.gif)
Lumen (anatomy)
Encyclopedia
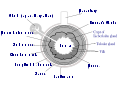
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
.
Examples of lumina
- The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an arteryArteryArteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
or veinVeinIn the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
through which bloodBloodBlood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
flows. - The interior of the gastrointestinal tractGastrointestinal tractThe human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
- The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs
- The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ductsCollecting duct systemThe collecting duct system of the kidney consists of a series of tubules and ducts that connect the nephrons to the ureter. It participates in electrolyte and fluid balance through reabsorption and excretion, processes regulated by the hormones aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone.There are several...
- The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vaginaVaginaThe vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
, splitting up in two lumina in the uterusUterusThe uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
, both which continue through the fallopian tubeFallopian tubeThe Fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges are two very fine tubes lined with ciliated epithelia, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the utero-tubal junction...
s - Within a cell, the inner membraneInner membraneThe inner membrane is the biological membrane of an organelle or Gram-negative bacteria that is within an outer membrane....
space of a thylakoidThylakoidA thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as...
, endoplasmic reticulumEndoplasmic reticulumThe endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
, Golgi apparatusGolgi apparatusThe Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi, after whom the Golgi apparatus is named....
, lysosomes, mitochondria or microtubuleMicrotubuleMicrotubules are a component of the cytoskeleton. These rope-like polymers of tubulin can grow as long as 25 micrometers and are highly dynamic. The outer diameter of microtubule is about 25 nm. Microtubules are important for maintaining cell structure, providing platforms for intracellular...
.
Transluminal procedures
Transluminal procedures are procedures occurring through lumina, including:- Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for example the stomachStomachThe stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
, vaginaVaginaThe vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
, bladderBladderBladder usually refers to an anatomical hollow organBladder may also refer to:-Biology:* Urinary bladder in humans** Urinary bladder ** Bladder control; see Urinary incontinence** Artificial urinary bladder, in humans...
or colonColon (anatomy)The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a... - Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in the lumina of blood vesselBlood vesselThe blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s

