
Lydian alphabet
Encyclopedia
Lydian script was used to write the Lydian language
. That the language preceded the script is indicated by names in Lydian, which must have existed before they were written. Like other scripts of Anatolia
in the Iron Age
, the Lydian alphabet is a modification of the East Greek alphabet, but it has unique features. The same Greek letters may not represent the same sounds in both languages or in any other Anatolian language (in some cases it may). Moreover, the Lydian script is alphabetic.
Early Lydian texts are written both from left to right and from right to left. Later texts are exclusively written from right to left. One text is boustrophedon
. Spaces separate words except that one text uses dots. Lydian uniquely features a quotation mark in the shape of a right triangle.
The first codification was made by Roberto Gusmani in 1964 in a combined lexicon (vocabulary), grammar, and text collection.
as well as to the Greek alphabet
. It contains letters for 26 sounds. Some are represented by more than one symbol, which is considered one "letter." Unlike the Carian alphabet
, which had an f derived from Φ, the Lydian f has the peculiar 8 shape also found in the Etruscan alphabet.
In addition two digraphs, aa and ii, appear to be allophones of [a] and [i] under speculative circumstances, such as lengthening from stress. A schwa
was evidently not written: dctdid, kśbλtok-.
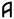
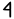
 - Ora - "Month"
- Ora - "Month"
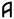
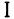

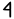
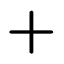
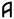
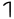 - Laqrisa - "Wall"
- Laqrisa - "Wall"
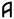
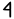

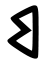 - Bira - "House, Home"
- Bira - "House, Home"
Standard in April, 2008 with the release of version 5.1. It is encoded in Plane 1 (Supplementary Multilingual Plane).
The Unicode block for Lydian is U+10920–U+1093F. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points.
Lydian language
Lydian was an Indo-European language spoken in the region of Lydia in western Anatolia . It belongs to the Anatolian group of the Indo-European language family....
. That the language preceded the script is indicated by names in Lydian, which must have existed before they were written. Like other scripts of Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
in the Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
, the Lydian alphabet is a modification of the East Greek alphabet, but it has unique features. The same Greek letters may not represent the same sounds in both languages or in any other Anatolian language (in some cases it may). Moreover, the Lydian script is alphabetic.
Early Lydian texts are written both from left to right and from right to left. Later texts are exclusively written from right to left. One text is boustrophedon
Boustrophedon
Boustrophedon , is a type of bi-directional text, mostly seen in ancient manuscripts and other inscriptions. Every other line of writing is flipped or reversed, with reversed letters. Rather than going left-to-right as in modern English, or right-to-left as in Arabic and Hebrew, alternate lines in...
. Spaces separate words except that one text uses dots. Lydian uniquely features a quotation mark in the shape of a right triangle.
The first codification was made by Roberto Gusmani in 1964 in a combined lexicon (vocabulary), grammar, and text collection.
The alphabet
The Lydian alphabet is closely related to the other alphabets of Asia MinorAlphabets of Asia Minor
Various alphabetic writing systems were in use in Iron Age Anatolia to record Anatolian dialects and the Phrygian language. Previously several of these languages had been written with logographic and syllabic systems....
as well as to the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
. It contains letters for 26 sounds. Some are represented by more than one symbol, which is considered one "letter." Unlike the Carian alphabet
Carian script
The Carian alphabets are a number of regional scripts used to write the Carian language of western Anatolia. They consisted of some 30 alphabetic letters, with several geographic variants in Caria and a homogeneous variant attested from the Nile delta, where Carian mercenaries fought for the...
, which had an f derived from Φ, the Lydian f has the peculiar 8 shape also found in the Etruscan alphabet.
| Lydian Letter | Transliteration | Sound | Table Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 𐤠 | 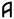 |
a | [a] | |
| 𐤵 | 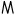 |
ã | nasal vowel Nasal vowel A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the velum so that air escapes both through nose as well as the mouth. By contrast, oral vowels are ordinary vowels without this nasalisation... |
Perhaps [ãː]. Only occurs accented. Ã or a is found before a nasal consonant: aliksãntru ~ aliksantru. |
| 𐤡 | 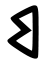 |
b | [p], [b] | Voiced to [b] before nasals and probably [r] |
| 𐤹 |  |
c | [dz]? | An undetermined voiced affricate or fricative: [z], [dz], or [dʒ], etc. At least one origin is assibilated Assibilation In linguistics, assibilation is the term for a sound change resulting in a sibilant consonant. It is commonly the final phase of palatalization.-Romance languages:... *d. |
| 𐤣 | d | [ð]? | Or perhaps some other voiced fricative such as [z]. | |
| 𐤤 | 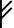 |
e | [eː] | Fairly high and long, like Greek ει; only occurs accented. |
| 𐤶 | 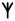 |
ẽ | nasal vowel Nasal vowel A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the velum so that air escapes both through nose as well as the mouth. By contrast, oral vowels are ordinary vowels without this nasalisation... |
Not [ẽ]; perhaps [ã]. Only occurs accented. |
| 𐤱 | 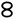 |
f | [f] | |
| 𐤢 | Ɔ | g | [ɡ] | Occasionally substituted for voiced /k/. |
| 𐤦 |  |
i | [i] | |
| 𐤧 | 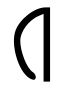 |
y | ? | Apparently an allophone of /i/, perhaps when unstressed. Attested only 11 times: artymu- ~ artimu-. It may be a borrowing of Carian 𐊹. |
| 𐤨 | 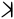 |
k | [k], [ɡ] | Voiced to [ɡ] before nasals and probably [r] |
| 𐤩 | 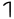 |
l | [l] | |
| 𐤷 | λ | [ʎ] | Palatalized Palatalization In linguistics, palatalization , also palatization, may refer to two different processes by which a sound, usually a consonant, comes to be produced with the tongue in a position in the mouth near the palate.... *l. |
|
| 𐤪 | m | [m] | ||
| 𐤫 | 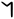 |
n | [n] | |
| 𐤸 | ν | [ɲ] or [ŋ]? | Arose from word-final *m and *n; later loss of final vowels caused it to contrast with those sounds. | |
| 𐤬 |  |
o | [oː] | Fairly high and long, like Greek ου; only occurs accented. |
| 𐤲 | 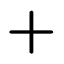 |
q | [kʷ] | At least historically [kʷ]; it's not clear if this pronunciation was still current. |
| 𐤭 | q | r | [r] | |
| 𐤳 | 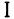 |
s | [ç] or [ʃ] | Palatalized Palatalization In linguistics, palatalization , also palatization, may refer to two different processes by which a sound, usually a consonant, comes to be produced with the tongue in a position in the mouth near the palate.... *s. |
| 𐤮 | 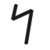 |
ś | [s] | A simple [s], despite its transcription. |
| 𐤯 | T | t | [t], [d] | Voiced to [d] before nasals and probably [r] |
| 𐤴 | τ | [ts] or [tʃ] | ||
| 𐤰 | y | u | [u] | |
| 𐤥 | 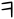 |
v | [v] | |
In addition two digraphs, aa and ii, appear to be allophones of [a] and [i] under speculative circumstances, such as lengthening from stress. A schwa
Schwa
In linguistics, specifically phonetics and phonology, schwa can mean the following:*An unstressed and toneless neutral vowel sound in some languages, often but not necessarily a mid-central vowel...
was evidently not written: dctdid, kśbλtok-.
Examples of words
𐤬𐤭𐤠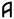
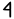
 - Ora - "Month"
- Ora - "Month"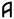
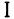

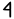
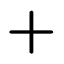
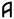
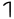 - Laqrisa - "Wall"
- Laqrisa - "Wall"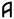
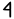

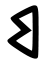 - Bira - "House, Home"
- Bira - "House, Home"Unicode
The Lydian alphabet was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in April, 2008 with the release of version 5.1. It is encoded in Plane 1 (Supplementary Multilingual Plane).
The Unicode block for Lydian is U+10920–U+1093F. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points.

