
Lituus (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
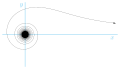
Spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a central point, getting progressively farther away as it revolves around the point.-Spiral or helix:...
in which the angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
is inversely proportional to the square of the radius
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius of a circle or sphere is any line segment from its center to its perimeter. By extension, the radius of a circle or sphere is the length of any such segment, which is half the diameter. If the object does not have an obvious center, the term may refer to its...
(as expressed in polar coordinates).
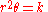
This spiral, which has two branches depending on the sign of
 , is asymptotic
, is asymptoticAsymptote
In analytic geometry, an asymptote of a curve is a line such that the distance between the curve and the line approaches zero as they tend to infinity. Some sources include the requirement that the curve may not cross the line infinitely often, but this is unusual for modern authors...
to the
 axis. Its points of inflexion are at
axis. Its points of inflexion are at  and
and 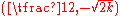 .
.The curve was named by Roger Cotes
Roger Cotes
Roger Cotes FRS was an English mathematician, known for working closely with Isaac Newton by proofreading the second edition of his famous book, the Principia, before publication. He also invented the quadrature formulas known as Newton–Cotes formulas and first introduced what is known today as...
in a collection of papers entitled Harmonia Mensurarum (1722), which was published six years after his death.

