Liverpool Canal Link
Encyclopedia
Leeds and Liverpool Canal
The Leeds and Liverpool Canal is a canal in Northern England, linking the cities of Leeds and Liverpool. Over a distance of , it crosses the Pennines, and includes 91 locks on the main line...
, at Liverpool
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough of Merseyside, England, along the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary. It was founded as a borough in 1207 and was granted city status in 1880...
, to the South Docks. The new link adds 1.4 miles (2.3 km) of navigable waterway to the canal system.
History
It was always intended that the Leeds and Liverpool CanalLeeds and Liverpool Canal
The Leeds and Liverpool Canal is a canal in Northern England, linking the cities of Leeds and Liverpool. Over a distance of , it crosses the Pennines, and includes 91 locks on the main line...
would be linked to the docks in Liverpool
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough of Merseyside, England, along the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary. It was founded as a borough in 1207 and was granted city status in 1880...
. It was only in 1846, 30 years after the canal's completion, that the canal was directly linked to the docks via the Stanley Dock
Stanley Dock
Stanley Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the Vauxhall area of Liverpool and is part of the northern dock system. The dock is connected to the Leeds and Liverpool Canal to the east and Collingwood Dock to the west.Designed by Jesse...
Branch. Georges Dock was filled in at the beginning of the 20th Century to allow the building of the Liver Building, Cunard Building
Cunard Building
The Cunard Building is a Grade II* listed building located in Liverpool, England. It is sited at the Pier Head and along with the neighbouring Liver Building and Port of Liverpool Building is one of Liverpool's Three Graces, which line the city's waterfront...
and the Mersey Docks and Harbour Board Building, the Three Graces. This meant the North and South Docks were no longer directly linked. Boats wishing to travel from the North Docks to the South Docks had to go via the River Mersey
River Mersey
The River Mersey is a river in North West England. It is around long, stretching from Stockport, Greater Manchester, and ending at Liverpool Bay, Merseyside. For centuries, it formed part of the ancient county divide between Lancashire and Cheshire....
.
Planning

Huddersfield Narrow Canal
The Huddersfield Narrow Canal is an inland waterway in northern England. It runs just under from Lock 1E at the rear of the University of Huddersfield campus, near Aspley Basin at Huddersfield to the junction with the Ashton Canal at Whitelands Basin in Ashton-under-Lyne...
, the Ribble Link
Ribble Link
The Millennium Ribble Link is a Linear Water Park and new navigation which links the once-isolated Lancaster Canal in Lancashire, England to the River Ribble...
and Rochdale Canal
Rochdale Canal
The Rochdale Canal is a navigable "broad" canal in northern England, part of the connected system of the canals of Great Britain. The "Rochdale" in its name refers to the town of Rochdale, Greater Manchester, through which the canal passes....
. The Waterways Regeneration Task Force, part of British Waterways
British Waterways
British Waterways is a statutory corporation wholly owned by the government of the United Kingdom, serving as the navigation authority in England, Scotland and Wales for the vast majority of the canals as well as a number of rivers and docks...
took over the South Docks from English Partnerships. The Task Force approached the Liverpool City Council
Liverpool City Council
Liverpool City Council is the governing body for the city of Liverpool in Merseyside, England. It consists of 90 councillors, three for each of the city's 30 wards. The council is currently controlled by the Labour Party and is led by Joe Anderson.-Domain:...
's Liverpool City Vision with the suggestion of linking the Leeds and Liverpool Canal
Leeds and Liverpool Canal
The Leeds and Liverpool Canal is a canal in Northern England, linking the cities of Leeds and Liverpool. Over a distance of , it crosses the Pennines, and includes 91 locks on the main line...
to the South Docks by building a new waterway across Pier Head.
Four routes were proposed and after public consultation in 2001 a route was chosen. The winning route was across the front of the Three Graces at the Pier Head.
Feasibility work was funded by the North West Regional Development Agency, British Waterways
British Waterways
British Waterways is a statutory corporation wholly owned by the government of the United Kingdom, serving as the navigation authority in England, Scotland and Wales for the vast majority of the canals as well as a number of rivers and docks...
Regeneration Task Force and a detailed proposal drawn up during 2003.
Funding for the work came from the NWRDA, (50%) with the rest coming from Europe via the ERDF Objective 1 programme. The original estimate was £17 million.
After some changes to the plans following the failed Fourth Grace project and objections by English Heritage
English Heritage
English Heritage . is an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport...
a new plan was drawn up by March 2005 which took account of the new Museum of Liverpool. Planning permission was applied for in August 2005 and granted in early 2006.
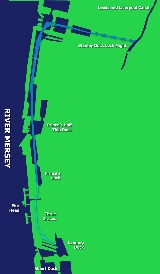
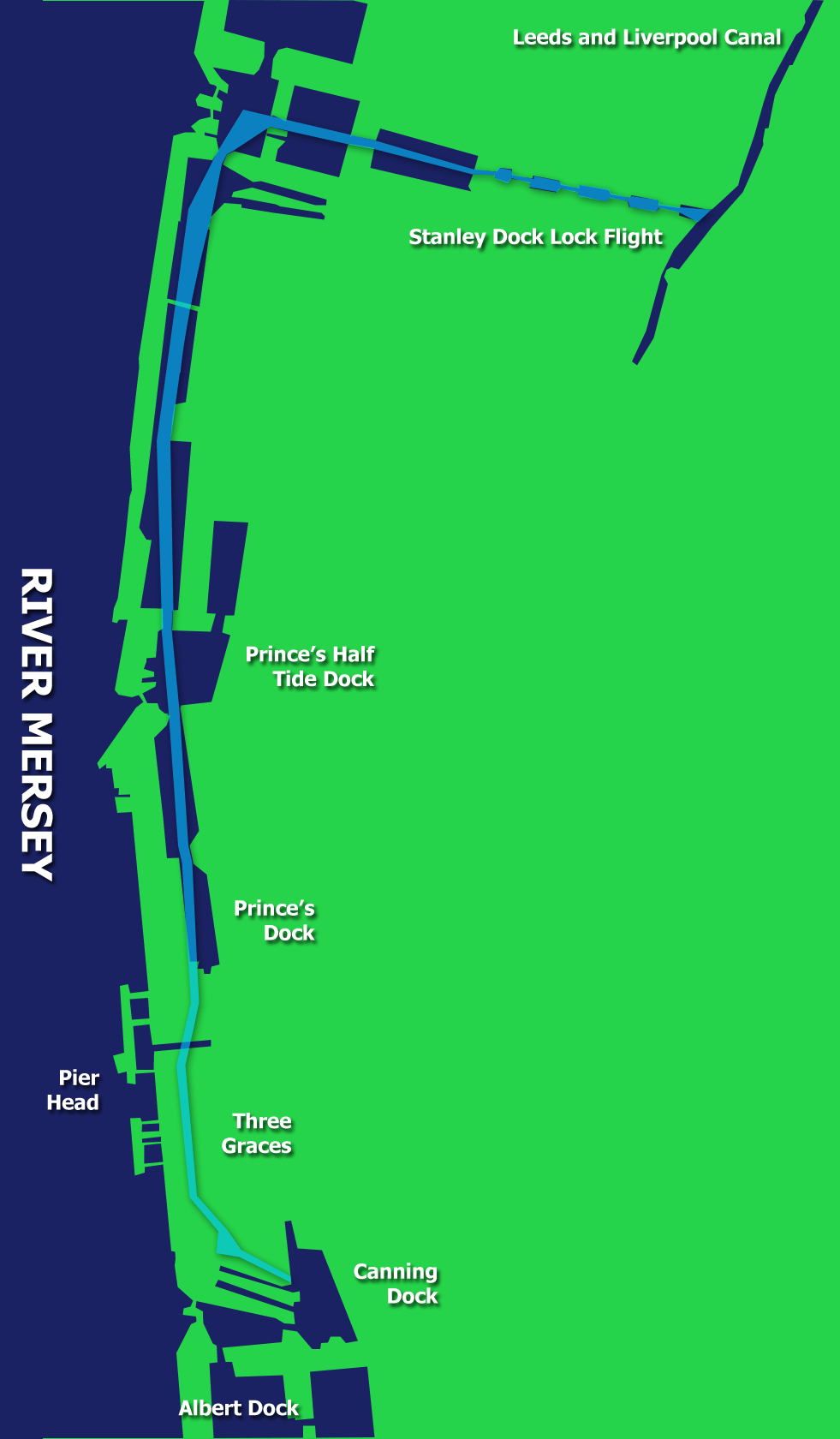
Route

The docks between Salisbury Dock and Princes Half Tide Dock had been filled in with just a small drainage channel remaining. Following dredging in the 1990s this section was in water and navigable. Further dredging took place at the northern edge of the Trafalgar Dock infill.
Between Trafalgar Dock and the Princes Half Tide Dock
Princes Half Tide Dock
Princes Half Tide Dock on the River Mersey, England, is a half tide dock and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall, connected to East Waterloo Dock and West Waterloo Dock to the north and Princes Dock to the south. The dock opened in 1810 and...
a 21 feet (6.4 m) wide channel through Trafalgar Dock and the northern end of West Waterloo Dock
West Waterloo Dock
West Waterloo Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall and connected to Princes Half Tide Dock to the south...
was built, with a new crossing at the dock passage between Trafalgar and West Waterloo Dock. The channel from West Waterloo Dock to Princess Dock was dredged and the level of the docks reduced.
From the northern end of Prince's Dock through to the start of the Pier Head area a new fixed bridge and lock was built at Princes Dock
Princes Dock
Princes Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is the most southerly of the docks situated in the northern part of the Liverpool dock system, connected to Princes Half Tide Dock to the north...
. Prince's Dock Footbridge has been raised to allow boats to pass underneath and the bridge approaches have been landscaped. A new culvert across land known as Plot 7 was built along with another new culvert beneath St. Nicholas Place and the new Cruise Liner Facility.
The final section of the canal link commences south of the Floating Roadway Basin, crosses the Pier Head and terminates at Canning Dock
Canning Dock
Canning Dock is a dock, on the River Mersey, England and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Salthouse Dock to the south and Canning Half Tide Dock to the west. The Canning Graving Docks are accessed from the dock.-History:The dock was opened in...
. 500 metres (546.8 yd) of new canal was built along with associated bridge crossings and a lock structure. A new basin was built at Mann Island
Mann Island
Mann Island is a small area in Liverpool, England.It lies on the waterfront next to the River Mersey between the Albert Dock to the south and the Pier Head to the north.-History:...
along with extensive landscaping for the general public.
Construction
The canal link was completed in December 2008 with the Pier HeadPier Head
The Pier Head is a riverside location in the city centre of Liverpool, England. It is part of the Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City UNESCO World Heritage Site, which was inscribed in 2004....
section finished earlier in September. After a period of testing and commissioning the canal link opened on 25 March 2009.

