proportional to time, the equation can be written as:
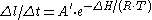
Taking the natural log:
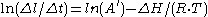
After some rearrangement the relation finally becomes:
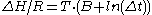 , where B =
, where B = 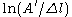
This equation is of the same form as the Larson-Miller relation.
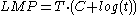
where the quantity LMP is known as the Larson-Miller parameter. Using the assumption that activation energy is independent of applied stress, the equation can be used to relate the difference in rupture life to differences in temperature for a given stress. The material constant C is typically found to be in the range of 20 to 22 for metals.
The Larson-Miller model is used for experimental tests so that results at certain temperatures and stresses can predict rupture lives of time spans that would be impractical to reproduce in the laboratory.
The equation was developed during the 1950s while Miller and Larson were employed by GE performing research on turbine blade life.
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep is the tendency of a solid material to slowly move or deform permanently under the influence of stresses. It occurs as a result of long term exposure to high levels of stress that are below the yield strength of the material....
and rupture life of engineering materials.
Background and usage
F.R. Larson and J. Miller proposed that creep rate could adequately be described by the Arrhenius type equation: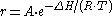
Where r is the creep process rate, A is a constant, R is the universal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, and
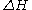 is the activation energy
is the activation energyActivation energy
In chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
for the creep process. Taking the natural log of both sides:
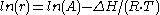
With some rearrangement:
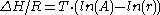
Using the fact that creep rate is inversely proportional to time, the equation can be written as:
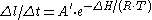
Taking the natural log:
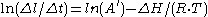
After some rearrangement the relation finally becomes:
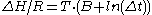 , where B =
, where B = 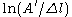
This equation is of the same form as the Larson-Miller relation.
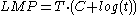
where the quantity LMP is known as the Larson-Miller parameter. Using the assumption that activation energy is independent of applied stress, the equation can be used to relate the difference in rupture life to differences in temperature for a given stress. The material constant C is typically found to be in the range of 20 to 22 for metals.
The Larson-Miller model is used for experimental tests so that results at certain temperatures and stresses can predict rupture lives of time spans that would be impractical to reproduce in the laboratory.
The equation was developed during the 1950s while Miller and Larson were employed by GE performing research on turbine blade life.

