
Lombardy
Encyclopedia
Lombardy is one of the 20 regions of Italy
. The capital is Milan
. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe. Major tourist destinations in the region include the historic, cultural and artistic cities of Milan (which is Italy's second top tourist destination), Brescia
, Mantua
, Pavia
, Como
, Cremona
, Bergamo
, Sondrio
, Lecco
, Lodi, Varese
, Monza
, and the lakes of Garda
, Como
, Maggiore
, and Iseo
.
The official language, as in the rest of Italy
, is Italian
. The traditional local languages are the various dialects of Lombard (Western Lombard
and Eastern Lombard), as well as some dialects of Emilian
, spoken in some parts of the provinces of Mantua
, Pavia
, and Cremona
. According to Istat
, almost 27% of Lombards are bilingual with Lombard and Italian languages; 9.1% are monolingual in Lombard and 57.6% are monolingual in Italian.
 Lombardy is bordered by Switzerland
Lombardy is bordered by Switzerland
(north: Canton Ticino and Canton Graubünden) and by the Italian regions of Emilia-Romagna
(south), Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Veneto
(east), and Piedmont
(west). Three distinct natural zones can be fairly easily distinguished in the Lombardy region: mountains, hills and plains - the latter being divided in Alta (high plains) and Bassa (low plains).
The most important mountainous area is an Alpine zone including the Lepontine
and Rhaetian Alps
, (Piz Bernina - La Spedla, 4,020 m), the Bergamo Alps
, the Ortler Alps
and the Adamello massif; it is followed by an Alpine foothills zone Prealpi, which include the main peaks are the Grigna Group (2,410 m), Resegone (1,875 m) and Presolana
(2,521 m). The great Lombard lakes, all of glacial origin lie in this zone. From west to east these are Lake Maggiore
, Lake Lugano
(only a small part is Italian), Lake Como
, Lake Iseo
, Lake Idro
, then Lake Garda
, the largest in Italy. South of the Alps lie the hills characterized by a succession of low heights of morainic origin, formed during the last Ice Age
and small barely fertile plateaux, with typical heaths and conifer woods. A minor mountainous area lies south of the Po, in the Appennines range.
The plains of Lombardy, formed from alluvial deposits, can be divided into the Alta - an upper, permeable ground zone in the north and a lower zone characterized - the Bassa - by the so-called line of fontanili (the spring waters rising on impermeable ground). Anomalous compared with the three distinctions already made is the small region of the Oltrepò Pavese
, formed by the Apennine foothills beyond the Po River. A large number of rivers, all direct or indirect tributaries of the Po, cross the plains of Lombardy. Major rivers, flowing west to east, are the Ticino
, the outlet of Lake Maggiore
, the Olona
, the Lambro
, the Adda
, outlet of Lake Como
, the Mincio
, outlet of Lake Garda
, and the Oglio
, the Lake Iseo
outflow. There is a wide network of canals for irrigation purposes. In the plains, intensively cultivated for centuries, little of the original environment remains. The rare elm
, alder
, sycamore
, poplar
, willow
and hornbeam
woods and heaths are covered now by several protected areas. In the area of the great Alpine foothills lakes, however, grow olive trees, cypresses and larches, as well as varieties of subtropical flora such as magnolias, azaleas, acacias, etc. The mountains area is characterized by the typical vegetation of the whole range of the Italian Alps. At a lower levels (up to approximately 1,100 m) oak woods or broadleafed trees grow; on the mountain slopes (up to 2,000–2,200 m) beech trees grow at the lowest limits, with conifer woods higher up. Shrubs such as rhododendron, dwarf pine and juniper are native to the summital zone (beyond 2,200 m).
The climate of this region is continental, though with variations depending on altitude or the presence of inland waters. The continental nature of the climate is more accentuated on the plains, with high annual temperature changes (at Milan an average January temperature is 1.5 °C (35 °F) and 24 °C (75 °F) in July), and thick fog between October and February. The Alpine foothills lakes exercise a mitigating influence, permitting the cultivation of typically Mediterranean produce (olives, citrus fruit). In the Alpine zone, the valley floor is relatively mild in contrast with the colder higher areas (Bormio, 1,225 m, -1.4 °C average in January, 17.3 °C (63 °F) in July). Precipitations are more frequent in the Prealpine zone (up to 1,500–2,000 mm annually) than on the plains and Alpine zones (600 mm to 850 mm annually). The numerous species of endemic flora (the Lombard native species), typical mainly of the Lake Como area, include some kinds of saxifrage
, the Lombard garlic, groundsels bellflowers and the cottony bellflowers. Lombardy counts many protected areas: the most important are the Stelvio National Park
(the largest Italian natural park), with typically alpine wildlife: red deer
, roe-deer, ibex, chamois
, foxes, ermine
and also golden eagles; and the Ticino Valley Natural Park, instituted in 1974 on the Lombard side of the Ticino River
to protect and conserve one of the last major examples of fluvial forest in Northern Italy
.

The area of current Lombardy was settled at least since the 2nd millennium BC, as shown by the archaeological findings of ceramics, arrows, axes and carved stones. In the following centuries it was inhabited by different peoples amongst whom the Etruscans
, who founded the city of Mantua
and spread the use of writing; later, starting from the 5th century BC, the area was invaded by Celtic - Gallic
tribes. These people settled in several cities (including Milan
) and extended their rule to the Adriatic Sea. Their development was halted by the Roman
expansion in the Po Valley
from the 3rd century BC onwards: after centuries of struggle, in 194 BC
the entire area of what is now Lombardy became a Roman province with the name of Gallia Cisalpina ("Gaul
on the nearer side of the Alps
"). The Roman culture and language overwhelmed the former civilization in the following years, and Lombardy became one of the most developed and rich areas of Italy with the construction of a wide array of roads and the development of agriculture and trade. Important figures like Pliny the Elder
(in Como
) and Virgil
(in Mantua) were born here. In late antiquity the strategic role of Lombardy was emphasized by the temporary moving of the capital of the Western Empire
to Mediolanum
(Milan). Here, in 313 AD, emperor Constantine
issued the famous edict that gave freedom of confession to all religions within the Empire.
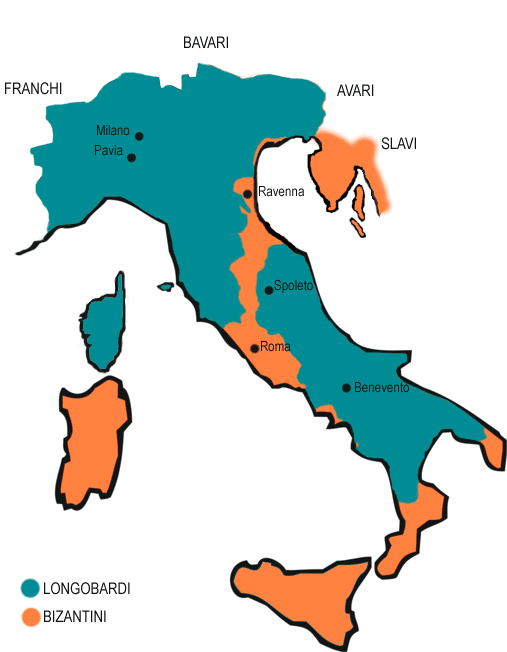 During and after the fall of the Western Empire, Lombardy suffered heavily from destruction brought about by a series of invasions by tribal peoples. The last and most effective was that of the Lombards
During and after the fall of the Western Empire, Lombardy suffered heavily from destruction brought about by a series of invasions by tribal peoples. The last and most effective was that of the Lombards
, or Longobardi, who came around 570s and whose long-lasting reign (whose capital was set in Pavia
) gave the current name to the region. There was a close relationship between the Frankish
, Bavaria
n and Lombard nobility for many centuries. After the initial struggles, relationships between the Lombard people and the Latin-speaking people improved. In the end, the Lombard language and culture assimilated with the Latin culture, leaving evidence in many names, the legal code and laws among other things. The end of Lombard rule came in 774
, when the Frankish
king Charlemagne
conquered Pavia and annexed the Kingdom of Italy (mostly northern and central Italy) to his empire. The former Lombard dukes and nobles were replaced by other German vassals, prince-bishops or marquises. The 11th century marked a significant boom in the region's economy, due to improved trading and, mostly, agricultural conditions. In a similar way to other areas of Italy, this led to a growing self-acknowledgement of the cities, whose increasing richness made them able to defy the traditional feudal supreme power, represented by the German emperors and their local legates. This process reached its apex in the 12th and 13th centuries, when different Lombard League
s formed by allied cities of Lombardy, usually led by Milan, managed to defeat the Hohenstaufen
Emperor Frederick I, at Legnano
, and his grandson Frederick II
, at Parma
.
This did not prevent other important Lombard centres, like Cremona
(then rivalling Milan for size and wealth) and others, from supporting the imperial power if this could grant them an immediate advantage. Taking advantage of the flourishing agriculture, the area around the Po River
, together with Venice
and Tuscany
, continued to expand its industry and commerce until it became the economic centre of the whole of Europe. The enterprising class of the communes extended its trade and banking activities well into northern Europe: "Lombard" designated the merchant or banker coming from northern Italy (see, for instance, Lombard Street
in London). The name "Lombardy" came to designate the whole of Northern Italy until the 15th century and sometimes later. From the 14th century onwards, the instability created by the unceasing internal and external struggles ended in the creation of noble seignories, the most significant of which were those of the Viscontis
(later Sforzas
) in Milan and of the Gonzagas
in Mantua. In the 15th century the Duchy of Milan
was a major political, economical and military force at the European level. Milan and Mantua became two centres of the Renaissance
whose culture, with men like Leonardo da Vinci
and Mantegna
, and pieces of art were highly regarded (for example, Leonardo da Vinci's The Last Supper). This richness, however, attracted the now more organized armies of national powers like France and Austria, which waged a lengthy battle for Lombardy in the late 15th-early 16th century.
, the Duchy of Milan became a possession of the Habsburgs of Spain
: the new rulers did little to improve the economy of Lombardy, instead imposing a growing series of taxes needed to support their unending series of European wars. The eastern part of modern Lombardy, with cities like Bergamo
The eastern part of modern Lombardy, with cities like Bergamo
and Brescia
, was under the Republic of Venice
, which had begun to extend its influence in the area from the 14th century onwards (see also Italian Wars
). Pestilences (like that of 1628/1630, described by Alessandro Manzoni
in his I Promessi Sposi) and the generally declining conditions of Italy's economy in the 17th and 18th centuries halted the further development of Lombardy. In 1706 the Austrians
came to power and introduced some economical and social measures which granted a certain recovery. Their rule was smashed in the late 18th century by the French armies, however, and with the formation of the Napoleonic Empire
, Lombardy became one of the semi-independent province of Napoleonic France. The restoration of Austrian rule in 1815, in the form of the puppet state called Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
, had however to contend with new social ideals introduced by the Napoleonic era. Lombardy became one of the intellectual centres leading to Italian unification
. The popular republic of 1848 was short-lived, its suppression leading to renewed Austrian rule. This came to a decisive end when Lombardy was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy
1859 as a result of the Second Italian Independence War. When annexed to the Kingdom of Italy in 1859 Lombardy achieved its actual territorial shape by adding the Oltrepò Pavese
(formerly southern part of Novara
's Province) to the province of Pavia
. Starting from the late 19th century, and with a boom after World War II
, Lombardy sharpened its status of richest and most industrialized region of Italy.
population or about 10 million people live in Lombardy (16.2% of the national population; 2% of the European Union
population), making it the second most densely populated region in Italy after Campania
with a strong concentration in the Milan
metropolitan area and the Alpine foothills areas of the provinces of Varese
, Como
, Lecco
, Monza and Brianza
and Bergamo
, (1,200 inh./km2), a lower average density (250 inh./km2) in the Po valley and the lower Brescia
valleys, and much lower densities (less than 60 inh./km2) in the northern mountain areas and the southern Oltrepò Pavese
subregion.
The growth of the regional population was particularly sustained during the 1950s-60s, thanks to a prolonged economic boom, high birth rates, and strong immigration flows (especially from Southern Italy). During the last two decades, Lombardy became the destination of a large number of international immigrants, insomuch that today more than a quarter of all foreign immigrants in Italy lives in this region. As of 2008, the Italian national institute of statistics ISTAT estimated that 815,335 foreign-born immigrants live in Lombardy, equal to 8.4% of the total regional population.
The primary religion is Catholicism
; significative religious minorities include Christian Waldenses, Protestants and Orthodox
, as well as Jews
, Sikh
and Muslims
.
Lombardy's development has been marked by the growth of the services sector since the 1980s, and in particular by the growth of innovative activities in the sector of services to enterprises and in credit and financial services. At the same time, the strong industrial vocation of the region has not suffered from it. Lombardy remains, in fact, the main industrial area of the country. The presence, and development, of a very high number of enterprises belonging to the services sector represents a favourable situation for the improvement of the efficiency of the productive process, as well as for the growth of the regional economy. Lombardy is one of the Four Motors for Europe.
The region can broadly be divided into three areas as regards the productive activity. Milan, where the services sector makes up for 65.3% of the employment; a group of provinces, Varese, Como, Lecco, Bergamo and Brescia, highly industrialised, although in the two latter ones, in the plains, there is also a rich agricultural sector. Finally, in the provinces of Sondrio, Pavia, Cremona, Mantova and Lodi, there is a consistent agricultural activity, and at the same time an above average development of the services sector. The productivity of agriculture is enhanced by a well-developed use of fertilizers and the traditional abundance of water, boosted since the Middle Ages by the construction (partly designed by Leonardo da Vinci) of a wide net of irrigation systems. Lower plains are characterized by fodder crops, which are mowed up to eight times a years, cereals (rice, wheat and maize) and sugarbeet. Productions of the higher plains include cereals, vegetables, fruit trees and mulberries. The higher areas, up to the Prealps and Alps
sectors of the north, produce fruit and vines. Cattle (with the highest density in Italy), pigs and sheep are raised.
Following a steep decline in GDP during the global recession in 2009 which saw industry heavily hit, Lombardy's economy is predicted to outperform the Italian economy this year with growth of between 1-1.3% expected. Only Emilia Romagna, Lazio and Tuscany are expected to outperform the region in 2010. The revival of the industrial sector is an important factor, but it is the service sector - and especially the financial sector which will drive the Lombard economy to a sustainable recovery.
representative democracy
, whereby the President of the Region (Presidente della Regione) is the head of government
, and of a pluriform multi-party system
. Executive power
is exercised by the Regional Government (Giunta Regionale). Legislative power is vested in the Regional Council
(Consiglio Regionale).
The Christian Democrats
maintained a large majority of the popular support and the control of the most important cities and provinces since the birth of the Italian Republic until the late 1980s. The Italian Communist Party
was a considerable presence only in the eastern and southern parts of Lombardy from the late 1960s to the mid 1980's. Their base however was increasingly eroded by the Italian Socialist Party
until, in the early 1990s, the Mani Pulite
corruption scandal which spread from Milan to the whole of Italy wiped away the old political class almost entirely. This, together with the general disaffection towards Rome's government (considered as favouring excessively the less developed regions of southern Italy in economical matters), led to the sudden growth of the secessionist (later Northern League), that is particularly strong in mountain and rural areas. In recent years, Lombardy stayed as a conservative stronghold, that gave about 60 per cent of its votes to Silvio Berlusconi
at the last general election
. Notwithstanding, the capital city of Milan landslide elected a new progressive mayor
at the 2011 municipal elections.
to the present day, through the Roman period and the Renaissance and can be found both in museums and churches that enrich cities and towns around the region.
to Middle Ages
.
The many artifacts (pottery, personal items and weapons) found in the necropolis near the Lake Maggiore
, and Ticino
demonstrate the presence of civilization Golasecca who lived in Western Lombardy between the ninth and the fourth century BC.
(Milan), the Accademia Carrara
(Bergamo), the Museum of Santa Giulia (Brescia), the Volta Temple (Como), the Stradivari Museum (Cremona), the Palazzo Te (Mantua), the Museum Sacred Art of the Nativity and the basilica of Santa Maria Assunta at Gandino
, the Royal Villa of Monza and many others.
is popular in the region, often found in soups as well as risotti, such as "risotto alla Milanese", with saffron
. In the city of Monza
a popular recipe also adds pieces of sausages to the risotto. Regional cheeses include robiola
, crescenza, taleggio, gorgonzola
and grana padano (the plains of central and southern Lombardy allow intensive cattle-raising). Butter
and cream
are used. Single pot dishes, which take less work to prepare, are popular. In Bergamo
, Brescia
, and Valtellina
, polenta
is common. In Valtellina, Pizzoccheri
too. In Mantua
festivals feature tortelli di zucca (ravioli
with pumpkin
filling) accompanied by melted butter and followed by turkey
stuffed with chicken
or other stewed meat
s.
and home of the Teatro Donizetti; Brescia is hosts the impressive 1709 Teatro Grande; Cremona is regarded as the birthplace of the commonly used violin
, and is home to several of the most prestigious luthier
s in the world, and Mantua was one of the founding and most important cities in 16th and 17th opera and classical music. Other cities such as Lecco, Lodi, Varese and Pavia also have rich musical traditions, but Milan is the hub and centre of the Lombard musical scene. It was the birthplace of Giuseppe Verdi
, one of the most famous and influential opera composers of the 19th century, and boasts a variety of acclaimed theatres, such as the Piccolo Teatro and the Teatro Arcimboldi; however, the most famous is the 1778 Teatro alla Scala, one of the most important and prestigious operahouses in the world.
, Lombard is the local language of Lombardy. Lombard is a member of the Gallo-Italic group within the Romance languages
. It is spoken natively in Northern Italy
(most of Lombardy and some areas of neighbouring regions, notably the eastern side of Piedmont
) and Southern Switzerland
(Ticino
and Graubünden
).
The two main varieties (Western Lombard language and Eastern Lombard language
) show differences and are often, but not always, mutually comprehensible. The union of Western Lombard or Insubric
, Eastern Lombard and intermediate varieties under the denomination of "Lombard" is a matter of debate, and it has been argued that the two might potentially form separate languages.
, Vigevano
and Cremona
, but Milan
is the region's most important centre for clothing and high fashion. In 2009, Milan was regarded as the world fashion capital
, even surpassing New York
, Paris
, Rome
and London
. Most of the major Italian fashion
brands, such as Valentino
, Versace
, Prada
, Armani and Dolce & Gabbana
(to name a few), are currently headquartered in the city.
Regions of Italy
The regions of Italy are the first-level administrative divisions of the state, constituting its first NUTS administrative level. There are twenty regions, of which five are constitutionally given a broader amount of autonomy granted by special statutes....
. The capital is Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe. Major tourist destinations in the region include the historic, cultural and artistic cities of Milan (which is Italy's second top tourist destination), Brescia
Brescia
Brescia is a city and comune in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, between the Mella and the Naviglio, with a population of around 197,000. It is the second largest city in Lombardy, after the capital, Milan...
, Mantua
Mantua
Mantua is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy and capital of the province of the same name. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family, made it one of the main artistic, cultural and notably musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole...
, Pavia
Pavia
Pavia , the ancient Ticinum, is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 35 km south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It is the capital of the province of Pavia. It has a population of c. 71,000...
, Como
Como
Como is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy.It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como....
, Cremona
Cremona
Cremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments...
, Bergamo
Bergamo
Bergamo is a town and comune in Lombardy, Italy, about 40 km northeast of Milan. The comune is home to over 120,000 inhabitants. It is served by the Orio al Serio Airport, which also serves the Province of Bergamo, and to a lesser extent the metropolitan area of Milan...
, Sondrio
Sondrio
Sondrio is an Italian town and comune located in the heart of the Valtellina. Sondrio counts approximately 22,000 inhabitants and it is the administrative centre for the Lombard Province of Sondrio.- History :...
, Lecco
Lecco
Lecco is a town of c. 47,760 inhabitants in Lombardy, northern Italy, north of Milan, the capital of the province of Lecco. It lies at the end of the south-eastern branch of Lake Como...
, Lodi, Varese
Varese
Varese is a town and comune in north-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 55 km north of Milan.It is the capital of the Province of Varese. The hinterland or urban part of the city is called Varesotto.- Geography :...
, Monza
Monza
Monza is a city and comune on the river Lambro, a tributary of the Po, in the Lombardy region of Italy some 15 km north-northeast of Milan. It is the capital of the Province of Monza and Brianza. It is best known for its Grand Prix motor racing circuit, the Autodromo Nazionale Monza.On June...
, and the lakes of Garda
Lake Garda
Lake Garda is the largest lake in Italy. It is located in Northern Italy, about half-way between Brescia and Verona, and between Venice and Milan. Glaciers formed this alpine region at the end of the last ice age...
, Como
Lake Como
Lake Como is a lake of glacial origin in Lombardy, Italy. It has an area of 146 km², making it the third largest lake in Italy, after Lake Garda and Lake Maggiore...
, Maggiore
Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. Lake Maggiore is the most westerly of the three great prealpine lakes of Italy, it extends for about 70 km between Locarno and Arona.The climate is mild...
, and Iseo
Lake Iseo
Lake Iseo or Lago d'Iseo or Sebino is the fourth largest lake in Lombardy, Italy, fed by the Oglio river.It is in the north of the country in the Val Camonica area, near the cities of Brescia and Bergamo. The lake is almost equally divided between the Provinces of Bergamo and Brescia...
.
The official language, as in the rest of Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, is Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
. The traditional local languages are the various dialects of Lombard (Western Lombard
Western Lombard
Western Lombard is a Romance language spoken in Italy, in the Lombard provinces of Milan, Monza, Varese, Como, Lecco, Sondrio, a small part of Cremona , Lodi and Pavia, and the Piedmont provinces of Novara, Verbano-Cusio-Ossola and a small part of Vercelli , and Switzerland...
and Eastern Lombard), as well as some dialects of Emilian
Emilian language
The term Emilian refers to a group of local languages, popularly also called dialects, which are part of the Gallo-Italic group, and are spoken in the historical region of Emilia...
, spoken in some parts of the provinces of Mantua
Province of Mantua
The Province of Mantua is a province in the Lombardy region of northern Italy. Its capital is the city of Mantua.-Communes:It includes 70 comuni , ranging in area from Viadana, with 102.19 km², to Mariana Mantovana, with 8.81 km²....
, Pavia
Province of Pavia
The Province of Pavia is a province in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. Pavia is the capital.It has an area of 2,965 km², and a total population of 493,753...
, and Cremona
Province of Cremona
The Province of Cremona is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Cremona.The province has an area of 1,771 km² and in 2008 census, had a population of 358,628. There are 115 comuni...
. According to Istat
ISTAT
ISTAT may refer to:* International Society of Transport Aircraft Trading, an aircraft standards organization.* Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, the Italian National Institute of Statistics....
, almost 27% of Lombards are bilingual with Lombard and Italian languages; 9.1% are monolingual in Lombard and 57.6% are monolingual in Italian.
Geography

Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
(north: Canton Ticino and Canton Graubünden) and by the Italian regions of Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
Emilia–Romagna is an administrative region of Northern Italy comprising the two historic regions of Emilia and Romagna. The capital is Bologna; it has an area of and about 4.4 million inhabitants....
(south), Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Veneto
Veneto
Veneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
(east), and Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
(west). Three distinct natural zones can be fairly easily distinguished in the Lombardy region: mountains, hills and plains - the latter being divided in Alta (high plains) and Bassa (low plains).
The most important mountainous area is an Alpine zone including the Lepontine
Lepontine Alps
The Lepontine Alps are a mountain range in the central part of the Alps. They are located in Switzerland and Italy .On the north the upper Rhône valley separate them from the Bernese Alps and the Furka Pass and the upper Reuss valley separates them from the Urner Alps; on the west the Simplon Pass...
and Rhaetian Alps
Rhaetian Alps
The Rhaetian Alps are a part of the Central Eastern Alps along the Italian–Swiss and Austrian–Swiss borders, mostly located in the Graubünden canton in eastern Switzerland.Piz Bernina , set on the Italian border, is the highest peak....
, (Piz Bernina - La Spedla, 4,020 m), the Bergamo Alps
Bergamo Alps
The Bergamo Alps are a mountain range in the Italian Alps which forms part of the Central Eastern Alps. They are located in northern Lombardy and named after the city Bergamo, south of the mountains....
, the Ortler Alps
Ortler Alps
The Ortler Alps are a mountain range in the central Alps of Italy. They are considered to be part of the Central Eastern Alps or the Southern Limestone Alps....
and the Adamello massif; it is followed by an Alpine foothills zone Prealpi, which include the main peaks are the Grigna Group (2,410 m), Resegone (1,875 m) and Presolana
Presolana
Presolana is a mountain located in Lombardy, northern Italy, about 35 km north of Bergamo. Part of the Bergamo Alps, it is included in the province of Bergamo, and divides the Val Seriana and Valle di Scalve....
(2,521 m). The great Lombard lakes, all of glacial origin lie in this zone. From west to east these are Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. Lake Maggiore is the most westerly of the three great prealpine lakes of Italy, it extends for about 70 km between Locarno and Arona.The climate is mild...
, Lake Lugano
Lake Lugano
Lake Lugano is a glacial lake in the south-east of Switzerland, at the border between Switzerland and Italy. The lake, named after the city of Lugano, is situated between Lake Como and Lago Maggiore...
(only a small part is Italian), Lake Como
Lake Como
Lake Como is a lake of glacial origin in Lombardy, Italy. It has an area of 146 km², making it the third largest lake in Italy, after Lake Garda and Lake Maggiore...
, Lake Iseo
Lake Iseo
Lake Iseo or Lago d'Iseo or Sebino is the fourth largest lake in Lombardy, Italy, fed by the Oglio river.It is in the north of the country in the Val Camonica area, near the cities of Brescia and Bergamo. The lake is almost equally divided between the Provinces of Bergamo and Brescia...
, Lake Idro
Lake Idro
Lake Idro is an Italian prealpine lake of glacial origin situated largely within the Province of Brescia and in part in Trentino.At 368 metres above sea level it is the highest of the Lombard prealpine lakes. The lake is fed principally by the waters of the river Chiese; that river is also its...
, then Lake Garda
Lake Garda
Lake Garda is the largest lake in Italy. It is located in Northern Italy, about half-way between Brescia and Verona, and between Venice and Milan. Glaciers formed this alpine region at the end of the last ice age...
, the largest in Italy. South of the Alps lie the hills characterized by a succession of low heights of morainic origin, formed during the last Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
and small barely fertile plateaux, with typical heaths and conifer woods. A minor mountainous area lies south of the Po, in the Appennines range.
The plains of Lombardy, formed from alluvial deposits, can be divided into the Alta - an upper, permeable ground zone in the north and a lower zone characterized - the Bassa - by the so-called line of fontanili (the spring waters rising on impermeable ground). Anomalous compared with the three distinctions already made is the small region of the Oltrepò Pavese
Oltrepò Pavese
The Oltrepò Pavese is the area of the Province of Pavia, in the north-west Italian region of Lombardy, which lies to the south of the river Po. Extending over an area of c...
, formed by the Apennine foothills beyond the Po River. A large number of rivers, all direct or indirect tributaries of the Po, cross the plains of Lombardy. Major rivers, flowing west to east, are the Ticino
Ticino
Canton Ticino or Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. Named after the Ticino river, it is the only canton in which Italian is the sole official language...
, the outlet of Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. Lake Maggiore is the most westerly of the three great prealpine lakes of Italy, it extends for about 70 km between Locarno and Arona.The climate is mild...
, the Olona
Olona
The Olona is a 71 km long Italian river, which runs through the provinces of Varese and Milan.The Olona has more than one source; in fact it has six main springs...
, the Lambro
Lambro
For the river in Cilento, see Lambro . For the genus, see Lambro .The Lambro is a river of Lombardy, northern Italy, a left tributary of the Po....
, the Adda
Adda River
The Adda is a river in North Italy, a tributary of the Po. It rises in the Alps near the border with Switzerland and flows through Lake Como. The Adda joins the Po a few kilometres upstream of Cremona. It is 313 kilometres long...
, outlet of Lake Como
Lake Como
Lake Como is a lake of glacial origin in Lombardy, Italy. It has an area of 146 km², making it the third largest lake in Italy, after Lake Garda and Lake Maggiore...
, the Mincio
Mincio
Mincio is a river in the Lombardy region of northern Italy.Called the Sarca River before entering Lake Garda, it flows from there about 65 km past Mantua into the Po River....
, outlet of Lake Garda
Lake Garda
Lake Garda is the largest lake in Italy. It is located in Northern Italy, about half-way between Brescia and Verona, and between Venice and Milan. Glaciers formed this alpine region at the end of the last ice age...
, and the Oglio
Oglio
The Oglio is a left-side tributary of the Po River in Lombardy, Italy. It is 280 km long....
, the Lake Iseo
Lake Iseo
Lake Iseo or Lago d'Iseo or Sebino is the fourth largest lake in Lombardy, Italy, fed by the Oglio river.It is in the north of the country in the Val Camonica area, near the cities of Brescia and Bergamo. The lake is almost equally divided between the Provinces of Bergamo and Brescia...
outflow. There is a wide network of canals for irrigation purposes. In the plains, intensively cultivated for centuries, little of the original environment remains. The rare elm
Elm
Elms are deciduous and semi-deciduous trees comprising the genus Ulmus in the plant family Ulmaceae. The dozens of species are found in temperate and tropical-montane regions of North America and Eurasia, ranging southward into Indonesia. Elms are components of many kinds of natural forests...
, alder
Alder
Alder is the common name of a genus of flowering plants belonging to the birch family . The genus comprises about 30 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, few reaching large size, distributed throughout the North Temperate Zone and in the Americas along the Andes southwards to...
, sycamore
Sycamore
Sycamore is a name which is applied at various times and places to three very different types of trees, but with somewhat similar leaf forms....
, poplar
Poplar
Populus is a genus of 25–35 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar , aspen, and cottonwood....
, willow
Willow
Willows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere...
and hornbeam
Hornbeam
Hornbeams are relatively small hardwood trees in the genus Carpinus . Though some botanists grouped them with the hazels and hop-hornbeams in a segregate family, Corylaceae, modern botanists place the hornbeams in the birch subfamily Coryloideae...
woods and heaths are covered now by several protected areas. In the area of the great Alpine foothills lakes, however, grow olive trees, cypresses and larches, as well as varieties of subtropical flora such as magnolias, azaleas, acacias, etc. The mountains area is characterized by the typical vegetation of the whole range of the Italian Alps. At a lower levels (up to approximately 1,100 m) oak woods or broadleafed trees grow; on the mountain slopes (up to 2,000–2,200 m) beech trees grow at the lowest limits, with conifer woods higher up. Shrubs such as rhododendron, dwarf pine and juniper are native to the summital zone (beyond 2,200 m).
The climate of this region is continental, though with variations depending on altitude or the presence of inland waters. The continental nature of the climate is more accentuated on the plains, with high annual temperature changes (at Milan an average January temperature is 1.5 °C (35 °F) and 24 °C (75 °F) in July), and thick fog between October and February. The Alpine foothills lakes exercise a mitigating influence, permitting the cultivation of typically Mediterranean produce (olives, citrus fruit). In the Alpine zone, the valley floor is relatively mild in contrast with the colder higher areas (Bormio, 1,225 m, -1.4 °C average in January, 17.3 °C (63 °F) in July). Precipitations are more frequent in the Prealpine zone (up to 1,500–2,000 mm annually) than on the plains and Alpine zones (600 mm to 850 mm annually). The numerous species of endemic flora (the Lombard native species), typical mainly of the Lake Como area, include some kinds of saxifrage
Saxifrage
Saxifraga is the largest genus in the family Saxifragaceae, containing about 440 species of Holarctic perennial plants, known as saxifrages. The Latin word saxifraga means literally "stone-breaker", from Latin + ...
, the Lombard garlic, groundsels bellflowers and the cottony bellflowers. Lombardy counts many protected areas: the most important are the Stelvio National Park
Stelvio National Park
Stelvio National Park is a national park in the north-east of Italy, founded in 1935.The park is the largest in Italy and covers part of two regions: Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol and Lombardia, in 24 municipalities....
(the largest Italian natural park), with typically alpine wildlife: red deer
Red Deer
The red deer is one of the largest deer species. Depending on taxonomy, the red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Asia Minor, parts of western Asia, and central Asia. It also inhabits the Atlas Mountains region between Morocco and Tunisia in northwestern Africa, being...
, roe-deer, ibex, chamois
Chamois
The chamois, Rupicapra rupicapra, is a goat-antelope species native to mountains in Europe, including the Carpathian Mountains of Romania, the European Alps, the Tatra Mountains, the Balkans, parts of Turkey, and the Caucasus. The chamois has also been introduced to the South Island of New Zealand...
, foxes, ermine
Ermine
Ermine has several uses:* A common name for the stoat * The white fur and black tail end of this animal, which is historically worn by and associated with royalty and high officials...
and also golden eagles; and the Ticino Valley Natural Park, instituted in 1974 on the Lombard side of the Ticino River
Ticino River
The river Ticino is a left-bank tributary of the Po River. It has given its name to the Swiss canton through which its upper portion flows.-The course:...
to protect and conserve one of the last major examples of fluvial forest in Northern Italy
Northern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
.
Early history

The area of current Lombardy was settled at least since the 2nd millennium BC, as shown by the archaeological findings of ceramics, arrows, axes and carved stones. In the following centuries it was inhabited by different peoples amongst whom the Etruscans
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
, who founded the city of Mantua
Mantua
Mantua is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy and capital of the province of the same name. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family, made it one of the main artistic, cultural and notably musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole...
and spread the use of writing; later, starting from the 5th century BC, the area was invaded by Celtic - Gallic
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
tribes. These people settled in several cities (including Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
) and extended their rule to the Adriatic Sea. Their development was halted by the Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
expansion in the Po Valley
Po River
The Po |Ligurian]]: Bodincus or Bodencus) is a river that flows either or – considering the length of the Maira, a right bank tributary – eastward across northern Italy, from a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face...
from the 3rd century BC onwards: after centuries of struggle, in 194 BC
194 BC
Year 194 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Africanus and Longus...
the entire area of what is now Lombardy became a Roman province with the name of Gallia Cisalpina ("Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
on the nearer side of the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
"). The Roman culture and language overwhelmed the former civilization in the following years, and Lombardy became one of the most developed and rich areas of Italy with the construction of a wide array of roads and the development of agriculture and trade. Important figures like Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
(in Como
Como
Como is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy.It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como....
) and Virgil
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro, usually called Virgil or Vergil in English , was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He is known for three major works of Latin literature, the Eclogues , the Georgics, and the epic Aeneid...
(in Mantua) were born here. In late antiquity the strategic role of Lombardy was emphasized by the temporary moving of the capital of the Western Empire
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was the western half of the Roman Empire after its division by Diocletian in 285; the other half of the Roman Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire, commonly referred to today as the Byzantine Empire....
to Mediolanum
Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient Milan, was an important Celtic and then Roman centre of northern Italy. This article charts the history of the city from its settlement by the Insubres around 600 BC, through its conquest by the Romans and its development into a key centre of Western Christianity and capital...
(Milan). Here, in 313 AD, emperor Constantine
Constantine I
Constantine the Great , also known as Constantine I or Saint Constantine, was Roman Emperor from 306 to 337. Well known for being the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity, Constantine and co-Emperor Licinius issued the Edict of Milan in 313, which proclaimed religious tolerance of all...
issued the famous edict that gave freedom of confession to all religions within the Empire.
Middle Ages

Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
, or Longobardi, who came around 570s and whose long-lasting reign (whose capital was set in Pavia
Pavia
Pavia , the ancient Ticinum, is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 35 km south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It is the capital of the province of Pavia. It has a population of c. 71,000...
) gave the current name to the region. There was a close relationship between the Frankish
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
, Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
n and Lombard nobility for many centuries. After the initial struggles, relationships between the Lombard people and the Latin-speaking people improved. In the end, the Lombard language and culture assimilated with the Latin culture, leaving evidence in many names, the legal code and laws among other things. The end of Lombard rule came in 774
774
Year 774 was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 774 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Europe :* Charlemagne conquers the kingdom of the...
, when the Frankish
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
king Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
conquered Pavia and annexed the Kingdom of Italy (mostly northern and central Italy) to his empire. The former Lombard dukes and nobles were replaced by other German vassals, prince-bishops or marquises. The 11th century marked a significant boom in the region's economy, due to improved trading and, mostly, agricultural conditions. In a similar way to other areas of Italy, this led to a growing self-acknowledgement of the cities, whose increasing richness made them able to defy the traditional feudal supreme power, represented by the German emperors and their local legates. This process reached its apex in the 12th and 13th centuries, when different Lombard League
Lombard League
The Lombard League was an alliance formed around 1167, which at its apex included most of the cities of northern Italy , including, among others, Crema, Cremona, Mantua, Piacenza, Bergamo, Brescia, Milan, Genoa, Bologna, Padua, Modena, Reggio Emilia, Treviso, Venice, Vercelli, Vicenza, Verona,...
s formed by allied cities of Lombardy, usually led by Milan, managed to defeat the Hohenstaufen
Hohenstaufen
The House of Hohenstaufen was a dynasty of German kings in the High Middle Ages, lasting from 1138 to 1254. Three of these kings were also crowned Holy Roman Emperor. In 1194 the Hohenstaufens also became Kings of Sicily...
Emperor Frederick I, at Legnano
Battle of Legnano
The Battle of Legnano was fought on May 29, 1176, between the forces of the Holy Roman Empire, led by Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, and the Lombard League.-The Lombard League:...
, and his grandson Frederick II
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II , was one of the most powerful Holy Roman Emperors of the Middle Ages and head of the House of Hohenstaufen. His political and cultural ambitions, based in Sicily and stretching through Italy to Germany, and even to Jerusalem, were enormous...
, at Parma
Battle of Parma
The Battle of Parma was fought on February 18, 1248 between the forces of Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and the Guelphs. The Guelphs attacked the Imperial camp when Frederick II was away. The Imperial forces were defeated and much of Frederick's treasure was lost.-Background:The free commune of...
.
This did not prevent other important Lombard centres, like Cremona
Cremona
Cremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments...
(then rivalling Milan for size and wealth) and others, from supporting the imperial power if this could grant them an immediate advantage. Taking advantage of the flourishing agriculture, the area around the Po River
Po River
The Po |Ligurian]]: Bodincus or Bodencus) is a river that flows either or – considering the length of the Maira, a right bank tributary – eastward across northern Italy, from a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face...
, together with Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
and Tuscany
Tuscany
Tuscany is a region in Italy. It has an area of about 23,000 square kilometres and a population of about 3.75 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence ....
, continued to expand its industry and commerce until it became the economic centre of the whole of Europe. The enterprising class of the communes extended its trade and banking activities well into northern Europe: "Lombard" designated the merchant or banker coming from northern Italy (see, for instance, Lombard Street
Lombard Street, London
Lombard Street is a street in the City of London.It runs from the corner of the Bank of England at its north-west end, where it meets a major junction including Poultry, King William Street, and Threadneedle Street, south-east to Gracechurch Street....
in London). The name "Lombardy" came to designate the whole of Northern Italy until the 15th century and sometimes later. From the 14th century onwards, the instability created by the unceasing internal and external struggles ended in the creation of noble seignories, the most significant of which were those of the Viscontis
House of Visconti
Visconti is the family name of two important Italian noble dynasties of the Middle Ages. There are two distinct Visconti families: The first one in the Republic of Pisa in the mid twelfth century who achieved prominence first in Pisa, then in Sardinia where they became rulers of Gallura...
(later Sforzas
House of Sforza
Sforza was a ruling family of Renaissance Italy, based in Milan.-History:The dynasty was founded by Muzio Attendolo , called Sforza , a condottiero from Romagna serving the Angevin kings of Naples...
) in Milan and of the Gonzagas
House of Gonzaga
The Gonzaga family ruled Mantua in Northern Italy from 1328 to 1708.-History:In 1433, Gianfrancesco I assumed the title of Marquis of Mantua, and in 1530 Federico II received the title of Duke of Mantua. In 1531, the family acquired the Duchy of Monferrato through marriage...
in Mantua. In the 15th century the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
was a major political, economical and military force at the European level. Milan and Mantua became two centres of the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
whose culture, with men like Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
and Mantegna
Andrea Mantegna
Andrea Mantegna was an Italian painter, a student of Roman archeology, and son in law of Jacopo Bellini. Like other artists of the time, Mantegna experimented with perspective, e.g., by lowering the horizon in order to create a sense of greater monumentality...
, and pieces of art were highly regarded (for example, Leonardo da Vinci's The Last Supper). This richness, however, attracted the now more organized armies of national powers like France and Austria, which waged a lengthy battle for Lombardy in the late 15th-early 16th century.
Modern era
After the decisive Battle of PaviaBattle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–26.A Spanish-Imperial army under the nominal command of Charles de Lannoy attacked the French army under the personal command of Francis I of France in the great hunting preserve...
, the Duchy of Milan became a possession of the Habsburgs of Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
: the new rulers did little to improve the economy of Lombardy, instead imposing a growing series of taxes needed to support their unending series of European wars.

Bergamo
Bergamo is a town and comune in Lombardy, Italy, about 40 km northeast of Milan. The comune is home to over 120,000 inhabitants. It is served by the Orio al Serio Airport, which also serves the Province of Bergamo, and to a lesser extent the metropolitan area of Milan...
and Brescia
Brescia
Brescia is a city and comune in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, between the Mella and the Naviglio, with a population of around 197,000. It is the second largest city in Lombardy, after the capital, Milan...
, was under the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
, which had begun to extend its influence in the area from the 14th century onwards (see also Italian Wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
). Pestilences (like that of 1628/1630, described by Alessandro Manzoni
Alessandro Manzoni
Alessandro Francesco Tommaso Manzoni was an Italian poet and novelist.He is famous for the novel The Betrothed , generally ranked among the masterpieces of world literature...
in his I Promessi Sposi) and the generally declining conditions of Italy's economy in the 17th and 18th centuries halted the further development of Lombardy. In 1706 the Austrians
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
came to power and introduced some economical and social measures which granted a certain recovery. Their rule was smashed in the late 18th century by the French armies, however, and with the formation of the Napoleonic Empire
Formation of the Napoleonic Empire
Between 1795 and 1799, the constitution governing France dictated there be an executive arm of government – the Directoire, composed of five Directors. One of these five, Emmanuel Joseph Sieyès, approached General Napoleon Bonaparte in 1799, seeking his support for a coup d'état to overthrow the...
, Lombardy became one of the semi-independent province of Napoleonic France. The restoration of Austrian rule in 1815, in the form of the puppet state called Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
The Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia was created at the Congress of Vienna, which recognised the House of Habsburg's rights to Lombardy and Venetia after the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed by Napoleon in 1805, had collapsed...
, had however to contend with new social ideals introduced by the Napoleonic era. Lombardy became one of the intellectual centres leading to Italian unification
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
. The popular republic of 1848 was short-lived, its suppression leading to renewed Austrian rule. This came to a decisive end when Lombardy was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
1859 as a result of the Second Italian Independence War. When annexed to the Kingdom of Italy in 1859 Lombardy achieved its actual territorial shape by adding the Oltrepò Pavese
Oltrepò Pavese
The Oltrepò Pavese is the area of the Province of Pavia, in the north-west Italian region of Lombardy, which lies to the south of the river Po. Extending over an area of c...
(formerly southern part of Novara
Novara
Novara is the capital city of the province of Novara in the Piedmont region in northwest Italy, to the west of Milan. With c. 105,000 inhabitants, it is the second most populous city in Piedmont after Turin. It is an important crossroads for commercial traffic along the routes from Milan to Turin...
's Province) to the province of Pavia
Pavia
Pavia , the ancient Ticinum, is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 35 km south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It is the capital of the province of Pavia. It has a population of c. 71,000...
. Starting from the late 19th century, and with a boom after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Lombardy sharpened its status of richest and most industrialized region of Italy.
Demographics
One sixth of the ItalianItaly
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
population or about 10 million people live in Lombardy (16.2% of the national population; 2% of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
population), making it the second most densely populated region in Italy after Campania
Campania
Campania is a region in southern Italy. The region has a population of around 5.8 million people, making it the second-most-populous region of Italy; its total area of 13,590 km² makes it the most densely populated region in the country...
with a strong concentration in the Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
metropolitan area and the Alpine foothills areas of the provinces of Varese
Varese
Varese is a town and comune in north-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 55 km north of Milan.It is the capital of the Province of Varese. The hinterland or urban part of the city is called Varesotto.- Geography :...
, Como
Como
Como is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy.It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como....
, Lecco
Lecco
Lecco is a town of c. 47,760 inhabitants in Lombardy, northern Italy, north of Milan, the capital of the province of Lecco. It lies at the end of the south-eastern branch of Lake Como...
, Monza and Brianza
Province of Monza e Brianza
The Province of Monza and Brianza is an administrative province of Lombardy region, Italy. It was officially created splitting the eastern part from the province of Milan on May 12, 2004, and became executive after the provincial elections of 6 and 7 June 2009....
and Bergamo
Bergamo
Bergamo is a town and comune in Lombardy, Italy, about 40 km northeast of Milan. The comune is home to over 120,000 inhabitants. It is served by the Orio al Serio Airport, which also serves the Province of Bergamo, and to a lesser extent the metropolitan area of Milan...
, (1,200 inh./km2), a lower average density (250 inh./km2) in the Po valley and the lower Brescia
Brescia
Brescia is a city and comune in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, between the Mella and the Naviglio, with a population of around 197,000. It is the second largest city in Lombardy, after the capital, Milan...
valleys, and much lower densities (less than 60 inh./km2) in the northern mountain areas and the southern Oltrepò Pavese
Oltrepò Pavese
The Oltrepò Pavese is the area of the Province of Pavia, in the north-west Italian region of Lombardy, which lies to the south of the river Po. Extending over an area of c...
subregion.
The growth of the regional population was particularly sustained during the 1950s-60s, thanks to a prolonged economic boom, high birth rates, and strong immigration flows (especially from Southern Italy). During the last two decades, Lombardy became the destination of a large number of international immigrants, insomuch that today more than a quarter of all foreign immigrants in Italy lives in this region. As of 2008, the Italian national institute of statistics ISTAT estimated that 815,335 foreign-born immigrants live in Lombardy, equal to 8.4% of the total regional population.
The primary religion is Catholicism
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
; significative religious minorities include Christian Waldenses, Protestants and Orthodox
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises the Christian traditions and churches that developed in the Balkans, Eastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Middle East, Northeastern Africa, India and parts of the Far East over several centuries of religious antiquity. The term is generally used in Western Christianity to...
, as well as Jews
Judaism
Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people...
, Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
and Muslims
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
.
Economy
The gross domestic product in Lombardia (equal to over €328 billion in 2008) accounts for 20% of the total gross domestic product of Italy. When this measure is considered by inhabitant, it results in a value of €31,600 per inhabitant, which is almost 25% higher than the national average of €24,300.Lombardy's development has been marked by the growth of the services sector since the 1980s, and in particular by the growth of innovative activities in the sector of services to enterprises and in credit and financial services. At the same time, the strong industrial vocation of the region has not suffered from it. Lombardy remains, in fact, the main industrial area of the country. The presence, and development, of a very high number of enterprises belonging to the services sector represents a favourable situation for the improvement of the efficiency of the productive process, as well as for the growth of the regional economy. Lombardy is one of the Four Motors for Europe.
The region can broadly be divided into three areas as regards the productive activity. Milan, where the services sector makes up for 65.3% of the employment; a group of provinces, Varese, Como, Lecco, Bergamo and Brescia, highly industrialised, although in the two latter ones, in the plains, there is also a rich agricultural sector. Finally, in the provinces of Sondrio, Pavia, Cremona, Mantova and Lodi, there is a consistent agricultural activity, and at the same time an above average development of the services sector. The productivity of agriculture is enhanced by a well-developed use of fertilizers and the traditional abundance of water, boosted since the Middle Ages by the construction (partly designed by Leonardo da Vinci) of a wide net of irrigation systems. Lower plains are characterized by fodder crops, which are mowed up to eight times a years, cereals (rice, wheat and maize) and sugarbeet. Productions of the higher plains include cereals, vegetables, fruit trees and mulberries. The higher areas, up to the Prealps and Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
sectors of the north, produce fruit and vines. Cattle (with the highest density in Italy), pigs and sheep are raised.
Following a steep decline in GDP during the global recession in 2009 which saw industry heavily hit, Lombardy's economy is predicted to outperform the Italian economy this year with growth of between 1-1.3% expected. Only Emilia Romagna, Lazio and Tuscany are expected to outperform the region in 2010. The revival of the industrial sector is an important factor, but it is the service sector - and especially the financial sector which will drive the Lombard economy to a sustainable recovery.
Government and politics
The politics of Lombardy take place in a framework of a presidentialPresidential system
A presidential system is a system of government where an executive branch exists and presides separately from the legislature, to which it is not responsible and which cannot, in normal circumstances, dismiss it....
representative democracy
Representative democracy
Representative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
, whereby the President of the Region (Presidente della Regione) is the head of government
Head of government
Head of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
, and of a pluriform multi-party system
Multi-party system
A multi-party system is a system in which multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government separately or in coalition, e.g.The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition in the United Kingdom formed in 2010. The effective number of parties in a multi-party system is normally...
. Executive power
Executive Power
Executive Power is Vince Flynn's fifth novel, and the fourth to feature Mitch Rapp, an American agent that works for the CIA as an operative for a covert counter terrorism unit called the "Orion Team."-Plot summary:...
is exercised by the Regional Government (Giunta Regionale). Legislative power is vested in the Regional Council
Regional Council of Lombardy
The Regional Council of Lombardy is the legislative assembly of Lombardy.It was first elected in 1970, when the ordinary regions were instituted, on the basis of the Constitution of Italy of 1948.-Composition:...
(Consiglio Regionale).
The Christian Democrats
Christian Democracy (Italy)
Christian Democracy was a Christian democratic party in Italy. It was founded in 1943 as the ideological successor of the historical Italian People's Party, which had the same symbol, a crossed shield ....
maintained a large majority of the popular support and the control of the most important cities and provinces since the birth of the Italian Republic until the late 1980s. The Italian Communist Party
Italian Communist Party
The Italian Communist Party was a communist political party in Italy.The PCI was founded as Communist Party of Italy on 21 January 1921 in Livorno, by seceding from the Italian Socialist Party . Amadeo Bordiga and Antonio Gramsci led the split. Outlawed during the Fascist regime, the party played...
was a considerable presence only in the eastern and southern parts of Lombardy from the late 1960s to the mid 1980's. Their base however was increasingly eroded by the Italian Socialist Party
Italian Socialist Party
The Italian Socialist Party was a socialist and later social-democratic political party in Italy founded in Genoa in 1892.Once the dominant leftist party in Italy, it was eclipsed in status by the Italian Communist Party following World War II...
until, in the early 1990s, the Mani Pulite
Mani pulite
Mani pulite was a nationwide Italian judicial investigation into political corruption held in the 1990s. Mani pulite led to the demise of the so-called First Republic, resulting in the disappearance of many parties. Some politicians and industry leaders committed suicide after their crimes were...
corruption scandal which spread from Milan to the whole of Italy wiped away the old political class almost entirely. This, together with the general disaffection towards Rome's government (considered as favouring excessively the less developed regions of southern Italy in economical matters), led to the sudden growth of the secessionist (later Northern League), that is particularly strong in mountain and rural areas. In recent years, Lombardy stayed as a conservative stronghold, that gave about 60 per cent of its votes to Silvio Berlusconi
Silvio Berlusconi
Silvio Berlusconi , also known as Il Cavaliere – from knighthood to the Order of Merit for Labour which he received in 1977 – is an Italian politician and businessman who served three terms as Prime Minister of Italy, from 1994 to 1995, 2001 to 2006, and 2008 to 2011. Berlusconi is also the...
at the last general election
Italian general election, 2008
A snap general election was held in Italy on 13 April and 14 April 2008. The election came after President Giorgio Napolitano dissolved parliament on 6 February 2008 following the defeat of the government of Prime Minister Romano Prodi in a January 2008 Senate vote, and the unsuccessful tentative...
. Notwithstanding, the capital city of Milan landslide elected a new progressive mayor
Giuliano Pisapia
Giuliano Pisapia is an Italian lawyer and politician, twice member of the Parliament and Mayor of Milan since 1 June 2011...
at the 2011 municipal elections.
Culture
Although Lombardy as a region is often identified as merely an economic and industrial powerhouse, it has interesting examples http://www.lombardiadautore.regione.lombardia.it even from the standpoint of cultural and artistic. The many examples range from prehistoryPrehistory
Prehistory is the span of time before recorded history. Prehistory can refer to the period of human existence before the availability of those written records with which recorded history begins. More broadly, it refers to all the time preceding human existence and the invention of writing...
to the present day, through the Roman period and the Renaissance and can be found both in museums and churches that enrich cities and towns around the region.
Prehistory
The rock carvings (some 300,000) left by the ancient Camuni in the Valcamonica depicting animals, people and symbols date back to the period from NeolithicNeolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
to Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
.
The many artifacts (pottery, personal items and weapons) found in the necropolis near the Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. Lake Maggiore is the most westerly of the three great prealpine lakes of Italy, it extends for about 70 km between Locarno and Arona.The climate is mild...
, and Ticino
Ticino
Canton Ticino or Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. Named after the Ticino river, it is the only canton in which Italian is the sole official language...
demonstrate the presence of civilization Golasecca who lived in Western Lombardy between the ninth and the fourth century BC.
Museums
Lombardy contains numerous museums (over 330) of different types: ethnographic, historical, technical-scientific, artistic and naturalistic which testify to the historical-cultural and artistic development of the region. Among the most famous are the National Museum of Science and Technology "Leonardo da Vinci" (Milan), the The Last Supper of Leonardo da VinciLeonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
(Milan), the Accademia Carrara
Accademia Carrara
The Accademia Carrara is an art gallery and an academy of fine arts in Bergamo, Italy.-History:The origins of the art gallery lie with the Count Giacomo Carrara, a wealthy collector and patron of the arts, who left a generous legacy to the city of Bergamo at the end of the 18th century.After the...
(Bergamo), the Museum of Santa Giulia (Brescia), the Volta Temple (Como), the Stradivari Museum (Cremona), the Palazzo Te (Mantua), the Museum Sacred Art of the Nativity and the basilica of Santa Maria Assunta at Gandino
Gandino
Gandino is a comune in the Province of Bergamo in the Italian region of Lombardy, located about 70 km northeast of Milan and about 20 km northeast of Bergamo...
, the Royal Villa of Monza and many others.
Main sights
- Cathedral of Milan
- Castello SforzescoCastello SforzescoCastello Sforzesco is a castle in Milan, Italy, that used to be the seat and residence of the Duchy of Milan and one of the biggest citadels in Europe and now houses several of the city's museums and art collections.-History:...
- Basilica di Sant'Ambrogio
- Convent of Sta. Maria delle Grazie
- The Last Supper
- Teatro alla Scala
- Basilica of San Lorenzo
- Basilica of Sant'EustorgioBasilica of Sant'EustorgioThe Basilica of Sant'Eustorgio is a church in Milan, northern Italy. It was for many years an important centre for pilgrims on their journey to Rome or to the Holy Land, because it was the site of the tomb of the Three Magi or Three Kings....
- Portinari ChapelPortinari ChapelThe Portinari Chapel is a Renaissance chapel at the Basilica of Sant'Eustorgio, Milan, northern Italy. Commenced in 1460 and completed in 1468, it was commissioned by Pigello Portinari as a private sepulchre and to house a silver shrine given by Archbishop Giovanni Visconti in 1340 containing the...
- Brera Gallery
- Certosa di PaviaCertosa di PaviaThe Certosa di Pavia Gra-Car , Shrine of the Blessed Virgin Mary Mother of Grace, is a monastery and complex in Lombardy, northern Italy, situated near a small town of the same name in the Province of Pavia, 8 km north of Pavia...
- Petroglyphs of Valcamonica
- BellagioBellagioBellagio is a comune in the Province of Como in the Italian region Lombardy, located on Lake Como. It has long been famous for its setting at the intersection of the three branches of the Y-shaped lake, which is also known as Lario....
- Lake of Como
- Lake of Garda
- Industrial village of Crespi d'AddaCrespi d'AddaCrespi d'Adda is a historical settlement in Capriate San Gervasio, Lombardy, northern Italy. It is an outstanding example of the 19th and early 20th-century "company towns" built in Europe and North America by enlightened industrialists to meet the workers' needs...
- Duomo and TorrazzoTorrazzo of CremonaThe Torrazzo of Cremona is the bell tower of the Cathedral of Cremona. At 112.7 metres , it is the third tallest brickwork bell tower in the world, the first being the tower of St. Martin's Church in Landshut, Bavaria, the second being that of the Church of Our Lady in Bruges, Belgium...
in CremonaCremonaCremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments... - Royal Villa of Monza
- Tempio Civico della Beata Vergine IncoronataTempio Civico della Beata Vergine IncoronataThe Tempio Civico della Beata Vergine Incoronata is a church in Lodi, Lombardy, Italy. It is considered one of the masterworks of the Lombard Renaissance art...
in Lodi - Palazzo Te, Castello di San Giorgio, Basilica di Sant'AndreaBasilica di Sant'Andrea di MantovaThe Basilica concattedrale di Sant'Andrea is a Renaissance roman catholic church and minor basilica in Mantua, Lombardy .Commissioned by Ludovico II Gonzaga, the church was begun in 1462 according to designs by Leon Battista Alberti on a site occupied by a Benedictine monastery, of which the bell...
and CathedralCathedralA cathedral is a Christian church that contains the seat of a bishop...
in MantuaMantuaMantua is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy and capital of the province of the same name. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family, made it one of the main artistic, cultural and notably musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole...
Cuisine
RiceRice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
is popular in the region, often found in soups as well as risotti, such as "risotto alla Milanese", with saffron
Saffron
Saffron is a spice derived from the flower of Crocus sativus, commonly known as the saffron crocus. Crocus is a genus in the family Iridaceae. Each saffron crocus grows to and bears up to four flowers, each with three vivid crimson stigmas, which are each the distal end of a carpel...
. In the city of Monza
Monza
Monza is a city and comune on the river Lambro, a tributary of the Po, in the Lombardy region of Italy some 15 km north-northeast of Milan. It is the capital of the Province of Monza and Brianza. It is best known for its Grand Prix motor racing circuit, the Autodromo Nazionale Monza.On June...
a popular recipe also adds pieces of sausages to the risotto. Regional cheeses include robiola
Robiola
Robiola is an Italian soft-ripened cheese of the Stracchino family, made with varying proportions of cow’s, goat’s milk and sheep milk. One theory is that the cheese gets its name from the town of Robbio in the province of Pavia; another that the name comes from the word rubeole because of the...
, crescenza, taleggio, gorgonzola
Gorgonzola (cheese)
Gorgonzola is a veined Italian blue cheese, made from unskimmed cow's and/or goat's milk. It can be buttery or firm, crumbly and quite salty, with a "bite" from its blue veining.- History :...
and grana padano (the plains of central and southern Lombardy allow intensive cattle-raising). Butter
Butter
Butter is a dairy product made by churning fresh or fermented cream or milk. It is generally used as a spread and a condiment, as well as in cooking applications, such as baking, sauce making, and pan frying...
and cream
Cream
Cream is a dairy product that is composed of the higher-butterfat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, over time, the lighter fat rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream this process is accelerated by using centrifuges called "separators"...
are used. Single pot dishes, which take less work to prepare, are popular. In Bergamo
Bergamo
Bergamo is a town and comune in Lombardy, Italy, about 40 km northeast of Milan. The comune is home to over 120,000 inhabitants. It is served by the Orio al Serio Airport, which also serves the Province of Bergamo, and to a lesser extent the metropolitan area of Milan...
, Brescia
Brescia
Brescia is a city and comune in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, between the Mella and the Naviglio, with a population of around 197,000. It is the second largest city in Lombardy, after the capital, Milan...
, and Valtellina
Valtellina
Valtellina or the Valtelline valley ; is a valley in the Lombardy region of northern Italy, bordering Switzerland. Today it is known for its skiing, its hot spring spas, its cheeses and its wines...
, polenta
Polenta
Polenta is a dish made from boiled cornmeal. The word "polenta" is borrowed from Italian.-Description:Polenta is made with ground yellow or white cornmeal , which can be ground coarsely or finely depending on the region and the texture desired.As it is known today, polenta derives from earlier...
is common. In Valtellina, Pizzoccheri
Pizzoccheri
Pizzoccheri are a type of short tagliatelle, a flat ribbon pasta, made with 80% buckwheat flour and 20% wheat flour. When classically prepared in Valtellina or in Graubünden, they are cooked along with greens , and cubed potatoes...
too. In Mantua
Mantua
Mantua is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy and capital of the province of the same name. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family, made it one of the main artistic, cultural and notably musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole...
festivals feature tortelli di zucca (ravioli
Ravioli
Ravioli are a traditional type of Italian filled pasta. They are composed of a filling sealed between two layers of thin egg pasta dough and are served either in broth or with a pasta sauce. The word ravioli is reminiscent of the Italian verb riavvolgere , though the two words are not...
with pumpkin
Pumpkin
A pumpkin is a gourd-like squash of the genus Cucurbita and the family Cucurbitaceae . It commonly refers to cultivars of any one of the species Cucurbita pepo, Cucurbita mixta, Cucurbita maxima, and Cucurbita moschata, and is native to North America...
filling) accompanied by melted butter and followed by turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
stuffed with chicken
Chicken
The chicken is a domesticated fowl, a subspecies of the Red Junglefowl. As one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, and with a population of more than 24 billion in 2003, there are more chickens in the world than any other species of bird...
or other stewed meat
Meat
Meat is animal flesh that is used as food. Most often, this means the skeletal muscle and associated fat and other tissues, but it may also describe other edible tissues such as organs and offal...
s.
Typical Dishes
- PolentaPolentaPolenta is a dish made from boiled cornmeal. The word "polenta" is borrowed from Italian.-Description:Polenta is made with ground yellow or white cornmeal , which can be ground coarsely or finely depending on the region and the texture desired.As it is known today, polenta derives from earlier...
(Asino e Polenta, Polenta e Osei, Vunscia Polenta, Polenta e Gorgonzola) - PizzoccheriPizzoccheriPizzoccheri are a type of short tagliatelle, a flat ribbon pasta, made with 80% buckwheat flour and 20% wheat flour. When classically prepared in Valtellina or in Graubünden, they are cooked along with greens , and cubed potatoes...
(short tagliatelle made out of buckwheat flour and wheat, laced with butter, green vegetables, garlic, sage, potatoes and onions, all topped with Casera cheese) - Quartirolo lombardo
- RisottoRisottoRisotto is a class of Italian dishes of rice cooked in broth to a creamy consistency. The broth may be meat-, fish-, or vegetable-based; many kinds include Parmesan cheese, butter, and onion...
(alla Milanese) - Osso bucoOsso bucoOssobuco is a Milanese specialty of cross-cut veal shanks braised with vegetables, white wine and broth. It is often garnished with gremolata and traditionally served with risotto alla milanese....
- CotolettaCotolettaCotoletta is an Italian word for a breaded veal cutlet....
(Cutlet) ("alla Milanese") - CassoeulaCassoeulaThe Cassoeula , in Milan, sometimes Italianized Cazzuola or bottaggio is a typical winter dish popular in Northern Italy, mostly in Lombardy...
- GorgonzolaGorgonzolaGorgonzola is a comune in the province of Milan, part of Lombardy, northern Italy. Once a rural community, and famous for the cheese which bears its name, today it forms part of the Milanese conurbation and has three stops on the Milan Metro.- History :...
cheese - BittoBitto-Plot:This story revovles around a innocent girl with a life full of hardships....
cheese - Grana Padano cheese
- PanettonePanettonethumb|200px|right|A non-traditionally shaped panettone loaf.Panettone is a type of sweet bread loaf originally from Milan , usually prepared and enjoyed for Christmas and New Year in Italy, Malta, Brazil, Germany and Switzerland, and is one of the symbols of the city of Milan. Maltese nationals are...
- Lo Spiedo Bresciano - a traditional spit roast consisting of different cuts of meat, butter and sage
- Tortelli di Zucca (Pumpkins filled pasta)
- Sbrisolona cake
Wines
- Nebbiolo red
- Bellavista
- Santi
- Nino Negri
- Bonarda Lombardy
- Inferno (Valtellina)
- Grumello (Valtellina)
- Sassella (Valtellina)
Music
Besides Milan, the region of Lombardy has 11 other provinces, most of them with equally great musical traditions. Bergamo is famous for being the birthplace of Gaetano DonizettiGaetano Donizetti
Domenico Gaetano Maria Donizetti was an Italian composer from Bergamo, Lombardy. His best-known works are the operas L'elisir d'amore , Lucia di Lammermoor , and Don Pasquale , all in Italian, and the French operas La favorite and La fille du régiment...
and home of the Teatro Donizetti; Brescia is hosts the impressive 1709 Teatro Grande; Cremona is regarded as the birthplace of the commonly used violin
Violin
The violin is a string instrument, usually with four strings tuned in perfect fifths. It is the smallest, highest-pitched member of the violin family of string instruments, which includes the viola and cello....
, and is home to several of the most prestigious luthier
Luthier
A luthier is someone who makes or repairs lutes and other string instruments. In the United States, the term is used interchangeably with a term for the specialty of each maker, such as violinmaker, guitar maker, lute maker, etc...
s in the world, and Mantua was one of the founding and most important cities in 16th and 17th opera and classical music. Other cities such as Lecco, Lodi, Varese and Pavia also have rich musical traditions, but Milan is the hub and centre of the Lombard musical scene. It was the birthplace of Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi was an Italian Romantic composer, mainly of opera. He was one of the most influential composers of the 19th century...
, one of the most famous and influential opera composers of the 19th century, and boasts a variety of acclaimed theatres, such as the Piccolo Teatro and the Teatro Arcimboldi; however, the most famous is the 1778 Teatro alla Scala, one of the most important and prestigious operahouses in the world.
Language
Apart from standardized ItalianItalian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, Lombard is the local language of Lombardy. Lombard is a member of the Gallo-Italic group within the Romance languages
Romance languages
The Romance languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family, more precisely of the Italic languages subfamily, comprising all the languages that descend from Vulgar Latin, the language of ancient Rome...
. It is spoken natively in Northern Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(most of Lombardy and some areas of neighbouring regions, notably the eastern side of Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
) and Southern Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
(Ticino
Ticino
Canton Ticino or Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. Named after the Ticino river, it is the only canton in which Italian is the sole official language...
and Graubünden
Graubünden
Graubünden or Grisons is the largest and easternmost canton of Switzerland. The canton shares borders with the cantons of Ticino, Uri, Glarus and St. Gallen and international borders with Italy, Austria and Liechtenstein...
).
The two main varieties (Western Lombard language and Eastern Lombard language
Eastern Lombard language
Eastern Lombard is a group of related languages, spoken in the eastern side of Lombardy, mainly in the provinces of Bergamo, Brescia and Mantua, in the area around Crema and in a part of Trentino . Its main variants are Bergamasque and Brescian ....
) show differences and are often, but not always, mutually comprehensible. The union of Western Lombard or Insubric
Western Lombard
Western Lombard is a Romance language spoken in Italy, in the Lombard provinces of Milan, Monza, Varese, Como, Lecco, Sondrio, a small part of Cremona , Lodi and Pavia, and the Piedmont provinces of Novara, Verbano-Cusio-Ossola and a small part of Vercelli , and Switzerland...
, Eastern Lombard and intermediate varieties under the denomination of "Lombard" is a matter of debate, and it has been argued that the two might potentially form separate languages.
Fashion
Lombardy has always been an important centre for silk and textile production, notably the cities of PaviaPavia
Pavia , the ancient Ticinum, is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 35 km south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It is the capital of the province of Pavia. It has a population of c. 71,000...
, Vigevano
Vigevano
Vigevano is a town and comune in the province of Pavia, Lombardy, northern Italy, which possesses many artistic treasures and runs a huge industrial business. It is at the center of a district called Lomellina, a great rice-growing agricultural centre...
and Cremona
Cremona
Cremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments...
, but Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
is the region's most important centre for clothing and high fashion. In 2009, Milan was regarded as the world fashion capital
Fashion capital
A Fashion City or Fashion Capital is a city where the fashion industry has a relevant and important position for the local economy. Production and exporting of fashion goods, as well as fashion events like fashion weeks, trade fairs and awards, boosts its economy and raises its annual revenue,...
, even surpassing New York
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
, Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
and London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. Most of the major Italian fashion
Italian fashion
Italy is one of the leading countries in fashion design, alongside others such as France, USA, Great Britain and Japan. Fashion has always been an important part of the country's cultural life and society, and Italians are well known for their attention to dressing-up well; "la bella figura", or...
brands, such as Valentino
Valentino SpA
Valentino SpA is a clothing company founded in 1959 by Valentino Garavani. Nowadays it is a part of Valentino Fashion Group. New creative directors Maria Grazia Chiuri and Pier Paolo Piccioli will take Alessandra Facchinetti's seat as creative designer...
, Versace
Versace
Gianni Versace S.p.A. , usually referred to as Versace, is an Italian fashion label founded by Gianni Versace in 1978.The first Versace boutique was opened in Milan's Via della Spiga in 1978, and its popularity was immediate. Today, Versace is one of the world's leading international fashion houses...
, Prada
Prada
Prada S.p.A. is an Italian fashion label specializing in luxury goods for men and women , founded by Mario Prada.-Foundations:...
, Armani and Dolce & Gabbana
Dolce & Gabbana
Dolce & Gabbana is an Italian luxury industry fashion house. The company was started by the Italian designers Domenico Dolce and Stefano Gabbana in Milan, Italy. By 2005 their turnover was €597 million....
(to name a few), are currently headquartered in the city.
Administrative divisions
Lombardy is divided into 12 provinces:
| Province |
Area (km²) |
Population |
Density (inh./km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Province of Bergamo Province of Bergamo The Province of Bergamo is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. It has a population of 1,098,740 , an area of 2,722.86 square km, and contains 244 comuni... |
2,723 | 1,070,060 | 392.9 |
| Province of Brescia Province of Brescia The Province of Brescia is a Province in Lombardy, Italy. It borders with the province of Sondrio in the N and NW, the province of Bergamo in the W, province of Cremona in the SW and S, the province of Mantova to the S, and to the east, the province of Verona and Trentino .Source for statistical... |
4,784 the biggest | 1,223,900 | 255.8 |
| Province of Como Province of Como The Province of Como is a province in the north of the Lombardy region of Italy and borders the Swiss cantons of Ticino and Grigioni to the North, the Italian provinces of Sondrio and Lecco to the East, the Province of Milan to the south and the Province of Varese to the West... |
1,288 | 582,736 | 452.4 |
| Province of Cremona Province of Cremona The Province of Cremona is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Cremona.The province has an area of 1,771 km² and in 2008 census, had a population of 358,628. There are 115 comuni... |
1,772 | 358,628 | 202.4 |
| Province of Lecco Province of Lecco The Province of Lecco is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Lecco.On 1 January 2001 the province had a population of 311,452 on a surface of 816 km² divided in 90 communes... |
816 | 334,059 | 409.4 |
| Province of Lodi Province of Lodi The Province of Lodi is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Lodi.It has an area of 782 km², and a total population of 209,874 . There are 61 comuni in the province . As of May 31, 2005, the main comuni by population are:- External links :... |
782 | 222,223 | 284.2 |
| Province of Mantova | 2,339 | 407,983 | 174.4 |
| Province of Milan Province of Milan The Province of Milan : /) is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Milan. The provincial territory is highly urbanized, resulting in the third highest population density among the Italian provinces with more than 2,000 inhabitants/km2, just behind the provinces of... |
1,575 | 3,121,832 the biggest | 1,982 |
| Province of Monza and Brianza | 405 the smallest | 840,711 | 2,075 |
| Province of Pavia Province of Pavia The Province of Pavia is a province in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. Pavia is the capital.It has an area of 2,965 km², and a total population of 493,753... |
2,965 | 535,948 | 180.7 |
| Province of Sondrio Province of Sondrio The Province of Sondrio is in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the town of Sondrio.It has an area of 3,212 km², and a total population of 176,856... |
3,212 | 181,841 the smallest | 56.6 |
| Province of Varese Province of Varese The Province of Varese is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Varese but its largest city is Busto Arsizio.... |
1,199 | 868,777 | 724.6 |
UNESCO World Heritage Sites
- Church and DominicanDominican OrderThe Order of Preachers , after the 15th century more commonly known as the Dominican Order or Dominicans, is a Catholic religious order founded by Saint Dominic and approved by Pope Honorius III on 22 December 1216 in France...
ConventConventA convent is either a community of priests, religious brothers, religious sisters, or nuns, or the building used by the community, particularly in the Roman Catholic Church and in the Anglican Communion...
of Santa Maria delle GrazieSanta Maria delle Grazie (Milan)Santa Maria delle Grazie is a church and Dominican convent in Milan, northern Italy, included in the UNESCO World Heritage sites list...
with "The Last Supper" by Leonardo da VinciLeonardo da VinciLeonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance... - Crespi d'AddaCrespi d'AddaCrespi d'Adda is a historical settlement in Capriate San Gervasio, Lombardy, northern Italy. It is an outstanding example of the 19th and early 20th-century "company towns" built in Europe and North America by enlightened industrialists to meet the workers' needs...
- Rock Drawings in ValcamonicaRock Drawings in ValcamonicaThe stone carvings of Val Camonica constitute one of the largest collections of prehistoric petroglyphs in the world. The collection was recognized by Unesco in 1979 and was Italy's first recognized World Heritage Site...
- Sacri Monti of Piedmont and Lombardy
- Mantua and SabbionetaMantuaMantua is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy and capital of the province of the same name. Mantua's historic power and influence under the Gonzaga family, made it one of the main artistic, cultural and notably musical hubs of Northern Italy and the country as a whole...

