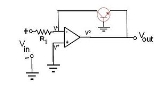
Log amplifier
Encyclopedia
A log
amplifier
(logarithmic converter) is one for which the output voltage Vout is K times the natural log of the input voltage Vin. This can be expressed as,
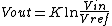
where Vref is the normalization constant in volts and K is the scale factor.
 The relationship between the input voltage
The relationship between the input voltage 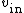 and the output voltage
and the output voltage 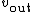 is given by:
is given by:
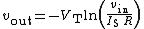
 A necessary condition for successful operation of a log amplifier is that the input voltage, Vin is always positive. This may be ensured by using a rectifier
A necessary condition for successful operation of a log amplifier is that the input voltage, Vin is always positive. This may be ensured by using a rectifier
and filter
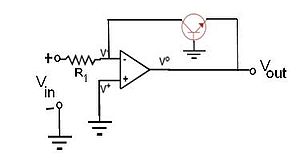
to condition the input signal before applying to the log amp input. As Vin is positive, Vout is obliged to be negative (since the op amp is in the inverting configuration) and is large enough to forward bias the emitter-base junction of the BJT keeping it in the active mode of operation. Now,
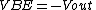
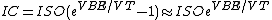
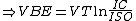
where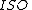 is the saturation current of the emitter-base diode and
is the saturation current of the emitter-base diode and 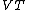 is the thermal voltage.
is the thermal voltage.
Due to the virtual ground
at the op amp differential input,
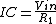 , and
, and
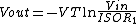
The output voltage is expressed as the natural log of the input voltage. Both the saturation current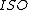 and the thermal voltage
and the thermal voltage 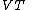 are temperature dependent, hence, temperature compensating circuits may be required.
are temperature dependent, hence, temperature compensating circuits may be required.
Logarithmic output
Analog electronics with Op Amps by A. J. Peyton, V. Walsh
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
(logarithmic converter) is one for which the output voltage Vout is K times the natural log of the input voltage Vin. This can be expressed as,
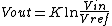
where Vref is the normalization constant in volts and K is the scale factor.
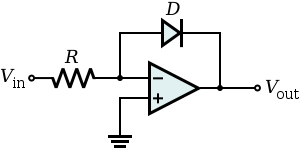
Basic op-amp diode circuit

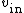 and the output voltage
and the output voltage 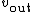 is given by:
is given by: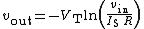
- where
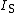 is the saturation current and
is the saturation current and 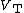 is the thermal voltage.
is the thermal voltage.
Transdiode configuration

Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
and filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
to condition the input signal before applying to the log amp input. As Vin is positive, Vout is obliged to be negative (since the op amp is in the inverting configuration) and is large enough to forward bias the emitter-base junction of the BJT keeping it in the active mode of operation. Now,
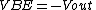
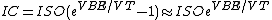
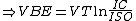
where
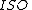 is the saturation current of the emitter-base diode and
is the saturation current of the emitter-base diode and 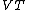 is the thermal voltage.
is the thermal voltage.Due to the virtual ground
Virtual ground
Virtual ground is a node of the circuit that is maintained at a steady reference potential, without being connected directly to the reference potential...
at the op amp differential input,
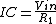 , and
, and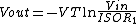
The output voltage is expressed as the natural log of the input voltage. Both the saturation current
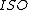 and the thermal voltage
and the thermal voltage 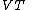 are temperature dependent, hence, temperature compensating circuits may be required.
are temperature dependent, hence, temperature compensating circuits may be required.See also
DiodeLogarithmic output
External links
Integrated DC logarithmic amplifiers from Maxim's AN 36211Analog electronics with Op Amps by A. J. Peyton, V. Walsh

