Low-barrier hydrogen bond
Encyclopedia
A Low-barrier hydrogen bond or LBHB is a special type of hydrogen bond
. This type of bond is especially strong because the distance between acceptor and donor is especially short. In regular hydrogen bonds (for example the O···O distance is at least 2.8 Ångström
) the hydrogen ion
clearly belongs to one of the heteroatom
s. When the distance decreases to about 2.55 Å the proton is free to move between the two atoms (hence the low-barrier) and the LBHB forms. When the distance decreases even further (< 2.29 Å) the bond is characterized as a short-strong hydrogen bond or SSHB.
Low-barrier hydrogen bonds are especially relevant to enzyme catalysis
because when they form in an transition state
they can significantly accelerate otherwise difficult reactions.
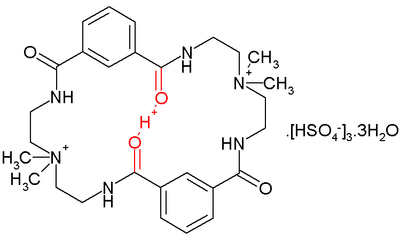
A low-barrier hydrogen bond was found inside a certain aza crown-type compound depicted below:
In this compound a proton sits comfortably between two amide
carbonyl oxygens separated by a distance of 2.45 Å. It would not be expected there because the macrocyclic ring already has two positively charged quaternary ammonium units.
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
. This type of bond is especially strong because the distance between acceptor and donor is especially short. In regular hydrogen bonds (for example the O···O distance is at least 2.8 Ångström
Ångström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
) the hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
clearly belongs to one of the heteroatom
Heteroatom
In organic chemistry, a heteroatom is any atom that is not carbon or hydrogen. Usually, the term is used to indicate that non-carbon atoms have replaced carbon in the backbone of the molecular structure...
s. When the distance decreases to about 2.55 Å the proton is free to move between the two atoms (hence the low-barrier) and the LBHB forms. When the distance decreases even further (< 2.29 Å) the bond is characterized as a short-strong hydrogen bond or SSHB.
Low-barrier hydrogen bonds are especially relevant to enzyme catalysis
Enzyme catalysis
Enzyme catalysis is the catalysis of chemical reactions by specialized proteins known as enzymes. Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital due to the very low reaction rates of the uncatalysed reactions....
because when they form in an transition state
Transition state
The transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest energy along this reaction coordinate. At this point, assuming a perfectly irreversible reaction, colliding reactant molecules will always...
they can significantly accelerate otherwise difficult reactions.
A low-barrier hydrogen bond was found inside a certain aza crown-type compound depicted below:
In this compound a proton sits comfortably between two amide
Amide
In chemistry, an amide is an organic compound that contains the functional group consisting of a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom . The term refers both to a class of compounds and a functional group within those compounds. The term amide also refers to deprotonated form of ammonia or an...
carbonyl oxygens separated by a distance of 2.45 Å. It would not be expected there because the macrocyclic ring already has two positively charged quaternary ammonium units.