
Luso-Indian
Encyclopedia
Luso-Indians are Indian people who have mixed Indian and Portuguese ancestry or people of Portuguese descent born or living in India. Most of them live in former Portuguese colonies in India such as Goa
, Kerala
and Daman and Diu.
 In the 16th Century, a thousand years after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire
In the 16th Century, a thousand years after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire
, the Portuguese became the first European power to begin trading in the Indian Ocean
. They were in South India
a few years before the Moghuls appeared in the North. In the early 16th century, they set up their trading posts (factories) throughout the coastal areas of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, with their capital in Goa
in South West India on the Malabar Coast
.
In 1498, the number of Europeans residents in the area is merely a few tens of thousands. By 1580, Goa was a sophisticated city with its own brand of Indo-Portuguese society. Early in the development of Portuguese society in India, the Portuguese Admiral Afonso de Albuquerque
encouraged Portuguese soldiers to marry native (Muslim) women.
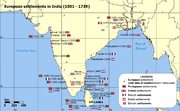 The English, French and Dutch East India Companies (EIC’s) became active in Far East trading in a meaningful way about a hundred and fifty years after the Portuguese. They too set up their posts throughout the Indian Ocean. By the middle of the 17th century there were several thousand Portuguese and Luso-Indians in India and a relatively small population of other Indo-Europeans. By the end of the 17th century, the East India Companies had established three major trading posts in India - Fort St. George (Chennai
The English, French and Dutch East India Companies (EIC’s) became active in Far East trading in a meaningful way about a hundred and fifty years after the Portuguese. They too set up their posts throughout the Indian Ocean. By the middle of the 17th century there were several thousand Portuguese and Luso-Indians in India and a relatively small population of other Indo-Europeans. By the end of the 17th century, the East India Companies had established three major trading posts in India - Fort St. George (Chennai
), Fort St William (Kolkata
) and Bombay Island. In 1670, the Portuguese population in Madras numbered around 3000.
and London
have been coming to Madras as settlers and traders. One of the first Jews who came to Madras with special permission to reside and trade there was Jacques (Jaime) de Paiva (Pavia) who convinced the English authorities to permit Jews to settle in Madras and he was the one who organized the Jews into the semblance of a community. On a plot of land in the suburbs he established a Jewish cemetery. The East India Company used Portuguese Jews based in Madras in its diplomatic efforts to expand English trading.
By the mid-eighteenth century there were almost no Portuguese Jews in Madras as most of them emigrated to London
. The gravestones of the old Jewish cemetery were moved to the Central Park of Madras in 1934 with the gate of the cemetery on which is written "Beit ha-Haim" in Hebrew letters, the last vestige of Jewish presence in Madras in the seventeenth century.
is rapidly disappearing from Goa. It is now spoken only by a small segment of the upper class families and about 3 to 5 % of the people still speak it (estimated at 30,000 to 50,000 people). The last Newspaper in Portuguese ended the publications in 1980s. However, the "Fundação do Oriente" and the Indo–Portuguese Friendship Society (Sociedade de Amizade Indo-Portuguesa) are still active. At Panaji many signs in Portuguese are still visible over shops, administrative buildings etc. There is a department of Portuguese at the Goa University
.
, Luso-Indians were generally knew with the name of "Topasses". They were Catholics and spoke Portuguese Creole. With the coming of the English rule in India, they began to speak English in place of the Portuguese and also Anglicized their names. They are, now, part of the Eurasian Anglo-Indian
community. In Negapatam, in 1883, there were 20 families that spoke Creole Portuguese. There are currently about 2000 people who speak Creole Portuguese in Damão while in Diu the language is nearly extinct. About 900 monolingual people currently speak Creole Portuguese in Korlai
. In Kochi
, Luso-Indians now numbered about 2,000.
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
and Daman and Diu.
Early History

Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was the western half of the Roman Empire after its division by Diocletian in 285; the other half of the Roman Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire, commonly referred to today as the Byzantine Empire....
, the Portuguese became the first European power to begin trading in the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
. They were in South India
South India
South India is the area encompassing India's states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Pondicherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area...
a few years before the Moghuls appeared in the North. In the early 16th century, they set up their trading posts (factories) throughout the coastal areas of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, with their capital in Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
in South West India on the Malabar Coast
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is a long and narrow coastline on the south-western shore line of the mainland Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain...
.
In 1498, the number of Europeans residents in the area is merely a few tens of thousands. By 1580, Goa was a sophisticated city with its own brand of Indo-Portuguese society. Early in the development of Portuguese society in India, the Portuguese Admiral Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque[p][n] was a Portuguese fidalgo, or nobleman, an admiral whose military and administrative activities as second governor of Portuguese India conquered and established the Portuguese colonial empire in the Indian Ocean...
encouraged Portuguese soldiers to marry native (Muslim) women.
Arrival of other Europeans

Chennai
Chennai , formerly known as Madras or Madarasapatinam , is the capital city of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, located on the Coromandel Coast off the Bay of Bengal. Chennai is the fourth most populous metropolitan area and the sixth most populous city in India...
), Fort St William (Kolkata
Kolkata
Kolkata , formerly known as Calcutta, is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located on the east bank of the Hooghly River, it was the commercial capital of East India...
) and Bombay Island. In 1670, the Portuguese population in Madras numbered around 3000.
British Raj
Also in the 17th century, Portuguese Jews from AmsterdamAmsterdam
Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. The current position of Amsterdam as capital city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is governed by the constitution of August 24, 1815 and its successors. Amsterdam has a population of 783,364 within city limits, an urban population...
and London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
have been coming to Madras as settlers and traders. One of the first Jews who came to Madras with special permission to reside and trade there was Jacques (Jaime) de Paiva (Pavia) who convinced the English authorities to permit Jews to settle in Madras and he was the one who organized the Jews into the semblance of a community. On a plot of land in the suburbs he established a Jewish cemetery. The East India Company used Portuguese Jews based in Madras in its diplomatic efforts to expand English trading.
By the mid-eighteenth century there were almost no Portuguese Jews in Madras as most of them emigrated to London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. The gravestones of the old Jewish cemetery were moved to the Central Park of Madras in 1934 with the gate of the cemetery on which is written "Beit ha-Haim" in Hebrew letters, the last vestige of Jewish presence in Madras in the seventeenth century.
Goa
The Portuguese languagePortuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
is rapidly disappearing from Goa. It is now spoken only by a small segment of the upper class families and about 3 to 5 % of the people still speak it (estimated at 30,000 to 50,000 people). The last Newspaper in Portuguese ended the publications in 1980s. However, the "Fundação do Oriente" and the Indo–Portuguese Friendship Society (Sociedade de Amizade Indo-Portuguesa) are still active. At Panaji many signs in Portuguese are still visible over shops, administrative buildings etc. There is a department of Portuguese at the Goa University
Goa University
Goa University was established in 1985 and merged with the Centre for Post Graduate Instruction and Research of the University of Bombay that functioned at state-capital Panaji or Panjim. Goa University offers both graduate and post-graduate studies and research programmes...
.
Elsewhere
In the Coromandel CoastCoromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
, Luso-Indians were generally knew with the name of "Topasses". They were Catholics and spoke Portuguese Creole. With the coming of the English rule in India, they began to speak English in place of the Portuguese and also Anglicized their names. They are, now, part of the Eurasian Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indians are people who have mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in India, now mainly historical in the latter sense. British residents in India used the term "Eurasians" for people of mixed European and Indian descent...
community. In Negapatam, in 1883, there were 20 families that spoke Creole Portuguese. There are currently about 2000 people who speak Creole Portuguese in Damão while in Diu the language is nearly extinct. About 900 monolingual people currently speak Creole Portuguese in Korlai
Korlai Fort
Korlai Fort is a Portuguese fortification in the town of Korlai, Maharashtra, India. It was built on an island which guards the way to the Revdanda Creek. It was meant as a companion to the fort at Chaul. At this strategic position the Portuguese could use it to defend their province which...
. In Kochi
Kochi
-Places:* Kochi, a city in the state of Kerala, India, formerly known as Cochin* Kingdom of Cochin, a former feudal city-state on Malabar Coast, India** Fort Kochi, one of the three main urban components which constitute the present day city of Kochi, Kerala, India...
, Luso-Indians now numbered about 2,000.
Notable Luso-Indians
- Henry Louis Vivian Derozio - Indian teacher and poet
- Gonsalo GarciaGonsalo GarciaSaint Gonsalo Garcia, O.F.M., was a Roman Catholic Franciscan friar from India, who died as a martyr in Japan and is venerated as a saint. Born in the western coastal town of Vasai, now an exurb of the city of Mumbai, he hailed from the town--then known as Bassein--during the time the town was...
- Roman Catholic saint - Juliana Dias da Costa - HaremHaremHarem refers to the sphere of women in what is usually a polygynous household and their enclosed quarters which are forbidden to men...
-QueenQueen consortA queen consort is the wife of a reigning king. A queen consort usually shares her husband's rank and holds the feminine equivalent of the king's monarchical titles. Historically, queens consort do not share the king regnant's political and military powers. Most queens in history were queens consort...
to the Mughal emperors of India Bahadur Shah IBahadur Shah IBahadur Shah was a Mughal Emperor, who ruled India from 1707 to 1712. His original name was Qutb ud-Din Muhammad Mu'azzam later titled as Shah Alam by his father. He took the throne name Bahadur Shah in 1707. His name Bahādur means "brave" & "hero" in Turko-Mongol languages...

