
Law of tangents
Encyclopedia
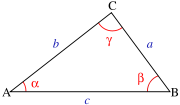
In trigonometry
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
, the law of tangents is a statement about the relationship between the tangents of two angles of a triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
and the lengths of the opposite sides.
In Figure 1, a, b, and c are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle, and α, β, and γ are the angles opposite those three respective sides. The law of tangent
Trigonometric function
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are functions of an angle. They are used to relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of the sides of a triangle...
s states that

The law of tangents, although not as commonly known as the law of sines
Law of sines
In trigonometry, the law of sines is an equation relating the lengths of the sides of an arbitrary triangle to the sines of its angles...
or the law of cosines
Law of cosines
In trigonometry, the law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a plane triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using notation as in Fig...
, is equivalent to the law of sines, and can be used in any case where two sides and the included angle, or two angles and a side, are known.
The law of tangents for spherical triangles was described in the 13th century by Persian mathematician Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Nasir al-Din al-Tusi
Khawaja Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad ibn Ḥasan Ṭūsī , better known as Naṣīr al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī , was a Persian polymath and prolific writer: an astronomer, biologist, chemist, mathematician, philosopher, physician, physicist, scientist, theologian and Marja Taqleed...
(1201–74), who also presented the law of sines for plane triangles in his five-volume work Treatise on the Quadrilateral.
Proof
To prove the law of tangents we can start with the law of sinesLaw of sines
In trigonometry, the law of sines is an equation relating the lengths of the sides of an arbitrary triangle to the sines of its angles...
:
Let
so that
It follows that
Using the trigonometric identity, the factor formula for sines specifically
we get

As an alternative to using the identity for the sum or difference of two sines, one may cite the trigonometric identity
(see tangent half-angle formula).
Application
The law of tangents can be used to compute the missing side and angles of a triangle in which two sides and the enclosed angle
and the enclosed angle  are given. From
are given. From one can compute
one can compute  ; together with
; together with  this yields
this yields  and
and  ; the remaining side
; the remaining side  can then be computed using the Law of sines
can then be computed using the Law of sinesLaw of sines
In trigonometry, the law of sines is an equation relating the lengths of the sides of an arbitrary triangle to the sines of its angles...
. In the time before electronic calculators were available, this method
was preferable to an application of the Law of cosines
Law of cosines
In trigonometry, the law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a plane triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using notation as in Fig...
 , as this latter law necessitated an additional lookups in a logarithm table, in order to compute the square root. In modern times the law of tangents may have better numerical
, as this latter law necessitated an additional lookups in a logarithm table, in order to compute the square root. In modern times the law of tangents may have better numericalNumerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis ....
properties than the law of cosines: If
 is small, and
is small, and  and
and  are almost equal, then an application of the law of cosines leads to a subtraction of almost equal values, which implies a loss of significant digits
are almost equal, then an application of the law of cosines leads to a subtraction of almost equal values, which implies a loss of significant digitsLoss of significance
Loss of significance is an undesirable effect in calculations using floating-point arithmetic. It occurs when an operation on two numbers increases relative error substantially more than it increases absolute error, for example in subtracting two large and nearly equal numbers. The effect is that...
.
See also
- Law of sinesLaw of sinesIn trigonometry, the law of sines is an equation relating the lengths of the sides of an arbitrary triangle to the sines of its angles...
- Law of cosinesLaw of cosinesIn trigonometry, the law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a plane triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using notation as in Fig...
- Mollweide's formulaMollweide's formulaIn trigonometry, Mollweide's formula, sometimes referred to in older texts as Mollweide's equations, named after Karl Mollweide, is a set of two relationships between sides and angles in a triangle...
- Half-side formulaHalf-side formulaIn spherical trigonometry, the half side formula relates the angles and lengths of the sides of spherical triangles, which are triangles drawn on the surface of a sphere and so have curved sides and do not obey the formulas for plane triangles....







