
Locule
Encyclopedia

Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
, plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
or fungus
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
).
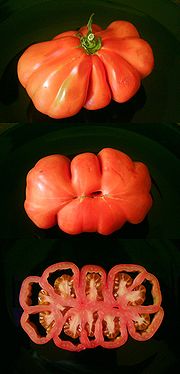
In plants, the term locule usually refers to a chamber within an ovary
Ovary (plants)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals...
(gynoecium
Gynoecium
Gynoecium is most commonly used as a collective term for all carpels in a flower. A carpel is the ovule and seed producing reproductive organ in flowering plants. Carpels are derived from ovule-bearing leaves which evolved to form a closed structure containing the ovules...
or carpel of the flower
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . The biological function of a flower is to effect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs...
and fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
s). Depending on the number of locules in the ovary, carpels and fruits can be classified as uni-locular, bi-locular or multi-locular. The locules contain the ovule
Ovule
Ovule means "small egg". In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument forming its outer layer, the nucellus , and the megaspore-derived female gametophyte in its center...
s or seed
Seed
A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant...
s. The term may also refer to chambers within anthers containing pollen
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
.
In the Loculoascomycetes, a group of sac fungi, locules are chambers similar to perithecia, but hallowed out from the host tissue rather than being a preformed structure. For this reason, a single locule is referred to as a pseudothecium. Locules do, however, still contain asci
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
,which hold ascospore
Ascospore
An ascospore is a spore contained in an ascus or that was produced inside an ascus. This kind of spore is specific to fungi classified as ascomycetes ....
s, as perithecia do.

