
Lieutenant
Encyclopedia
A lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer in many nations' armed forces
. Typically, the rank of lieutenant in naval usage, while still a junior officer rank, is senior to the army rank. It is also used in fire services, emergency medical services
, security services
and police
forces as a rank.
Lieutenant may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is "second-in-command
," and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organization utilizing both such ranks.
Notable uses include lieutenant governor
in various governments, and Quebec lieutenant
in Canadian politics.
; the lieu meaning "in place" as in a position (cf.
in lieu of); and tenant meaning "holding" as in "holding a position"; thus a "lieutenant" is somebody who holds a position in the absence of his or her superior (compare the Latin locum tenens). Similar words in other languages include the Arabic
mulāzim , meaning "holding a place", and the Hebrew
word segen , meaning "deputy" or "second to".
In the 19th century, British writers who either considered this word an imposition on the English language, or difficult for common soldiers and sailors, argued for it to be replaced by the calque
"steadholder." However, their efforts failed, and the French word is still used, along with its many variations, (e.g. lieutenant colonel
, lieutenant general
, lieutenant commander
, flight lieutenant
, second lieutenant
and many non-English-language examples), in both the Old and the New World
.
spellings suggest that the /ljuː-/ and /lɛf-/ pronunciations existed even then. The rare Old French
variant spelling luef for Modern French lieu ('place') supports the suggestion that a final [w] of the Old French word was in certain environments perceived as an [f].
In Royal Naval
tradition—and other English-speaking navies outside the United States—a reduced pronunciation ləˈtɛnənt was used. This is not recognized as current by the OED
, however, and by 1954 the Royal Canadian Navy
, at least, regarded it as "obsolescent" even while regarding "the army's 'LEF-tenant'" to be "a corruption of the worst sort".
Historically the "lieutenant" was the deputy to a "captain", and as the rank structure of armies began to formalise, this came to mean that a captain commanded a company
and had several lieutenants, each commanding a platoon
. Where more junior officers were employed as deputies to the lieutenant, they went by many names, including second lieutenant, sub-lieutenant, ensign
and cornet
. Some parts of the British Army
, including the Royal Artillery
, Royal Engineers
and fusilier
regiment
s, used first lieutenant as well as second lieutenant until the end of the 19th century, and some British Army regiments still preserve cornet as an official alternative to second lieutenant.
, and as lieutenant in the United Kingdom
and the rest of the English-speaking
world. In countries which do not speak English, the rank title usually translates as "lieutenant", but may also translate as "first lieutenant" or "senior lieutenant".
There is great variation in the insignia used worldwide. In most English-speaking and Arabic-speaking countries, as well as a number of European and South American nations, full lieutenants (and equivalents) usually wear two stars (pips) and second lieutenants (and equivalents) one. An example of an exception is the United States, whose armed forces distinguish their lieutenant ranks with one silver bar for first lieutenant and one gold (brass) bar for second lieutenant.
), ensign, leutnant (German Army), letnan (Indonesian National Armed Forces) or løjtnant (Danish Army).
". The Soviet Union
used three ranks of lieutenant, and Warsaw Pact
countries similarly standardised their ranking system. Some of the former Soviet and Warsaw Pact nations have now discarded the third rank.
sometimes referred to brevet
second lieutenant
s as "third lieutenants." These were typically newly commissioned officers for which no authorized second lieutenant position existed. Additionally, the Confederate States Army
also used "third lieutenant", typically as the lowest ranking commissioned officer in an infantry company. In modern times, Army ROTC cadets who participate in the Cadet Troop Leadership Training program are sometimes referred to as "third lieutenants" when serving in active duty units in a junior leadership position for training purposes.
The insignia of a lieutenant in many navies, including the Royal Navy, consists of two medium gold braid stripes (top stripe with loop) on a navy blue
or black background. This pattern was copied by the United States Navy and various Air Forces for their equivalent ranks grades, except that the loop is removed. (see flight lieutenant
).
and other Commonwealth navies, is a post or appointment, rather than a rank. Historically the lieutenants in a ship were ranked in accordance with seniority, with the most senior being termed the "first lieutenant" and acting as the second-in-command
. Although lieutenants are no longer numbered by seniority, the post of "first lieutenant" remains. In minor war vessels, destroyer
s and frigate
s the first lieutenant (either a lieutenant or lieutenant-commander) is second in command, executive officer
(XO) and head of the executive branch; in larger ships where a commander of the warfare specialisation is appointed as the executive officer, a first lieutenant (normally a lieutenant-commander) is appointed as his deputy. The post of first lieutenant in a shore establishment carries a similar responsibility to the first lieutenant of a capital ship
.
In the US Navy or US Coast Guard the billet of first lieutenant describes the officer in charge of the deck department
or division, depending upon the size of the ship. In smaller ships with only a single deck division, the billet is typically filled by an ensign while in larger ships with a deck department, consisting of multiple subordinate divisions, the billet may be filled by a lieutenant commander. On submarines and smaller Coast Guard cutters the billet of first lieutenant may be filled by a petty officer
.
until 1883, when it was renamed lieutenant, junior grade
. In many navies, a sub-lieutenant is a naval commissioned or subordinate officer
, ranking below a lieutenant, but in Brazil it is the highest non-commissioned rank, and in Spain it is the second highest non-commissioned rank.
and British Royal Marines
both use army ranks, while many former Eastern-Bloc marine forces retain the naval form. Before 1999 the Royal Marines enjoyed the same rank structure as the army, but at a grade higher; thus a Royal Marine captain ranked with and was paid the same as a British Army major. This historical remnant caused increasing confusion in multi-national operations and was abolished.
and many other Commonwealth
air forces use another rank system in which flight lieutenant
ranks with an army captain and naval lieutenant, a flying officer
ranks with an army lieutenant, and a pilot officer
with an army second lieutenant.
In the US Air Force, the Third Lieutenant Program refers specifically to a training program at active duty air force bases for cadets of the Air Force Academy
and Air Force ROTC the summer before their fourth and final year before graduation and commissioning. A single silver or subdued pip is used to designate this rank.
The Royal Air Force also has an Acting Pilot Officer
designation, the most junior commissioned rank in the British armed forces. It is functionally equivalent to third lieutenant (OF-1c / O-0).
. A number of city and burgh police forces in Scotland
used the rank of lieutenant (and detective lieutenant) from 1812 to 1948, when it was replaced by chief inspector
. The Royal Newfoundland Constabulary (founded 1871) had the rank of lieutenant between staff sergeant and inspector until 1997. In Australia, Queensland's first police force (founded 1864) had second lieutenants and lieutenants between sergeant and inspector-general. The first Lieutenant of Police, Gabriel Nicolas de La Reynie, was appointed in Paris by Louis XIV on 15 March 1667 to command a reformed police force. He was later elevated to lieutenant-general. There are examples in other countries.
are called Lords Lieutenant
. The Lord Lieutenant of Ireland
performed the function of viceroy
in Ireland
. In French history
, "lieutenant du roi" was a title borne by the officer sent with military powers to represent the king in certain provinces. It is in the sense of a deputy that it has entered into the titles of more senior officers, lieutenant general
and lieutenant colonel
.
The Salvation Army
also uses lieutenant to denote first time officers, or clergymen/women.
Armed forces
The armed forces of a country are its government-sponsored defense, fighting forces, and organizations. They exist to further the foreign and domestic policies of their governing body, and to defend that body and the nation it represents from external aggressors. In some countries paramilitary...
. Typically, the rank of lieutenant in naval usage, while still a junior officer rank, is senior to the army rank. It is also used in fire services, emergency medical services
Emergency medical services
Emergency medical services are a type of emergency service dedicated to providing out-of-hospital acute medical care and/or transport to definitive care, to patients with illnesses and injuries which the patient, or the medical practitioner, believes constitutes a medical emergency...
, security services
Security agency
A security agency is a governmental organization which conducts intelligence activities for the internal security of a nation. They are the domestic cousins of foreign intelligence agencies...
and police
Police
The police is a personification of the state designated to put in practice the enforced law, protect property and reduce civil disorder in civilian matters. Their powers include the legitimized use of force...
forces as a rank.
Lieutenant may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is "second-in-command
Second-in-command
The Second-in-Command is the deputy commander of any British Army or Royal Marines unit, from battalion or regiment downwards. He or she is thus the equivalent of an Executive Officer in the United States Army...
," and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organization utilizing both such ranks.
Notable uses include lieutenant governor
Lieutenant governor
A lieutenant governor or lieutenant-governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction, but is often the deputy or lieutenant to or ranking under a governor — a "second-in-command"...
in various governments, and Quebec lieutenant
Quebec lieutenant
In Canadian politics, a Quebec lieutenant is a politician, from Quebec, usually a francophone and most often a Member of Parliament or at least a current or former candidate for Parliament, who is selected by a senior politician such as the Prime Minister or the leader of a national federal party,...
in Canadian politics.
Etymology
The word lieutenant derives from FrenchFrench language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
; the lieu meaning "in place" as in a position (cf.
Cf.
cf., an abbreviation for the Latin word confer , literally meaning "bring together", is used to refer to other material or ideas which may provide similar or different information or arguments. It is mainly used in scholarly contexts, such as in academic or legal texts...
in lieu of); and tenant meaning "holding" as in "holding a position"; thus a "lieutenant" is somebody who holds a position in the absence of his or her superior (compare the Latin locum tenens). Similar words in other languages include the Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
mulāzim , meaning "holding a place", and the Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
word segen , meaning "deputy" or "second to".
In the 19th century, British writers who either considered this word an imposition on the English language, or difficult for common soldiers and sailors, argued for it to be replaced by the calque
Calque
In linguistics, a calque or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal, word-for-word or root-for-root translation.-Calque:...
"steadholder." However, their efforts failed, and the French word is still used, along with its many variations, (e.g. lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel is a rank of commissioned officer in the armies and most marine forces and some air forces of the world, typically ranking above a major and below a colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence...
, lieutenant general
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant General is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages where the title of Lieutenant General was held by the second in command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a Captain General....
, lieutenant commander
Lieutenant Commander
Lieutenant Commander is a commissioned officer rank in many navies. The rank is superior to a lieutenant and subordinate to a commander...
, flight lieutenant
Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many Commonwealth countries. It ranks above flying officer and immediately below squadron leader. The name of the rank is the complete phrase; it is never shortened to "lieutenant"...
, second lieutenant
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces.- United Kingdom and Commonwealth :The rank second lieutenant was introduced throughout the British Army in 1871 to replace the rank of ensign , although it had long been used in the Royal Artillery, Royal...
and many non-English-language examples), in both the Old and the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
.
Pronunciation
Pronunciation of lieutenant is generally split between the forms lɛfˈtɛnənt and ljuːˈtɛnənt , with the former generally associated with the United Kingdom, Ireland and Commonwealth countries, and the latter generally associated with the United States. The early history of the pronunciation is unclear; Middle EnglishMiddle English
Middle English is the stage in the history of the English language during the High and Late Middle Ages, or roughly during the four centuries between the late 11th and the late 15th century....
spellings suggest that the /ljuː-/ and /lɛf-/ pronunciations existed even then. The rare Old French
Old French
Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
variant spelling luef for Modern French lieu ('place') supports the suggestion that a final [w] of the Old French word was in certain environments perceived as an [f].
In Royal Naval
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
tradition—and other English-speaking navies outside the United States—a reduced pronunciation ləˈtɛnənt was used. This is not recognized as current by the OED
Oxford English Dictionary
The Oxford English Dictionary , published by the Oxford University Press, is the self-styled premier dictionary of the English language. Two fully bound print editions of the OED have been published under its current name, in 1928 and 1989. The first edition was published in twelve volumes , and...
, however, and by 1954 the Royal Canadian Navy
Royal Canadian Navy
The history of the Royal Canadian Navy goes back to 1910, when the naval force was created as the Naval Service of Canada and renamed a year later by King George V. The Royal Canadian Navy is one of the three environmental commands of the Canadian Forces...
, at least, regarded it as "obsolescent" even while regarding "the army's 'LEF-tenant'" to be "a corruption of the worst sort".
Army ranks
Conventionally, armies and other services or branches which use army-style rank titles have two grades of lieutenant, but a few also use a third, more junior, rank.Historically the "lieutenant" was the deputy to a "captain", and as the rank structure of armies began to formalise, this came to mean that a captain commanded a company
Company (military unit)
A company is a military unit, typically consisting of 80–225 soldiers and usually commanded by a Captain, Major or Commandant. Most companies are formed of three to five platoons although the exact number may vary by country, unit type, and structure...
and had several lieutenants, each commanding a platoon
Platoon
A platoon is a military unit typically composed of two to four sections or squads and containing 16 to 50 soldiers. Platoons are organized into a company, which typically consists of three, four or five platoons. A platoon is typically the smallest military unit led by a commissioned officer—the...
. Where more junior officers were employed as deputies to the lieutenant, they went by many names, including second lieutenant, sub-lieutenant, ensign
Ensign (rank)
Ensign is a junior rank of a commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries, normally in the infantry or navy. As the junior officer in an infantry regiment was traditionally the carrier of the ensign flag, the rank itself acquired the name....
and cornet
Cornet (military rank)
Cornet was originally the third and lowest grade of commissioned officer in a British cavalry troop, after captain and lieutenant. A cornet is a new and junior officer.- Traditional duties :The cornet carried the troop standard, also known as a "cornet"....
. Some parts of the British Army
British Army
The British Army is the land warfare branch of Her Majesty's Armed Forces in the United Kingdom. It came into being with the unification of the Kingdom of England and Scotland into the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707. The new British Army incorporated Regiments that had already existed in England...
, including the Royal Artillery
Royal Artillery
The Royal Regiment of Artillery, commonly referred to as the Royal Artillery , is the artillery arm of the British Army. Despite its name, it comprises a number of regiments.-History:...
, Royal Engineers
Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually just called the Royal Engineers , and commonly known as the Sappers, is one of the corps of the British Army....
and fusilier
Fusilier
Fusilier was originally the name of a soldier armed with a light flintlock musket called the fusil. The word was first used around 1680, and has later developed into a regimental designation.-History:...
regiment
Regiment
A regiment is a major tactical military unit, composed of variable numbers of batteries, squadrons or battalions, commanded by a colonel or lieutenant colonel...
s, used first lieutenant as well as second lieutenant until the end of the 19th century, and some British Army regiments still preserve cornet as an official alternative to second lieutenant.
Lieutenant/first lieutenant
The senior grade of lieutenant is known as first lieutenant in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, and as lieutenant in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and the rest of the English-speaking
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
world. In countries which do not speak English, the rank title usually translates as "lieutenant", but may also translate as "first lieutenant" or "senior lieutenant".
There is great variation in the insignia used worldwide. In most English-speaking and Arabic-speaking countries, as well as a number of European and South American nations, full lieutenants (and equivalents) usually wear two stars (pips) and second lieutenants (and equivalents) one. An example of an exception is the United States, whose armed forces distinguish their lieutenant ranks with one silver bar for first lieutenant and one gold (brass) bar for second lieutenant.
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||
| Canada | Germany | Greece | Ireland | Italy | Mexico | Romania | Russia | UK | US |
Second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is usually the most junior grade of commissioned officer. In most cases, newly commissioned officers do not remain at the rank for long before being promoted, and both university graduates and officers commissioned from the ranks may skip the rank altogether. In non-English-speaking countries, the equivalent rank title may translate as "second lieutenant", "lieutenant", "sub-lieutenant" or "junior lieutenant". Non-English terms include alférez (Spanish Army and Air Force), fänrik (Swedish Armed ForcesSwedish Armed Forces
The Swedish Armed Forces is a Swedish Government Agency responsible for the operation of the armed forces of the Realm. The primary task of the agency is to train, organize and to deploy military forces, domestically and abroad, while maintaining the long-term ability to defend the Realm in the...
), ensign, leutnant (German Army), letnan (Indonesian National Armed Forces) or løjtnant (Danish Army).
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||||
| Canada | Germany | Greece | Ireland | Italy | Mexico | Romania | Russia | UK | US |
East-European ranks
A few non-English-speaking militaries maintain a lower rank, frequently translated as "third lieutenant". The rank title may actually translate as "second lieutenant", "junior lieutenant", "sub-lieutenant" or "ensignEnsign (rank)
Ensign is a junior rank of a commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries, normally in the infantry or navy. As the junior officer in an infantry regiment was traditionally the carrier of the ensign flag, the rank itself acquired the name....
". The Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
used three ranks of lieutenant, and Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
countries similarly standardised their ranking system. Some of the former Soviet and Warsaw Pact nations have now discarded the third rank.
 |
| Russia |
American brevet second lieutenants
Throughout the 19th century and until as late as World War II the United States ArmyUnited States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
sometimes referred to brevet
Brevet (military)
In many of the world's military establishments, brevet referred to a warrant authorizing a commissioned officer to hold a higher rank temporarily, but usually without receiving the pay of that higher rank except when actually serving in that role. An officer so promoted may be referred to as being...
second lieutenant
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces.- United Kingdom and Commonwealth :The rank second lieutenant was introduced throughout the British Army in 1871 to replace the rank of ensign , although it had long been used in the Royal Artillery, Royal...
s as "third lieutenants." These were typically newly commissioned officers for which no authorized second lieutenant position existed. Additionally, the Confederate States Army
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
also used "third lieutenant", typically as the lowest ranking commissioned officer in an infantry company. In modern times, Army ROTC cadets who participate in the Cadet Troop Leadership Training program are sometimes referred to as "third lieutenants" when serving in active duty units in a junior leadership position for training purposes.
Lieutenant commander
Lieutenants were commonly put in command of smaller vessels not warranting a commander or captain: such a lieutenant was called a "lieutenant commanding" or "lieutenant commandant" in the United States Navy, and a "lieutenant in command" or "lieutenant and commander" in the Royal Navy. The USN settled on "lieutenant commander" in 1862, and made it a distinct rank; the Royal Navy followed suit in March 1914. The insignia of an additional half-stripe between the two full stripes of a lieutenant was introduced in 1877 for a Royal Navy lieutenant of 8 years seniority, and used for lieutenant commanders upon introduction of their rank.  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Canada | Greece | India | Poland | Portugal | Romania | UK | US |
Lieutenant
During the early days of the naval rank, a lieutenant might be very junior indeed, or might be on the cusp of promotion to captain; by modern standards he might rank with any army rank between second lieutenant and lieutenant colonel. As the rank structure of navies stabilised, and the ranks of commander, lieutenant commander and sub-lieutenant were introduced, the naval lieutenant came to rank with an army captain (NATO OF-2 or US O-3).The insignia of a lieutenant in many navies, including the Royal Navy, consists of two medium gold braid stripes (top stripe with loop) on a navy blue
Navy blue
Navy blue is a very dark shade of the color blue which almost appears as black. Navy blue got its name from the dark blue worn by officers in the British Royal Navy since 1748 and subsequently adopted by other navies around the world....
or black background. This pattern was copied by the United States Navy and various Air Forces for their equivalent ranks grades, except that the loop is removed. (see flight lieutenant
Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many Commonwealth countries. It ranks above flying officer and immediately below squadron leader. The name of the rank is the complete phrase; it is never shortened to "lieutenant"...
).
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Canada | France | Germany | Greece | India | Poland | Portugal | Romania | Spain | UK | US |
"First lieutenant" in naval usage
The first lieutenant in the Royal NavyRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
and other Commonwealth navies, is a post or appointment, rather than a rank. Historically the lieutenants in a ship were ranked in accordance with seniority, with the most senior being termed the "first lieutenant" and acting as the second-in-command
Second-in-command
The Second-in-Command is the deputy commander of any British Army or Royal Marines unit, from battalion or regiment downwards. He or she is thus the equivalent of an Executive Officer in the United States Army...
. Although lieutenants are no longer numbered by seniority, the post of "first lieutenant" remains. In minor war vessels, destroyer
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast and maneuverable yet long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against smaller, powerful, short-range attackers. Destroyers, originally called torpedo-boat destroyers in 1892, evolved from...
s and frigate
Frigate
A frigate is any of several types of warship, the term having been used for ships of various sizes and roles over the last few centuries.In the 17th century, the term was used for any warship built for speed and maneuverability, the description often used being "frigate-built"...
s the first lieutenant (either a lieutenant or lieutenant-commander) is second in command, executive officer
Executive officer
An executive officer is generally a person responsible for running an organization, although the exact nature of the role varies depending on the organization.-Administrative law:...
(XO) and head of the executive branch; in larger ships where a commander of the warfare specialisation is appointed as the executive officer, a first lieutenant (normally a lieutenant-commander) is appointed as his deputy. The post of first lieutenant in a shore establishment carries a similar responsibility to the first lieutenant of a capital ship
Capital ship
The capital ships of a navy are its most important warships; they generally possess the heaviest firepower and armor and are traditionally much larger than other naval vessels...
.
In the US Navy or US Coast Guard the billet of first lieutenant describes the officer in charge of the deck department
Deck department
The Deck Department is an organizational unit aboard naval and merchant ships. A Deck Officer is an officer serving in the deck department.-Merchant shipping:...
or division, depending upon the size of the ship. In smaller ships with only a single deck division, the billet is typically filled by an ensign while in larger ships with a deck department, consisting of multiple subordinate divisions, the billet may be filled by a lieutenant commander. On submarines and smaller Coast Guard cutters the billet of first lieutenant may be filled by a petty officer
Petty Officer
A petty officer is a non-commissioned officer in many navies and is given the NATO rank denotion OR-6. They are equal in rank to sergeant, British Army and Royal Air Force. A Petty Officer is superior in rank to Leading Rate and subordinate to Chief Petty Officer, in the case of the British Armed...
.
Sub-lieutenant
In the Royal Navy the commissioned rank of mate was created in 1840, and was renamed sub-lieutenant in 1860. In the US Navy the rank was called masterMaster (naval)
The master, or sailing master, was a historic term for a naval officer trained in and responsible for the navigation of a sailing vessel...
until 1883, when it was renamed lieutenant, junior grade
Lieutenant, Junior Grade
Lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer rank in the United States Navy, the United States Coast Guard, the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, United States Merchant Marine USMM, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Corps, with the pay grade...
. In many navies, a sub-lieutenant is a naval commissioned or subordinate officer
Subordinate officer
Subordinate officer is a term used in some armed forces for a grade of officer above a non-commissioned officer but still not actually commissioned, usually still in training...
, ranking below a lieutenant, but in Brazil it is the highest non-commissioned rank, and in Spain it is the second highest non-commissioned rank.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Canada | Greece | India | Netherlands | Poland | Portugal | Romania | Spain | Sweden | UK | US |
Marine rank
The United States Marine CorpsUnited States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States...
and British Royal Marines
Royal Marines
The Corps of Her Majesty's Royal Marines, commonly just referred to as the Royal Marines , are the marine corps and amphibious infantry of the United Kingdom and, along with the Royal Navy and Royal Fleet Auxiliary, form the Naval Service...
both use army ranks, while many former Eastern-Bloc marine forces retain the naval form. Before 1999 the Royal Marines enjoyed the same rank structure as the army, but at a grade higher; thus a Royal Marine captain ranked with and was paid the same as a British Army major. This historical remnant caused increasing confusion in multi-national operations and was abolished.
Air force rank
While some air forces use the army rank system, the British Royal Air ForceRoyal Air Force
The Royal Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Formed on 1 April 1918, it is the oldest independent air force in the world...
and many other Commonwealth
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
air forces use another rank system in which flight lieutenant
Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many Commonwealth countries. It ranks above flying officer and immediately below squadron leader. The name of the rank is the complete phrase; it is never shortened to "lieutenant"...
ranks with an army captain and naval lieutenant, a flying officer
Flying Officer
Flying officer is a junior commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many countries which have historical British influence...
ranks with an army lieutenant, and a pilot officer
Pilot Officer
Pilot officer is the lowest commissioned rank in the Royal Air Force and the air forces of many other Commonwealth countries. It ranks immediately below flying officer...
with an army second lieutenant.
| NATO OF-2 / US O-3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Thai Flight lieutenant |
UK Flight lieutenant |
Australian Flight lieutenant |
Indian Flight lieutenant |
|||
| NATO OF-1a / US O-2 | ||||||
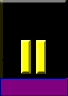 |
 |
 |
||||
| Canada Lieutenant |
Germany Oberleutnant |
Mexico Teniente |
Poland Porucznik |
Spain Teniente |
Sweden Löjtnant |
US First Lieutenant |
| NATO OF-1b / US O-1 | ||||||
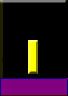 |
 |
|||||
| Canada Second lieutenant |
Germany Leutnant |
Mexico Subteniente |
Poland Podporucznik |
Spain Alférez |
US Second lieutenant |
|
In the US Air Force, the Third Lieutenant Program refers specifically to a training program at active duty air force bases for cadets of the Air Force Academy
United States Air Force Academy
The United States Air Force Academy is an accredited college for the undergraduate education of officer candidates for the United States Air Force. Its campus is located immediately north of Colorado Springs in El Paso County, Colorado, United States...
and Air Force ROTC the summer before their fourth and final year before graduation and commissioning. A single silver or subdued pip is used to designate this rank.
The Royal Air Force also has an Acting Pilot Officer
Acting Pilot Officer
Acting Pilot Officer is the lowest commissioned grade in the Royal Air Force, being immediately junior to Pilot Officer. Unlike other RAF ranks which officers may hold in an acting capacity, Acting Pilot Officer is maintained as a separate grade. It normally denotes an officer who has recently...
designation, the most junior commissioned rank in the British armed forces. It is functionally equivalent to third lieutenant (OF-1c / O-0).
Police rank
The rank of police lieutenant is used in most police forces in the United States. It is normally roughly equivalent to the British police inspectorInspector
Inspector is both a police rank and an administrative position, both used in a number of contexts. However, it is not an equivalent rank in each police force.- Australia :...
. A number of city and burgh police forces in Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
used the rank of lieutenant (and detective lieutenant) from 1812 to 1948, when it was replaced by chief inspector
Chief inspector
Chief inspector is a rank used in police forces which follow the British model. In countries outside Britain, it is sometimes referred to as chief inspector of police .-Australia:...
. The Royal Newfoundland Constabulary (founded 1871) had the rank of lieutenant between staff sergeant and inspector until 1997. In Australia, Queensland's first police force (founded 1864) had second lieutenants and lieutenants between sergeant and inspector-general. The first Lieutenant of Police, Gabriel Nicolas de La Reynie, was appointed in Paris by Louis XIV on 15 March 1667 to command a reformed police force. He was later elevated to lieutenant-general. There are examples in other countries.
 |
 |
|
| US Police Lieutenant |
Romanian Inspector de poliţie |
Indian Assistant Superintendent of Police |
Fire services rank
In the US the junior officer grade of the Fire Service is the lieutenant. The most common insignia for fire department lieutenants are collar and cover devices commonly called bugles (though they are really representative of 18th century speaking trumpets); a lieutenant usually displays a single silver bugle, though some variations exist. In addition to the bugle, lieutenants often display a single silver sleeve band and wear a helmet of a different color from those worn by their subordinates, most usually limited to a white helmet shield on a black or red helmet (jurisdictionally dependant). Many cities and towns, however, employ a wide variety of other ranks and insignia. Lieutenants are typically responsible for an individual engine or ladder company and its crew.Other uses
The British monarch's representatives in the counties of the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
are called Lords Lieutenant
Lord Lieutenant
The title Lord Lieutenant is given to the British monarch's personal representatives in the United Kingdom, usually in a county or similar circumscription, with varying tasks throughout history. Usually a retired local notable, senior military officer, peer or business person is given the post...
. The Lord Lieutenant of Ireland
Lord Lieutenant of Ireland
The Lord Lieutenant of Ireland was the British King's representative and head of the Irish executive during the Lordship of Ireland , the Kingdom of Ireland and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
performed the function of viceroy
Viceroy
A viceroy is a royal official who runs a country, colony, or province in the name of and as representative of the monarch. The term derives from the Latin prefix vice-, meaning "in the place of" and the French word roi, meaning king. A viceroy's province or larger territory is called a viceroyalty...
in Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
. In French history
History of France
The history of France goes back to the arrival of the earliest human being in what is now France. Members of the genus Homo entered the area hundreds of thousands years ago, while the first modern Homo sapiens, the Cro-Magnons, arrived around 40,000 years ago...
, "lieutenant du roi" was a title borne by the officer sent with military powers to represent the king in certain provinces. It is in the sense of a deputy that it has entered into the titles of more senior officers, lieutenant general
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant General is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages where the title of Lieutenant General was held by the second in command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a Captain General....
and lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel is a rank of commissioned officer in the armies and most marine forces and some air forces of the world, typically ranking above a major and below a colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence...
.
The Salvation Army
Salvation Army
The Salvation Army is a Protestant Christian church known for its thrift stores and charity work. It is an international movement that currently works in over a hundred countries....
also uses lieutenant to denote first time officers, or clergymen/women.

