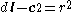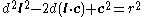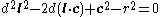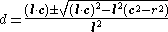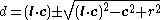Line–sphere intersection
Encyclopedia
Analytic geometry
Analytic geometry, or analytical geometry has two different meanings in mathematics. The modern and advanced meaning refers to the geometry of analytic varieties...
, a line
Line (mathematics)
The notion of line or straight line was introduced by the ancient mathematicians to represent straight objects with negligible width and depth. Lines are an idealization of such objects...
and a sphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
can intersect
Intersection (set theory)
In mathematics, the intersection of two sets A and B is the set that contains all elements of A that also belong to B , but no other elements....
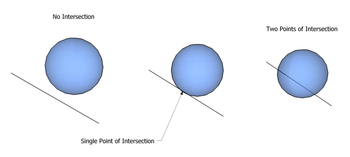
in three ways: no intersection at all, at exactly one point, or in two points. Methods for distinguishing these cases, and determining equations for the points in the latter cases, are useful in a number of circumstances. For example, this is a common calculation to perform during ray tracing
Ray tracing (physics)
In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces,...
(Eberly 2006:698).
Calculation using vectors in 3D
In vector notationVector notation
This page is an overview of the common notations used when working with vectors, which may be spatial or more abstract members of vector spaces....
, the equations are as follows:
Equation for a sphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
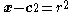
 - center point
- center point - radius
- radius
Equation for a line starting at (0,0,0)
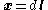
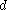 - distance along line from starting point
- distance along line from starting point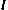 - direction of line (a unit vector)
- direction of line (a unit vector)
Solving for
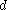 :
:- Equations combined
- Expanded
- Rearranged
- Quadratic formula and simplified. (This quadratic equation is an example of Joachimsthal's Equation).
- Note that
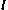 is a unit vector, and thus
is a unit vector, and thus 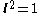 . Thus, we can simplify this further to
. Thus, we can simplify this further to
- If the value under the square-root (
 ) is less than zero, then it is clear that no solutions exist, i.e. the line does not intersect the sphere (case 1).
) is less than zero, then it is clear that no solutions exist, i.e. the line does not intersect the sphere (case 1). - If it is zero, then exactly one solution exists, i.e. the line just touches the sphere in one point (case 2).
- If it is greater than zero, two solutions exist, and thus the line touches the sphere in two points (case 3).
See also
- Analytic geometryAnalytic geometryAnalytic geometry, or analytical geometry has two different meanings in mathematics. The modern and advanced meaning refers to the geometry of analytic varieties...
- Line-plane intersectionLine-plane intersectionIn analytic geometry, the intersection of a line and a plane can be the empty set,a point, ora line. Distinguishing these cases, and determining equations for the point and line in the latter cases have use, for example, in computer graphics, motion planning, and collision detection.-Parametric...
- Line of intersection between two planesPlane (mathematics)In mathematics, a plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface. A plane is the two dimensional analogue of a point , a line and a space...