
Luminance (video)
Encyclopedia
Relative luminance follows the photometric definition of luminance
, but with the values normalized to 1 or 100 for a reference white. Like the photometric definition, it is related to the luminous flux density in a particular direction, which is radiant flux density weighted by the luminosity function
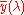 of the CIE Standard Observer.
of the CIE Standard Observer.
The use of relative values is useful in systems where absolute reproduction is impractical. For example, in prepress for print media, the absolute luminance of light reflecting off the print depends on the illumination and therefore absolute reproduction cannot be assured.
s such as XYZ
, xyY, etc. the letter Y refers to relative luminance. No computation is required to find relative luminance when it is explicit in a color representation in such spaces.
For RGB color spaces that use the ITU-R BT.709
primaries (or sRGB, which defines the same primaries), relative luminance can be calculated from linear RGB components:
The formula reflects the luminosity function
: green light contributes the most to the intensity perceived by humans, and blue light the least.
For other sets of primary chromaticities (defined by their x and y chromaticity coordinates), different linear coefficients are needed to get relative luminance. In general, the coefficients are all positive, the green coefficient is largest and blue smallest, and the three form the middle row of the RGB-to-XYZ color transformation matrix.
For nonlinear gamma-compressed R'G'B' spaces as typically used for computer images, a linearization of the R'G'B' components to RGB is needed before the linear combination.
For L*a*b* space, the L* component is the lightness
; a perceptual scale of the brightness as a nonlinear function of the relative luminance Y.
Note that (relative) luminance should not be confused with luma
, the weighted sum of the nonlinear gamma compressed
R'G'B' components. For color spaces that use luma, such as Y'UV or Y'CbCr (where Y' represents luma), computation of relative luminance can still be done. The R'G'B' components can be transformed into linear light components by undoing the gamma compression; these linear primary components can then be used to calculate luminance.
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
, but with the values normalized to 1 or 100 for a reference white. Like the photometric definition, it is related to the luminous flux density in a particular direction, which is radiant flux density weighted by the luminosity function
Luminosity function
The luminosity function or luminous efficiency function describes the average visual sensitivity of the human eye to light of different wavelengths. It should not be considered perfectly accurate in every case, but it is a very good representation of visual sensitivity of the human eye and it is...
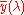 of the CIE Standard Observer.
of the CIE Standard Observer.The use of relative values is useful in systems where absolute reproduction is impractical. For example, in prepress for print media, the absolute luminance of light reflecting off the print depends on the illumination and therefore absolute reproduction cannot be assured.
Relative luminance in colorimetric spaces
For color spaceColor space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
s such as XYZ
CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
, xyY, etc. the letter Y refers to relative luminance. No computation is required to find relative luminance when it is explicit in a color representation in such spaces.
For RGB color spaces that use the ITU-R BT.709
Rec. 709
ITU-R Recommendation BT.709, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 709 or BT.709, standardizes the format of high-definition television, having 16:9 aspect ratio. The first edition of the standard was approved in 1990....
primaries (or sRGB, which defines the same primaries), relative luminance can be calculated from linear RGB components:
- Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B
The formula reflects the luminosity function
Luminosity function
The luminosity function or luminous efficiency function describes the average visual sensitivity of the human eye to light of different wavelengths. It should not be considered perfectly accurate in every case, but it is a very good representation of visual sensitivity of the human eye and it is...
: green light contributes the most to the intensity perceived by humans, and blue light the least.
For other sets of primary chromaticities (defined by their x and y chromaticity coordinates), different linear coefficients are needed to get relative luminance. In general, the coefficients are all positive, the green coefficient is largest and blue smallest, and the three form the middle row of the RGB-to-XYZ color transformation matrix.
For nonlinear gamma-compressed R'G'B' spaces as typically used for computer images, a linearization of the R'G'B' components to RGB is needed before the linear combination.
For L*a*b* space, the L* component is the lightness
Lightness (color)
Lightness is a property of a color, or a dimension of a color space, that is defined in a way to reflect the subjective brightness perception of a color for humans along a lightness–darkness axis. A color's lightness also corresponds to its amplitude.Various color models have an explicit term for...
; a perceptual scale of the brightness as a nonlinear function of the relative luminance Y.
Note that (relative) luminance should not be confused with luma
Luma (video)
In video, luma, sometimes called luminance, represents the brightness in an image . Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image without any color, while the chroma components represent the color information...
, the weighted sum of the nonlinear gamma compressed
Gamma correction
Gamma correction, gamma nonlinearity, gamma encoding, or often simply gamma, is the name of a nonlinear operation used to code and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems...
R'G'B' components. For color spaces that use luma, such as Y'UV or Y'CbCr (where Y' represents luma), computation of relative luminance can still be done. The R'G'B' components can be transformed into linear light components by undoing the gamma compression; these linear primary components can then be used to calculate luminance.

