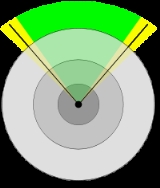
Level of detail
Encyclopedia
In computer graphics
, accounting for level of detail involves decreasing the complexity of a 3D object representation as it moves away from the viewer or according other metrics such as object importance, eye-space speed or position.
Level of detail techniques increases the efficiency of rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline
stages, usually vertex transformations.
The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast.
Although most of the time LOD is applied to geometry detail only, the basic concept can be generalized. Recently, LOD techniques included also shader
management to keep control of pixel complexity.
A form of level of detail management has been applied to textures for years, under the name of mipmapping, also providing higher rendering quality.
It is commonplace to say that "an object has been LOD'd" when the object is simplified by the underlying LOD-ing algorithm.
in the October 1976 issue of Communications of the ACM
.
At the time, computers were monolithic and rare, and graphics was being driven by researchers. The hardware itself was completely different, both architecturally and performance-wise. As such, many differences could be observed with regard to today's algorithms but also many common points.
The original algorithm presented a much more generic approach to what will be discussed here. After introducing some available algorithms for geometry management, it is stated that most fruitful gains came from "...structuring the environments being rendered", allowing to exploit faster transformations and clipping
operations.
The same environment structuring is now proposed as a way to control varying detail thus avoiding unnecessary computations, yet delivering adequate visual quality:
The proposed algorithm envisions a tree data structure
which encodes in its arcs both transformations and transitions to more detailed objects. In this way, each node encodes an object and according to a fast heuristic, the tree is descended to the leafs which provide each object with more detail. When a leaf is reached, other methods could be used when higher detail is needed, such as Catmull
's recursive subdivision.
The paper then introduces clipping (not to be confused with culling (computer graphics), although often similar), various considerations on the graphical working set and its impact on performance, interactions between the proposed algorithm and others to improve rendering speed. Interested readers are encouraged in checking the references for further details on the topic.
The first is based on subdividing the space in a finite amount of regions, each with a certain level of detail. The result is discrete amount of detail levels, from which the name Discrete LoD (DLOD). There's no way to support a smooth transition between LOD levels at this level, although alpha blending or morphing
can be used to avoid visual popping.
The latter considers the polygon mesh
being rendered as a function which must be evaluated requiring to avoid excessive errors which are a function of some heuristic (usually distance) themselves. The given "mesh" function is then continuously evaluated and an optimized version is produced according to a tradeoff between visual quality and performance. Those kind of algorithms are usually referred as Continuous LOD (CLOD).
 The basic concept of discrete LOD (DLOD) is to provide various models to represent the same object. Obtaining those models requires an external algorithm which is often non-trivial and subject of many polygon reduction techniques. Successive LOD-ing algorithms will simply assume those models are available.
The basic concept of discrete LOD (DLOD) is to provide various models to represent the same object. Obtaining those models requires an external algorithm which is often non-trivial and subject of many polygon reduction techniques. Successive LOD-ing algorithms will simply assume those models are available.
DLOD algorithms are often used in performance-intensive applications with small data sets which can easily fit in memory. Although out of core algorithms could be used, the information granularity is not well suited to this kind of application. This kind of algorithm is usually easier to get working, providing both faster performance and lower CPU
usage because of the few operations involved.
DLOD methods are often used for "stand-alone" moving objects, possibly including complex animation methods. A different approach is used for geomipmapping
, a popular terrain rendering
algorithm because this applies to terrain meshes which are both graphically and topologically different from "object" meshes. Instead of computing an error and simplify the mesh according to this, geomipmapping takes a fixed reduction method, evaluates the error introduced and computes a distance at which the error is acceptable. Although straightforward, the algorithm provides decent performance.
. A discrete LOD approach would cache a certain number of models to be used at different distances.
Because the model can trivially be procedurally generated
by its mathematical formulation, using a different amount of sample points distributed on the surface is sufficient to generate the various models required. This pass is not a LOD-ing algorithm.
To simulate a realistic transform bound scenario, we'll use an ad-hoc written application. We'll make sure we're not CPU bound
by using simple algorithms and minimum fragment operations.
Each frame, the program will compute each sphere's distance and choose a model from a pool according to this information. To easily show the concept, the distance at which each model is used is hard code
d in the source. A more involved method would compute adequate models according to the usage distance chosen.
We use OpenGL
for rendering because its high efficiency in managing small batch
es, storing each model in a display list
thus avoiding communication overheads. Additional vertex load is given by applying two directional light sources ideally located infinitely far away.
The following table compares the performance of LoD aware rendering and a full detail (brute force) method.
Computer graphics
Computer graphics are graphics created using computers and, more generally, the representation and manipulation of image data by a computer with help from specialized software and hardware....
, accounting for level of detail involves decreasing the complexity of a 3D object representation as it moves away from the viewer or according other metrics such as object importance, eye-space speed or position.
Level of detail techniques increases the efficiency of rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline
Graphics pipeline
In 3D computer graphics, the terms graphics pipeline or rendering pipeline most commonly refers to the current state of the art method of rasterization-based rendering as supported by commodity graphics hardware. The graphics pipeline typically accepts some representation of a three-dimensional...
stages, usually vertex transformations.
The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast.
Although most of the time LOD is applied to geometry detail only, the basic concept can be generalized. Recently, LOD techniques included also shader
Shader
In the field of computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that is used primarily to calculate rendering effects on graphics hardware with a high degree of flexibility...
management to keep control of pixel complexity.
A form of level of detail management has been applied to textures for years, under the name of mipmapping, also providing higher rendering quality.
It is commonplace to say that "an object has been LOD'd" when the object is simplified by the underlying LOD-ing algorithm.
Historical reference
The origin of all the LoD algorithms for 3D computer graphics can be traced back to an article by James H. ClarkJames H. Clark
James H. Clark is an American entrepreneur and computer scientist. He founded several notable Silicon Valley technology companies, including Silicon Graphics, Inc., Netscape Communications Corporation, myCFO and Healtheon...
in the October 1976 issue of Communications of the ACM
Communications of the ACM
Communications of the ACM is the flagship monthly journal of the Association for Computing Machinery . First published in 1957, CACM is sent to all ACM members, currently numbering about 80,000. The articles are intended for readers with backgrounds in all areas of computer science and information...
.
At the time, computers were monolithic and rare, and graphics was being driven by researchers. The hardware itself was completely different, both architecturally and performance-wise. As such, many differences could be observed with regard to today's algorithms but also many common points.
The original algorithm presented a much more generic approach to what will be discussed here. After introducing some available algorithms for geometry management, it is stated that most fruitful gains came from "...structuring the environments being rendered", allowing to exploit faster transformations and clipping
Clipping (computer graphics)
Any procedure which identifies that portion of a picture which is either inside or outside a picture is referred to as a clipping algorithm or clipping.The region against which an object is to be clipped is called clipping window.-Examples:...
operations.
The same environment structuring is now proposed as a way to control varying detail thus avoiding unnecessary computations, yet delivering adequate visual quality:
The proposed algorithm envisions a tree data structure
Tree (data structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely-used data structure that emulates a hierarchical tree structure with a set of linked nodes.Mathematically, it is an ordered directed tree, more specifically an arborescence: an acyclic connected graph where each node has zero or more children nodes and at...
which encodes in its arcs both transformations and transitions to more detailed objects. In this way, each node encodes an object and according to a fast heuristic, the tree is descended to the leafs which provide each object with more detail. When a leaf is reached, other methods could be used when higher detail is needed, such as Catmull
Edwin Catmull
Dr. Edwin Earl Catmull, Ph.D. is a computer scientist and current president of Walt Disney Animation Studios and Pixar Animation Studios. As a computer scientist, Catmull has contributed to many important developments in computer graphics....
's recursive subdivision.
The paper then introduces clipping (not to be confused with culling (computer graphics), although often similar), various considerations on the graphical working set and its impact on performance, interactions between the proposed algorithm and others to improve rendering speed. Interested readers are encouraged in checking the references for further details on the topic.
Well known approaches
Although the algorithm introduced above covers a whole range of level of detail management techniques, real world applications usually employ different methods according the information being rendered. Because of the appearance of the considered objects, two main algorithm families are used.The first is based on subdividing the space in a finite amount of regions, each with a certain level of detail. The result is discrete amount of detail levels, from which the name Discrete LoD (DLOD). There's no way to support a smooth transition between LOD levels at this level, although alpha blending or morphing
Morphing
Morphing is a special effect in motion pictures and animations that changes one image into another through a seamless transition. Most often it is used to depict one person turning into another through technological means or as part of a fantasy or surreal sequence. Traditionally such a depiction...
can be used to avoid visual popping.
The latter considers the polygon mesh
Polygon mesh
A polygon mesh or unstructured grid is a collection of vertices, edges and faces that defines the shape of a polyhedral object in 3D computer graphics and solid modeling...
being rendered as a function which must be evaluated requiring to avoid excessive errors which are a function of some heuristic (usually distance) themselves. The given "mesh" function is then continuously evaluated and an optimized version is produced according to a tradeoff between visual quality and performance. Those kind of algorithms are usually referred as Continuous LOD (CLOD).
Details on Discrete LOD

DLOD algorithms are often used in performance-intensive applications with small data sets which can easily fit in memory. Although out of core algorithms could be used, the information granularity is not well suited to this kind of application. This kind of algorithm is usually easier to get working, providing both faster performance and lower CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
usage because of the few operations involved.
DLOD methods are often used for "stand-alone" moving objects, possibly including complex animation methods. A different approach is used for geomipmapping
Geomipmapping
Geomipmapping or geometrical mipmapping is a real-time block-based terrain rendering algorithm developed by W.H. de Boer in 2000 that aims to reduce CPU processing time which is a common bottleneck in level of detail approaches to terrain rendering...
, a popular terrain rendering
Terrain rendering
Terrain rendering covers a variety of methods of depicting real-world or imaginary world surfaces. Most common terrain rendering is the depiction of Earth's surface.It is used in various applications to give an observer a frame of reference...
algorithm because this applies to terrain meshes which are both graphically and topologically different from "object" meshes. Instead of computing an error and simplify the mesh according to this, geomipmapping takes a fixed reduction method, evaluates the error introduced and computes a distance at which the error is acceptable. Although straightforward, the algorithm provides decent performance.
A discrete LOD example
As a simple example, consider the following sphereSphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
. A discrete LOD approach would cache a certain number of models to be used at different distances.
Because the model can trivially be procedurally generated
Procedural generation
Procedural generation is a widely used term in the production of media; it refers to content generated algorithmically rather than manually. Often, this means creating content on the fly rather than prior to distribution...
by its mathematical formulation, using a different amount of sample points distributed on the surface is sufficient to generate the various models required. This pass is not a LOD-ing algorithm.
| Image |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertices | ~5500 | ~2880 | ~1580 | ~670 | 140 |
| Notes | Maximum detail, for closeups. |
Minimum detail, very far objects. |
To simulate a realistic transform bound scenario, we'll use an ad-hoc written application. We'll make sure we're not CPU bound
CPU bound
In computer science, CPU bound is when the time for a computer to complete a task is determined principally by the speed of the central processor: processor utilization is high, perhaps at 100% usage for many seconds or minutes...
by using simple algorithms and minimum fragment operations.
Each frame, the program will compute each sphere's distance and choose a model from a pool according to this information. To easily show the concept, the distance at which each model is used is hard code
Hard code
Hard coding refers to the software development practice of embedding what may, perhaps only in retrospect, be regarded as input or configuration data directly into the source code of a program or other executable object, or fixed formatting of the data, instead of obtaining that data from external...
d in the source. A more involved method would compute adequate models according to the usage distance chosen.
We use OpenGL
OpenGL
OpenGL is a standard specification defining a cross-language, cross-platform API for writing applications that produce 2D and 3D computer graphics. The interface consists of over 250 different function calls which can be used to draw complex three-dimensional scenes from simple primitives. OpenGL...
for rendering because its high efficiency in managing small batch
Batch
Batch may refer to:Food and drink*Batch , an alcoholic fruit beverage*Batch loaf, a type of bread popular in Ireland*A dialect term for a bread roll used in Nuneaton and Coventry, England*Small batch, bourbon whiskey blended from selected barrels...
es, storing each model in a display list
Display list
A display list is a series of graphics commands that define an output image. The image is created by executing the commands....
thus avoiding communication overheads. Additional vertex load is given by applying two directional light sources ideally located infinitely far away.
The following table compares the performance of LoD aware rendering and a full detail (brute force) method.
| Brute | DLOD | Comparison | |
| Rendered images |
 |
 |
 |
| Render time | 27.27 ms | 1.29 ms | 21 × reduction |
| Scene vertices (thousands) |
2328.48 | 109.44 | 21 × reduction |
Hierarchical LOD
Because hardware is geared towards large amounts of detail, rendering low polygon objects may score sub-optimal performances. HLOD avoids the problem by grouping different objects together. This allows for higher efficiency as well as taking advantage of proximity considerations.See also
- MeshLabMeshLabMeshLab, is a free 3D mesh processing software program; MeshLab, started in late 2005, is an open-source general-purpose system aimed to help the processing of the typical not-so-small unstructured 3D models that arise in the pipeline of processing of the data coming from 3D scanning...
an open source mesh processing tool that is able to accurately simplify 3D polygonal meshes. - Polygon CruncherPolygon CruncherPolygon Cruncher is a 3D computer graphics software for generating 3D-optimized mesh, based on reduction and other optimization techniques. Polygon Cruncher is also available as an API through an SDK.- Overview :...
- SimplygonSimplygonSimplygon is a 3D computer graphics software for automatic 3D-optimization, based on proprietary methods for creating Level of detail LODs, through smart Polygon mesh reduction and other optimization techniques....
- Vizup
- Rational Reducer
- Pro Optimizer

