
MOS Technology 6510
Encyclopedia

Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
designed by MOS Technology, Inc.
MOS Technology
MOS Technology, Inc., also known as CSG , was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Norristown, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor, and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers.-History:MOS Technology, Inc...
, and is a modified form of the very successful 6502
MOS Technology 6502
The MOS Technology 6502 is an 8-bit microprocessor that was designed by Chuck Peddle and Bill Mensch for MOS Technology in 1975. When it was introduced, it was the least expensive full-featured microprocessor on the market by a considerable margin, costing less than one-sixth the price of...
.
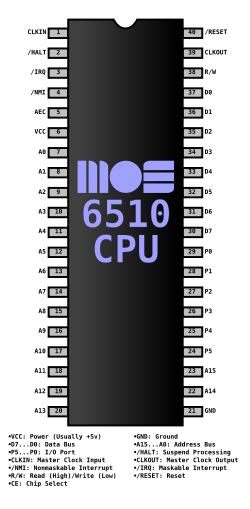
The primary change from the 6502 was the addition of an 8-bit general purpose I/O
Input/output
In computing, input/output, or I/O, refers to the communication between an information processing system , and the outside world, possibly a human, or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system, and outputs are the signals or data sent from it...
port (only six I/O pins were available in the most common version of the 6510). In addition, the address bus could be made tristate
Three-state logic
In digital electronics three-state, tri-state, or 3-state logic allows an output port to assume a high impedance state in addition to the 0 and 1 logic levels, effectively removing the output from the circuit...
.
The 6510 was only widely used in the Commodore 64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
home computer
Home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers entering the market in 1977, and becoming increasingly common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a single nontechnical user...
(and in significantly smaller numbers in the C64's portable
Portable computer
A portable computer is a computer that is designed to be moved from one place to another and includes a display and keyboard. Portable computers, by their nature, are generally microcomputers. Portable computers, because of their size, are also commonly known as 'Lunchbox' or 'Luggable' computers...
version, the SX-64
Commodore SX-64
The Commodore SX-64, also known as the Executive 64, or VIP-64 in Europe, is a portable, briefcase/suitcase-size "luggable" version of the popular Commodore 64 home computer and holds the distinction of being the first full-color portable computer....
). In both the C64 and SX-64 the extra pins of the processor were used to control the computer's memory map
Memory map
In computer science, a memory map is a structure of data that indicates how memory is laid out. Memory maps can have a different meaning in different parts of the operating system....
by bank switching
Bank switching
Bank switching is a technique to increase the amount of usable memory beyond the amount directly addressable by the processor. It can be used to configure a system differently at different times; for example, a ROM required to start a system from diskette could be switched out when no longer...
, and in the C64 also for controlling three of the four signal lines of the Datassette
Datassette
The Commodore 1530 Datasette , was Commodore's dedicated computer tape drive.It provided access to an inexpensive storage medium for Commodore's 8-bit home/personal computers, notably the PET, VIC-20, and C64...
tape recorder (the electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
control, key-press sensing and write data lines; the read data line went to another I/O chip). It was possible, by writing the correct bit pattern to the processor at address $01, to completely expose almost the full 64KB
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
of RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
in the C64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
, leaving no ROM
Read-only memory
Read-only memory is a class of storage medium used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be modified, or can be modified only slowly or with difficulty, so it is mainly used to distribute firmware .In its strictest sense, ROM refers only...
or I/O
I/O
I/O may refer to:* Input/output, a system of communication for information processing systems* Input-output model, an economic model of flow prediction between sectors...
hardware exposed except for the processor I/O port itself.
Variants
In 1985 MOS produced the 8500, an HMOSHMOS
Depletion-load nMOS/NMOS is a form of nMOS logic family which uses depletion-mode n-type MOSFETs as load transistors as a method to enable single voltage operation and achieve greater speed than possible with pure enhancement-load devices...
version of the 6510. Other than the process change, it is virtually identical to the NMOS
NMOS logic
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors to implement logic gates and other digital circuits...
version of the 6510. The 8500 was originally designed for use in the modernised C64, the C64C. However in 1985, limited quantities of 8500s were found on older NMOS based C64s. It finally made its official debut in 1987, appearing in a motherboard using the new 85xx HMOS chipset.
MOS Technology 8502
The MOS Technology 8502 was an 8-bit microprocessor designed by MOS Technology and used in the Commodore 128. Based on the MOS 6510 that was used in the Commodore 64, the 8502 added the ability to run at a double clock rate, in addition to the standard 1.024 MHz rate used by the Commodore 64.Since...
variant was used in the Commodore C128. All these CPUs are opcode
Opcode
In computer science engineering, an opcode is the portion of a machine language instruction that specifies the operation to be performed. Their specification and format are laid out in the instruction set architecture of the processor in question...
compatible (including undocumented opcodes
Illegal opcode
An Illegal Opcode, also called an Undocumented Instruction, is an instruction to a CPU that is not mentioned in any official documentation released by the CPU's designer or manufacturer, which nevertheless has an effect. Illegal opcodes were common on older CPUs designed during the 1970s, such as...
), except the 8502, where some differences concerning the undocumented opcodes have been reported.
The Commodore 1551
Commodore 1551
The Commodore 1551 was a floppy disk drive for the Commodore Plus/4 home computer. It resembled a charcoal-colored Commodore 1541 and plugged into the cartridge port, providing faster access than the C64/1541 combination...
disk drive used the 6510T, a version of the 6510 with eight I/O lines. The NMI
Non-Maskable interrupt
A non-maskable interrupt is a computer processor interrupt that cannot be ignored by standard interrupt masking techniques in the system. It is typically used to signal attention for non-recoverable hardware errors...
and RDY signals are not available.

