Light-independent reaction
Overview
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
are chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s that convert carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and other compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s into glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
. These reactions occur in the stroma
Stroma (fluid)
Stroma, in botany, refers to the colourless fluid surrounding the grana within the Plastid, chloroplast.Within the stroma are grana, stacks of thylakoids, the sub-organelles, where photosynthesis is commenced before the chemical changes are completed in the stroma.Photosynthesis occurs in two...
, the fluid-filled area of a chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
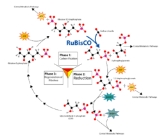
outside of the thylakoid membranes. These reactions take the light-dependent reactions and perform further chemical processes on them. There are three phases to the light-independent reactions, collectively called the Calvin cycle
Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle or Calvin–Benson-Bassham cycle or reductive pentose phosphate cycle or C3 cycle or CBB cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplasts in photosynthetic organisms...
: carbon fixation, reduction reactions, and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP) regeneration.
Despite its name, this process occurs only when light is available.
Unanswered Questions

