
List of RNA structure prediction software
Encyclopedia
This list of RNA structure prediction software is a compilation of software tools and web portals used for RNA structure
prediction.
s. For example, miRNA
s regulate protein coding gene expression by binding to 3' UTRs
, small nucleolar RNAs
guide post-transcriptional modifications by binding to rRNA, U4 spliceosomal RNA
and U6 spliceosomal RNA
bind to each other forming part of the spliceosome
and many small bacterial RNAs regulate gene expression by antisense interactions E.g. GcvB
, OxyS
and RyhB
.
regulate protein coding gene expression by binding to 3' UTRs
, there are tools specifically designed for predicting these interactions. For an evaluation of target prediction methods on high-throughput experimental data see (Selbach et al., Nature 2008) and (Alexiou et al., Bioinformatics 2009)
RNA structure
Biomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is...
prediction.
Single sequence secondary structure prediction
| Name | Description | Knots | Links | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CentroidFold | Secondary structure prediction based on generalized centroid estimator | no | sourcecode webserver | ||
| CentroidHomfold | Secondary structure prediction by using homologous sequence information | no | sourcecode webserver | ||
| CONTRAfold | Secondary structure prediction method based on conditional log-linear models (CLLMs), a flexible class of probabilistic models which generalize upon SCFGs by using discriminative training and feature-rich scoring. | no | sourcecode webserver | ||
| CyloFold | Secondary structure prediction method based on placement of helices allowing complex pseudoknots. | yes | webserver | ||
| KineFold | Folding kinetics of RNA sequences including pseudoknots by including an implementation of the partition function for knots. | yes | linuxbinary, webserver | ||
| Mfold | MFE Gibbs free energy In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure... (Minimum Free Energy) RNA structure prediction algorithm. |
no | sourcecode, webserver | ||
| Pknots | A dynamic programming algorithm for optimal RNA pseudoknot prediction using the nearest neighbour energy model. | yes | sourcecode | ||
| PknotsRG | A dynamic programming algorithm for the prediction of a restricted class of RNA pseudoknots. | yes | sourcecode, webserver | ||
| RNAfold | MFE RNA structure prediction algorithm. Includes an implementation of the partition function for computing basepair probabilities and circular RNA folding. | no | sourcecode, webserver | ||
| RNAshapes | MFE RNA structure prediction based on abstract shapes. Shape abstraction retains adjacency and nesting of structural features, but disregards helix lengths, thus reduces the number of suboptimal solutions without losing significant information. Furthermore, shapes represent classes of structures for which probabilities based on Boltzmann-weighted energies can be computed. | no | source & binaries, webserver | ||
| RNAstructure | A program to predict lowest free energy structures and base pair probabilities for RNA or DNA sequences. Programs are also available to predict Maximum Expected Accuracy structures and these can include pseudoknots. Structure prediction can be constrained using experimental data, including SHAPE, enzymatic cleavage, and chemical modification accessibility. Graphical user interfaces are available for Windows and for Mac OS-X/Linux. Programs are also available for use with Unix-style text interfaces. Additionally, a C++ class library is available. | yes | source & binaries | ||
| Sfold | Statistical sampling of all possible structures. The sampling is weighted by partition function probabilities. | no | webserver | ||
| UNAFold | The UNAFold software package is an integrated collection of programs that simulate folding, hybridization, and melting pathways for one or two single-stranded nucleic acid sequences. | no | sourcecode | ||
| Crumple | Crumple is simple, cleanly written software for producing the full set of possible secondary structures for a single sequence, given optional constraints. | no | sourcecode | ||
| Sliding Windows & Assembly | Sliding windows and assembly is a tool chain for folding long series of similar hairpins. | no | sourcecode |
Single sequence tertiary structure prediction
| Name | Description | Knots | Links | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BARNACLE Barnacle A barnacle is a type of arthropod belonging to infraclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosive settings. They are sessile suspension feeders, and have... |
A Python library for the probabilistic sampling of RNA structures that are compatible with a given nucleotide sequence and that are RNA-like on a local length scale. | yes | sourcecode | |||
| FARNA Farná Farná is a village and municipality in the Levice District in the Nitra Region of Slovakia.-Geography:The village lies at an altitude of 159 metres and covers an area of 32.745 km²... |
Automated de novo prediction of native-like RNA tertiary structures . | yes | sourcecode | |||
| iFoldRNA | three-dimensional RNA structure prediction and folding | ? | webserver | |||
| MC-Fold MC-Sym Pipeline | Thermodynamics and Nucleotide cyclic motifs for RNA structure prediction algorithm. 2D and 3D structures. | yes | sourcecode, webserver | |||
| NAST | Coarse-grained modeling of large RNA molecules with knowledge-based potentials and structural filters | ? | sourcecode | |||
| Pseudoknot A pseudoknot is a nucleic acid secondary structure containing at least two stem-loop structures in which half of one stem is intercalated between the two halves of another stem. The pseudoknot was first recognized in the turnip yellow mosaic virus in 1982... prediction, |
||||||
Comparative methods
The single sequence methods mentioned above have a difficult job detecting a small sample of reasonable secondary structures from a large space of possible structures. A good way to reduce the size of the space is to use evolutionary approaches. Structures that have been conserved by evolution are far more likely to be the functional form. The methods below use this approach.| Name | Description | Number of sequences | Alignment | Structure | Knots | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carnac | Comparative analysis combined with MFE folding. | any | no | yes | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| CentroidAlifold | Common secondary structure prediction based on generalized centroid estimator | any | yes | no | no | sourcecode webserver | |
| CentroidAlign | Fast and accurate multiple aligner for RNA sequences | any | yes | no | no | sourcecode | |
| CMfinder | an expectation maximization algorithm using covariance models for motif description. Uses heuristics for effective motif search, and a Bayesian framework for structure prediction combining folding energy and sequence covariation. | 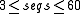 |
yes | yes | no | sourcecode, webserver, website | |
| CONSAN | implements a pinned Sankoff algorithm for simultaneous pairwise RNA alignment and consensus structure prediction. | 2 | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| Dynalign | an algorithm that improves the accuracy of structure prediction by combining free energy minimization and comparative sequence analysis to find a low free energy structure common to two sequences without requiring any sequence identity. | 2 | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| FoldalignM | A multiple RNA structural RNA alignment method, to a large extend based on the PMcomp program. | any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| KNetFold | Computes a consensus RNA secondary structure from an RNA sequence alignment based on machine learning. | any | input | yes | yes | linuxbinary, webserver | |
| LARA | Produce a global fold and alignment of ncRNA families using integer linear programming and Lagrangian relaxation. | any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| LocaRNA | LocaRNA is the successor of PMcomp with an improved time complexity. It is a variant of Sankoff's algorithm for simultaneous folding and alignment, which takes as input pre-computed base pair probability matrices from McCaskill's algorithm as produced by RNAfold -p. Thus the method can also be viewed as way to compare base pair probability matrices. | any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| MASTR | A sampling approach using Markov chain Monte Carlo in a simulated annealing Simulated annealing Simulated annealing is a generic probabilistic metaheuristic for the global optimization problem of locating a good approximation to the global optimum of a given function in a large search space. It is often used when the search space is discrete... framework, where both structure and alignment is optimized by making small local changes. The score combines the log-likelihood of the alignment, a covariation term and the basepair probabilities. |
any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| Murlet | a multiple alignment tool for RNA sequences using iterative alignment based on Sankoff's algorithm with sharply reduced computational time and memory. | any | yes | yes | no | webserver | |
| MXSCARNA | a multiple alignment tool for RNA sequences using progressive alignment based on pairwise structural alignment algorithm of SCARNA. | any | yes | yes | no | webserver sourcecode | |
| PARTS | A method for joint prediction of alignment and common secondary structures of two RNA sequences using a probabilistic model based on pseudo free energies obtained from precomputed base pairing and alignment probabilities. | 2 | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| Pfold | Folds alignments using a SCFG trained on rRNA alignments. | 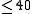 |
input | yes | no | webserver | |
| PETfold | Formally integrates both the energy-based and evolution-based approaches in one model to predict the folding of multiple aligned RNA sequences by a maximum expected accuracy scoring. The structural probabilities are calculated by RNAfold and Pfold. | any | input | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| PMcomp/PMmulti | PMcomp is a variant of Sankoff's algorithm for simultaneous folding and alignment, which takes as input pre-computed base pair probability matrices from McCaskill's algorithm as produced by RNAfold -p. Thus the method can also be viewed as way to compare base pair probability matrices. PMmulti is a wrapper program that does progressive multiple alignments by repeatedly calling pmcomp | 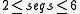 |
yes | yes | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| R-COFFEE T-Coffee T-Coffee is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment... |
uses RNAlpfold to compute the secondary structure of the provided sequences. A modified version of T-Coffee T-Coffee T-Coffee is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment... is then used to compute the multiple sequence alignment having the best agreement with the sequences and the structures. R-Coffee can be combined with any existing sequence alignment method. |
any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| RNAalifold | Folds precomputed alignments using a combination of free-energy and a covariation measures. Ships with the Vienna package. | any | input | yes | no | homepage | |
| RNAcast | enumerates the near-optimal abstract shape space, and predicts as the consensus an abstract shape common to all sequences, and for each sequence, the thermodynamically best structure which has this abstract shape. | any | no | yes | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| RNAforester | Compare and align RNA secondary structures via a "forest alignment" approach. | any | yes | input | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| RNAmine | Frequent stem pattern miner from unaligned RNA sequences is a software tool to extract the structural motifs from a set of RNA sequences. | any | no | yes | no | webserver | |
| RNASampler | A probabilistic sampling approach that combines intrasequence base pairing probabilities with intersequence base alignment probabilities. This is used to sample possible stems for each sequence and compare these stems between all pairs of sequences to predict a consensus structure for two sequences. The method is extended to predict the common structure conserved among multiple sequences by using a consistency-based score that incorporates information from all the pairwise structural alignments. | any | yes | yes | yes | sourcecode | |
| SCARNA | Stem Candidate Aligner for RNA (Scarna) is a fast, convenient tool for structural alignment of a pair of RNA sequences. It aligns two RNA sequences and calculates the similarities of them, based on the estimated common secondary structures. It works even for pseudoknotted secondary structures. | 2 | yes | yes | no | webserver | |
| SimulFold | simultaneously inferring RNA structures including pseudoknots, alignments, and trees using a Bayesian MCMC framework. | any | yes | yes | yes | sourcecode | |
| Stemloc Stemloc Stemloc is a program for pairwise RNA structural alignment based on probabilistic models of RNA structure known as Pair stochastic context-free grammars. Stemloc implements constrained versions of the Sankoff algorithms for simultaneous structure prediction and sequence alignment of multiple... |
a program for pairwise RNA structural alignment based on probabilistic models of RNA structure known as Pair stochastic context-free grammars. | any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| StrAl | an alignment tool designed to provide multiple alignments of non-coding RNAs following a fast progressive strategy. It combines the thermodynamic base pairing information derived from RNAfold calculations in the form of base pairing probability vectors with the information of the primary sequence. | 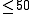 |
yes | no | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| TFold | A tool for predicting non-coding RNA secondary structures including pseudoknots. It takes in input an alignment of RNA sequences and returns the predicted secondary structure(s).It combines criteria of stability, conservation and covariation in order to search for stems and pseudoknots. Users can change different parameters values, set (or not) some known stems (if there are) which are taken into account by the system, choose to get several possible structures or only one, search for pseudoknots or not, etc. | any | yes | yes | yes | webserver | |
| WAR | a webserver that makes it possible to simultaneously use a number of state of the art methods for performing multiple alignment and secondary structure prediction for noncoding RNA sequences. | 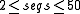 |
yes | yes | no | webserver | |
| Xrate Xrate XRATE is a program for prototyping phylogenetic hidden Markov models and stochastic context-free grammars.It is used to discover patterns of evolutionary conservation in sequence alignments.... |
a program for analysis of multiple sequence alignments using phylogenetic grammars, that may be viewed as a flexible generalization of the "Pfold" program. | any | yes | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| Sequence alignment In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are... , RNA structure Biomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is... , Pseudoknot A pseudoknot is a nucleic acid secondary structure containing at least two stem-loop structures in which half of one stem is intercalated between the two halves of another stem. The pseudoknot was first recognized in the turnip yellow mosaic virus in 1982... prediction, |
|||||||
Inter molecular interactions: RNA-RNA
Many ncRNAs function by binding to other RNARNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
s. For example, miRNA
Mirna
Mirna may refer to:geographical entities* Mirna , a river in Istria, Croatia* Mirna , a river in Slovenia, tributary of the river Sava* Mirna , a settlement in the municipality of Mirna in Southeastern Sloveniapeople...
s regulate protein coding gene expression by binding to 3' UTRs
Three prime untranslated region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region is a particular section of messenger RNA . It is preceeded by the coding region....
, small nucleolar RNAs
SnoRNA
Small nucleolar RNAs are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs...
guide post-transcriptional modifications by binding to rRNA, U4 spliceosomal RNA
U4 spliceosomal RNA
The U4 small nuclear Ribo-Nucleic Acid is a non-coding RNA component of the major or U2-dependent spliceosome – a eukaryotic molecular machine involved in the splicing of pre-messenger RNA...
and U6 spliceosomal RNA
U6 spliceosomal RNA
U6 snRNA is the non-coding small nuclear RNA component of U6 snRNP , an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs...
bind to each other forming part of the spliceosome
Spliceosome
A spliceosome is a complex of snRNA and protein subunits that removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA segment. This process is generally referred to as splicing.-Composition:...
and many small bacterial RNAs regulate gene expression by antisense interactions E.g. GcvB
GcvB RNA
The gcvB RNA gene encodes a small non-coding RNA involved in the regulation of a number of amino acid transport systems as well as amino acid biosynthetic genes. The GcvB gene is found in enteric bacteria such as Escherichia coli. GcvB regulates genes by acting as an antisense binding partner of...
, OxyS
OxyS RNA
OxyS RNA is a small non-coding RNA which is induced in response to oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. This RNA acts as a global regulator to activate or repress the expression of as many as 40 genes, by an antisense mechanism, including the fhlA-encoded transcriptional activator and the...
and RyhB
RyhB RNA
RyhB RNA is a 90 nucleotide non-coding RNA that down-regulates a set of iron-storage and iron-using proteins when iron is limiting; it is itself negatively regulated by the ferric uptake repressor protein, Fur . This ncRNA gene was independently identified in two screens, named RyhB by Wasserman et...
.
| Name | Description | Intra-molecular structure | Comparative | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GUUGle | A utility for fast determination of RNA-RNA matches with perfect hybridization via A-U, C-G, and G-U base pairing. | no | no | webserver | |
| IntaRNA | Efficient target prediction incorporating the accessibility of target sites | yes | no | sourcecode webserver | |
| NUPACK NUPACK The Nucleic Acid Package, is a growing software suite for the analysis and design of nucleic acid systems . Jobs can be run online on the NUPACK webserver or NUPACK source code can be downloaded and compiled locally. NUPACK algorithms are formulated in terms of nucleic acid secondary structure... |
Computes the full unpseudoknotted partition function of interacting strands in dilute solution. Calculates the concentrations, mfes, and base-pairing probabilities of the ordered complexes below a certain complexity. Also computes the partition function and basepairing of single strands including a class of pseudoknotted structures. Also enables design of ordered complexes. | yes | no | NUPACK | |
| OligoWalk/RNAstructure | Predicts bimolecular secondary structures with and without intramolecular structure. Also predicts the hybridization affinity of a short nucleic acid to an RNA target. | yes | no | http://rna.urmc.rochester.edu | |
| piRNA | calculates the partition function and thermodynamics of RNA-RNA interactions. It considers all possible joint secondary structure of two interacting nucleic acids that do not contain pseudoknots, interaction pseudoknots, or zigzags. | yes | no | linuxbinary | |
| RNAaliduplex | Based upon RNAduplex with bonuses for covarying sites | no | yes | sourcecode | |
| RNAcofold | works much like RNAfold, but allows to specify two RNA sequences which are then allowed to form a dimer structure. | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| RNAduplex | computes optimal and suboptimal secondary structures for hybridization. The calculation is simplified by allowing only inter-molecular base pairs. | no | no | sourcecode | |
| RNAhybrid | a tool for finding the minimum free energy hybridisation of a long and a short RNA. | no | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| RNAup | calculates the thermodynamics of RNA-RNA interactions. RNA-RNA binding is decomposed into two stages. (1) First the probability that a sequence interval (e.g. a binding site) remains unpaired is computed. (2) Then the binding energy given that the binding site is unpaired is calculated as the optimum over all possible types of bindings. | yes | no | sourcecode | |
| |
|||||
Inter molecular interactions: MicroRNA:UTR
MicroRNAsMirna
Mirna may refer to:geographical entities* Mirna , a river in Istria, Croatia* Mirna , a river in Slovenia, tributary of the river Sava* Mirna , a settlement in the municipality of Mirna in Southeastern Sloveniapeople...
regulate protein coding gene expression by binding to 3' UTRs
Three prime untranslated region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region is a particular section of messenger RNA . It is preceeded by the coding region....
, there are tools specifically designed for predicting these interactions. For an evaluation of target prediction methods on high-throughput experimental data see (Selbach et al., Nature 2008) and (Alexiou et al., Bioinformatics 2009)
| Name | Description | Species Specific | Intra-molecular structure | Comparative | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diana-microT | DIANA-microT 3.0 is an algorithm based on several parameters calculated individually for each microRNA and it combines conserved and non-conserved microRNA recognition elements into a final prediction score. | human, mouse | no | yes | webserver | |
| MicroTar | An animal miRNA target prediction tool based on miRNA-target complementarity and thermodynamic data. | no | no | no | sourcecode | |
| miTarget | microRNA target gene prediction using a support vector machine. | no | no | no | webserver | |
| PicTar | Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. | 8 vertebrates | no | yes | predictions | |
| PITA | Incorporates the role of target-site accessibility, as determined by base-pairing interactions within the mRNA, in microRNA target recognition. | no | yes | no | executable, webserver, predictions | |
| RNA22 | First finds putative microRNA binding sites in the sequence of interest, then identifies the targeting microRNA. | no | no | no | webserver | |
| RNAhybrid | a tool for finding the minimum free energy hybridisation of a long and a short RNA. | no | no | no | sourcecode, webserver | |
| Sylamer | Sylamer is a method for finding significantly over or under-represented words in sequences according to a sorted gene list. Typically it is used to find significant enrichment or depletion of microRNA or siRNA seed sequences from microarray expression data. | no | no | no | sourcecode webserver | |
| TAREF | TAREF stands for TARget REFiner. It predicts microRNA targets on the basis of multiple feature information derived from the flanking regions of the predicted target sites where traditional structure prediction approach may not be successful to assess the openness. It also provides an option to use encoded pattern to refine filtering. | Yes | no | no | server/sourcecode | |
| p-TAREF | p-TAREF stands for plant TARget REFiner. It identifies plant microRNA targets on the basis of multiple feature information derived from the flanking regions of the predicted target sites where traditional structure prediction approach may not be successful to assess the openness. It also provides an option to use encoded pattern to refine filtering. It first time employed power of machine learning approach with scoring scheme through Support Vector Regression(SVR) while considering structural and alignment aspects of targeting in plants with plant specific models. p-TAREF has been implemented in concurrent architecture in server as well as standalone form, making it one of the very few available target identification tools able to run concurrently on simple desktops while performing huge transcriptome level analysis accurately and fast. Besides this, it also provides an option to experimentally validate the predicted targets, on the spot, using expression data, which has been integrated in its back-end, to draw confidence on prediction along with SVR score.p-TAREF performance benchmarking has been done extensively through different tests and compared with other plant miRNA target identification tools. p-TAREF was found better performing. | Yes | no | no | server/standalone | |
| TargetScan | Predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer and 7mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA. Predictions are ranked using site number, site type, and site context, which includes factors that influence target-site accessibility. | vertebrates, flies, nematodes | evaluated indirectly | yes | sourcecode, webserver | |
| |
||||||
ncRNA gene prediction software
| Name | Description | Number of sequences | Alignment | Structure | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alifoldz | Assessing a multiple sequence alignment for the existence of an unusual stable and conserved RNA secondary structure. | any | input | yes | sourcecode | |
| eTeRNA Eterna Eterna is a Swiss luxury watch company founded in Grenchen, Canton Solothurn on the 7th of November 1856 by Dr Josef Girard and Urs Schild. They initially specialised in producing pocket watches with alarms. In 1906 the company name changed from U. Schild to Eterna. In 1908 they became the first... |
a crowd-surfing, genetically accurate RNA folding "game". The developers are utilizing the internet demographic to collect optimal folds of RNa sequence to involve in later research. | any | input | yes | http://eterna.cmu.edu/content/EteRNA | |
| EvoFold | a comparative method for identifying functional RNA structures in multiple-sequence alignments. It is based on a probabilistic model-construction called a phylo-SCFG and exploits the characteristic differences of the substitution process in stem-pairing and unpaired regions to make its predictions. | any | input | yes | linuxbinary | |
| MSARi | heuristic search for statistically significant conservation of RNA secondary structure in deep multiple sequence alignments. | any | input | yes | sourcecode | |
| QRNA | This is the code from Elena Rivas that accompanies a submitted manuscript "Noncoding RNA gene detection using camparative sequence analysis". QRNA uses comparative genome sequence analysis to detect conserved RNA secondary structures, including both ncRNA genes and cis-regulatory RNA structures. | 2 | input | yes | sourcecode | |
| RNAz | program for predicting structurally conserved and thermodynamic stable RNA secondary structures in multiple sequence alignments. It can be used in genome wide screens to detect functional RNA structures, as found in noncoding RNAs and cis-acting regulatory elements of mRNAs. | any | input | yes | sourcecode, webserver RNAz 2 | |
| Xrate Xrate XRATE is a program for prototyping phylogenetic hidden Markov models and stochastic context-free grammars.It is used to discover patterns of evolutionary conservation in sequence alignments.... |
a program for analysis of multiple sequence alignments using phylogenetic grammars, that may be viewed as a flexible generalization of the "Evofold" program. | any | yes | yes | sourcecode | |
| Sequence alignment In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are... , RNA structure Biomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is... , |
||||||
Family specific gene prediction software
| Name | Description | Family | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARAGORN | ARAGORN detects tRNA and tmRNA in nucleotide sequences. | tRNA tmRNA TmRNA Transfer-messenger RNA is a bacterial RNA molecule with dual tRNA-like and messenger RNA-like properties. The tmRNA forms a ribonucleoprotein complex together with Small Protein B , Elongation Factor Tu , and ribosomal protein S1... |
webserver source | |
| miRNAminer | Given a search query, candidate homologs are identified using BLAST search and then tested for their known miRNA properties, such as secondary structure, energy, alignment and conservation, in order to assess their fidelity. | MicroRNA | webserver | |
| RISCbinder | Prediction of guide strand of microRNAs. | Mature miRNA | webserver | |
| RNAmicro | A SVM-based approach that, in conjunction with a non-stringent filter for consensus secondary structures, is capable of recognizing microRNA precursors in multiple sequence alignments. | MicroRNA | homepage | |
| RNAmmer | RNAmmer uses HMMER HMMER HMMER is a free and commonly used software package for sequence analysis written by Sean Eddy. Its general usage is to identify homologous protein or nucleotide sequences. It does this by comparing a profile-HMM to either a single sequence or a database of sequences... to annotate rRNA genes in genome sequences. Profiles were built using alignments from the European ribosomal RNA database and the 5S Ribosomal RNA Database. |
rRNA | webserver source | |
| SnoReport | Uses a combination of RNA secondary structure prediction and machine learning that is designed to recognize the two major classes of snoRNAs, box C/D and box H/ACA snoRNAs, among ncRNA candidate sequences. | snoRNA SnoRNA Small nucleolar RNAs are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs... |
sourcecode | |
| SnoScan | Search for C/D box methylation guide snoRNA genes in a genomic sequence. | C/D box snoRNA SnoRNA Small nucleolar RNAs are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs... |
sourcecode, webserver | |
| snoSeeker | snoSeeker includes two snoRNA-searching programs, CDseeker and ACAseeker, specific to the detection of C/D snoRNA SnoRNA Small nucleolar RNAs are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs... s and H/ACA snoRNAs, respectively. snoSeeker has been used to scan four human–mammal whole-genome alignment (WGA) sequences and identified 54 novel candidates including 26 orphan candidates as well as 266 known snoRNA genes. |
snoRNA SnoRNA Small nucleolar RNAs are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs... |
webserver,stand-alone | |
| tRNAscan-SE | a program for the detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. | tRNA | sourcecode, webserver | |
| . | ||||
RNA homology search software
| Name | Description | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERPIN | "Easy RNA Profile IdentificatioN" is an RNA motif search program reads a sequence alignement and secondary structure, and automatically infers a statistical "secondary structure profile" (SSP). An original Dynamic Programming algorithm then matches this SSP onto any target database, finding solutions and their associated scores. | sourcecode webserver | |
| Infernal | "INFERence of RNA ALignment" is for searching DNA sequence databases for RNA structure and sequence similarities. It is an implementation of a special case of profile stochastic context-free grammars called covariance models (CMs). | sourcecode | |
| PHMMTS | "pair hidden Markov models on tree structures" is an extension of pair hidden Markov models defined on alignments of trees. | sourcecode, webserver | |
| RaveNnA Ravenna Ravenna is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy and the second largest comune in Italy by land area, although, at , it is little more than half the size of the largest comune, Rome... |
A slow and rigorous or fast and heuristic sequence-based filter for covariance models. | sourcecode | |
| RSEARCH | Takes a single RNA sequence with its secondary structure and utilizes a local alignment algorithm to search a database for homologous RNAs. | [ftp://selab.janelia.org/pub/software/rsearch/ sourcecode] | |
| . | |||
Benchmarks
| Name | Description | Structure | Alignment | Phylogeny | Links | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRalibase I | A comprehensive comparison of comparative RNA structure prediction approaches | yes | no | no | data | |
| BRalibase II | A benchmark of multiple sequence alignment programs upon structural RNAs | no | yes | no | data | |
| BRalibase 2.1 | A benchmark of multiple sequence alignment programs upon structural RNAs | no | yes | no | data | |
| BRalibase III | A critical assessment of the performance of homology search methods on noncoding RNA | no | yes | no | data | |
| CompaRNA | An independent comparison of single-sequence RNA secondary structure prediction programs | yes | no | no | CompaRNA | |
| Sequence alignment In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are... tools RNA structure Biomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is... prediction tools |
||||||
Alignment viewers/editors
| Name | Description | Alignment | Structure | Link | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4sale | A tool for Synchronous RNA Sequence and Secondary Structure Alignment and Editing | yes | yes | sourcecode | ||
| Colorstock, SScolor, Raton | Colorstock, a command-line script using ANSI terminal color; SScolor, a Perl script that generates static HTML pages; and Raton, an AJAX web application generating dynamic HTML. Each tool can be used to color RNA alignments by secondary structure and to visually highlight compensatory mutations in stems. | yes | yes | sourcecode | ||
| Integrated Genome Browser Integrated Genome Browser Integrated Genome Browser is an open source genome browser, a visualization tool used to observe biologically-interesting patterns in genomic data sets, including sequence data, gene models, alignments, and data from DNA microarrays.- History :... (IGB) |
a multiple alignment viewer written in Java. | yes | no | sourcecode | ||
| Jalview Jalview Jalview is a multiple sequence alignment editor and viewer written in the Java programming language. The programme was originally written by Michele Clamp whilst working in Geoff Barton's group at the EBI.... |
a multiple alignment editor written in Java. | yes | no | sourcecode | ||
| RALEE | a major mode for the Emacs Emacs Emacs is a class of text editors, usually characterized by their extensibility. GNU Emacs has over 1,000 commands. It also allows the user to combine these commands into macros to automate work.Development began in the mid-1970s and continues actively... text editor. It provides functionality to aid the viewing and editing of multiple sequence alignments of structured RNAs. |
yes | yes | sourcecode | ||
| SARSE | A graphical sequence editor for working with structural alignments of RNA. | yes | yes | sourcecode | ||
| Sequence alignment In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are... , RNA structure Biomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is... , |
||||||
Secondary structure viewers/editors
| Name | Description | Link | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| PseudoViewer | Automatically visualizing RNA pseudoknot structures as planar graphs. | webapp/binary | |
| RNA Movies | browse sequential paths through RNA secondary structure landscapes | sourcecode | |
| RNA2D3D | a program for generating, viewing, and comparing 3-dimensional models of RNA | binary | |
| RNAView/RnamlView | Use RNAView to automatically identify and classify the types of base pairs that are formed in nucleic acid structures. Use RnamlView to arrange RNA structures. | sourcecode | |
| VARNA | a tool for the automated drawing, visualization and annotation of the secondary structure of RNA, designed as a companion software for web servers and databases | sourcecode |
See also
- RNARNARibonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
- Non-coding RNANon-coding RNAA non-coding RNA is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA , non-messenger RNA and functional RNA . The term small RNA is often used for short bacterial ncRNAs...
- RNA structureRNA structureBiomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is...
- List of nucleic acid simulation software

