
List of cosmetic ingredients
Encyclopedia
Ingredients of cosmetic products are listed following International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI)
.
These INCI names often differ greatly from systematic chemical nomenclature or from more common trivial names.
The below tables are sorted as follows:
Neutralizer
INCI
The International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients, abbreviated INCI, is a system of names for waxes, oils, pigments, chemicals, and other ingredients of soaps, cosmetics, and the like, based on scientific names and other Latin and English words...
.
These INCI names often differ greatly from systematic chemical nomenclature or from more common trivial names.
The below tables are sorted as follows:
| INCI name | chemical meaning - structure, name or description | purpose - role(s) in a cosmetic formulation |
A
| alcohol denat. | denatured alcohol Methylated spirit Denatured alcohol or methylated spirits is ethanol that has additives to make it more poisonous or unpalatable, and thus, undrinkable. In some cases it is also dyed.... , ethanol Ethanol Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a... made unsuitable for drinking, often via addition of denatonium Denatonium Denatonium, usually available as denatonium benzoate and as denatonium saccharide, is the bitterest chemical compound known; with bitterness thresholds of 0.05 ppm for the benzoate and 0.01 ppm for the saccharide.It was discovered in 1958 during research on local anesthetics by Macfarlan... . |
solvent, carrier, astringent |
| alkyl benzoate C12 - C15 | benzoic acid ester, PhCOO(CH2)11-14CH3 | (commonly found in products that are fade resistand and water/sweat resistant) |
| allantoin Allantoin Allantoin is a chemical compound with formula C4H6N4O3. It is also called 5-ureidohydantoin or glyoxyldiureide. It is a diureide of glyoxylic acid.... |
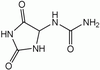 N-(2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl)urea N-(2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl)urea |
stops bleeding of cuts from shaving |
| alpha-isomethyl ionone | 3-methyl-4-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-2-enyl)but-3-en-2-one | ? |
| aluminium chlorohydrate Aluminium chlorohydrate Aluminium chlorohydrate is a group of specific aluminium salts having the general formula AlnClm. It is used in deodorants and antiperspirants and as a coagulant in water purification.... |
basic aluminium chloride Al2(OH)5Cl or Al2(OH)xCl6-x (0| antitranspirant |
|
| aqua | water Water Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a... |
solvent |
| ascorbyl palmitate | [2-(4,5-dihydroxy-3-oxo-2-furyl)-2-hydroxy-ethyl] hexadecanoate | Ascorbyl Palmitate is an ascorbate bonded to palmitic acid to form a Vitamin C ester, used as an anti-staling compound which retard the staling of food products, and soften the crumb. Other anti-staling compounds are sucrose stearate, polyoxyethylene monostearate, glyceryl monostearate, stearoyl tartrate (polyoxyethylene and monoglyceride derivatives of fatty acids) Ascorbyl palmitate is a synthetic ester composed of the 16-carbon chain saturated fatty acid palmitic acid and L-ascorbic acid. The ester linkage is at the 6 carbon of ascorbic acid. It is used as an antioxidant in foods, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, and is also used as a preservative for the natural oils, oleates, fragrances, colors, vitamins and other edible oils and waxes which are used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and foods. Ascorbyl palmitate is a white or yellowish powder having a slight odor. It is very slightly soluble in water and in vegetable oils. Ascorbic acid comprises 42.5% of the weight of ascorbyl palmitate. Its molecular weight is 414.54 daltons and its empirical formula is C22H38O7. Ascorbyl palmitate is also known as vitamin C palmitate, L-ascorbyl-6-palmitate and 3-oxo-L-gulofuranolactone 6-palmitate. Ascorbyl palmitate is marketed as a nutritional supplement and claimed by some to be a superior delivery form of vitamin C. Since ascorbyl palmitate is a fat-soluble derivative of ascorbic acid, theoretically it can concentrate into the lipid domains of biological systems and protect cell membranes and low density lipoproteins (LDL) against oxidation. Ascobyl palmitate works to protect fats from peroxidation, and it can be stored in the body in small amounts. It works best when taken in combination of ascorbic acid. Ascobyl palmitate also acts synergistically with other antioxidants such as vitamin E. The use of ascobyl palmitate in anti-aging was pioneered by the two times Nobel Laureate Dr. Linus Pauling, whose research and subsequent clinical studies showed that ascobyl palmitate, when used in combination with vitamin C and amino acids lysine and proline, is able to strengthen the vascular wall and reverse atherosclerotic heart disease. The use of vitamin C as part of an anti-aging protocol is widespread. At least 300000 mg to 2000 mg of vitamin C is widely accepted as the optimum anti-aging dose. However, vitamin C alone is insufficient for optimum health. Its half-life is short and retention time in the body is therefore low. Ascobyl palmitate is a good balancing and complementary nutrient. Together, the antioxidant properties are extended. Furthermore, the addition of lysine and proline helps to enhance the cardiovascular system. Those serious in anti-aging and optimum cardiovascular health should consider the intake of these four important nutrients a part of their daily routine. Ascobyl palmitate is a free radical scavengers. Free radicals include active oxygen species, such as superoxide, ×OH, ×OOH, etc., and the free radicals derived from the biochemical utilization of oxygen or the prooxidant stimulation of oxygen metabolism, initiate the peroxidation of unsaturated lipids - especially those that constitute bio-membranes. |
B
| butane Butane Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or... |
butane C4H10 | propellant (pressurized dispenser) |
| butyrospermum parkii | shea butter Shea butter Shea butter is a slightly yellowish or ivory-colored fat extracted from the nut of the African shea tree . It is widely used in cosmetics as a moisturizer, salve or lotion. Shea butter is edible and may be used in food preparation... , vegetable fat made from nuts of African shea Shea Vitellaria paradoxa, also classified as Butyrospermum parkii and B. paradoxa, commonly known as shea tree, shi tree, or , vitellaria or karité, is a tree of the Sapotaceae family indigenous to Africa, occurring in Mali, Cameroon, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, Togo, Nigeria, Senegal, Sudan,... tree |
moisturizer I - IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE Product Sheabutter Type Refined, obtained by mechanical crushing method Reference BKN 36 Latin (Linnaen name) Sapotaceae Multiflora Butyrospermum Parkii CTFA Name Sheabutter INCI Name Sheabutter CAS Number 68424-60-2 EINECS Number 270-311-6 II - INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS Butter obtained by crushing method from the shea nuts collected in West Africa. Stabilized with a natural anti-oxydizing TOCOPHEROL (0,2 %). III - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION No hazard IV - FIRST AID MEASURES Purposeless V - FIRE - FIGHTING MEASURES Putting out means : by suffocating with moss or powder VI - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES Purposeless VII - HANDLING AND STORAGE The melting point range begin at 29 ° Celsius. A 26° maximum will be necessary. For a long conservation a range of 15 to 20° Celsius will avoid acidity and peroxyde important modification. Limit oxygen contact. VIII - EXPOSURE CONTROLS Purposeless IX - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Appearance Butter Butter concrete Colour Colour Ivory - ¾ Gardner scale Odor Neutral Taste Neutral Gravity at 20° Celsius 0,900 to 0,903 Melting point 29 to 34° Celsius Solubility at 20 ° Celsius Not soluble in water X - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Stable product at usual temperature of storage (see section VII). Avoid oxydation by air. XI - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION Acute toxicity Purposeless Chronic Toxicity Purposeless XII - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Purposeless XIII - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Purposeless XIV - TRANSPORT INFORMATION No classification regarding transport XV - REGULATORY INFORMATION No classification according to EEC Commission |
H
| hydroxyethyl-cellulose | Cellulose fibre Cellulose Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units.... from wood pulp Wood pulp Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops or waste paper. Wood pulp is the most common raw material in papermaking.-History:... with –OCH2CH2OH groups added |
gives body |
| hydroxypropyl-cellulose | Cellulose fibre from wood pulp with –OCH2CH(OH)CH3 groups added | gives body |
I
| isobutane Butane Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or... |
Isobutane (CH3)2CHCH3 | propellant (pressurized dispenser) |
| isopentane Pentane Pentane is an organic compound with the formula C5H12 — that is, an alkane with five carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of three structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, pentane means exclusively the n-pentane isomer; the other two being called... |
Isopentane (CH3)2CHCH2CH3 | propellant (pressurized dispenser) |
P
| propane Propane Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central... |
Propane CH3CH2CH3 | propellant (pressurized dispenser) |
S
| sodium hydroxide | Sodium hydroxide NaOH | base |
T
| triethanolamine Triethanolamine Triethanolamine, often abbreviated as TEA, is an organic chemical compound which is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Like other amines, triethanolamine is a strong base due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. Triethanolamine can... |
N(CH2CH2OH)3 | base, emulsifier |
Neutralizer

