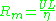Magnetic Reynolds number
Encyclopedia
The Magnetic Reynolds number is a dimensionless group
that
occurs in magnetohydrodynamics
. It gives an estimate of the effects of magnetic advection
to magnetic diffusion
, and is typically defined by:
where
General Characteristics for Large and Small
For 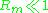 , advection is relatively unimportant, and so
, advection is relatively unimportant, and so
the magnetic field will tend to relax towards a purely diffusive state, determined by the boundary conditions rather than the flow.
For , diffusion is relatively unimportant on the length scale
, diffusion is relatively unimportant on the length scale 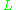 . Flux lines of the magnetic field are then advected with the fluid flow, until such time as gradients are concentrated into regions of short enough length scale that diffusion can balance advection.
. Flux lines of the magnetic field are then advected with the fluid flow, until such time as gradients are concentrated into regions of short enough length scale that diffusion can balance advection.
and the Reynolds number. All three can be regarded as giving the ratio of advective to diffusive effects for a particular physical field, and have a similar form of a velocity times a length divided by a diffusivity. The magnetic Reynolds number is related to the magnetic field in an MHD flow, while the Reynolds number is related to the fluid velocity itself, and the Péclet number a related to heat. The dimensionless groups arise in the non-dimensionalization of the respective governing equations, the induction equation, the momentum equation, and the heat equation
.
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
that
occurs in magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics is an academic discipline which studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes...
. It gives an estimate of the effects of magnetic advection
Advection
Advection, in chemistry, engineering and earth sciences, is a transport mechanism of a substance, or a conserved property, by a fluid, due to the fluid's bulk motion in a particular direction. An example of advection is the transport of pollutants or silt in a river. The motion of the water carries...
to magnetic diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
, and is typically defined by:
where
-
 is a typical velocity scale of the flow
is a typical velocity scale of the flow -
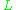 is a typical length scale of the flow
is a typical length scale of the flow -
 is the magnetic diffusivity
is the magnetic diffusivity
General Characteristics for Large and Small 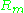
For 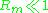 , advection is relatively unimportant, and so
, advection is relatively unimportant, and sothe magnetic field will tend to relax towards a purely diffusive state, determined by the boundary conditions rather than the flow.
For
 , diffusion is relatively unimportant on the length scale
, diffusion is relatively unimportant on the length scale 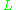 . Flux lines of the magnetic field are then advected with the fluid flow, until such time as gradients are concentrated into regions of short enough length scale that diffusion can balance advection.
. Flux lines of the magnetic field are then advected with the fluid flow, until such time as gradients are concentrated into regions of short enough length scale that diffusion can balance advection.Relationship to the Reynolds Number and Péclet Number
The Magnetic Reynolds number has a similar form to both the Péclet numberPéclet number
The Péclet number is a dimensionless number relevant in the study of transport phenomena in fluid flows. It is named after the French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion of the same...
and the Reynolds number. All three can be regarded as giving the ratio of advective to diffusive effects for a particular physical field, and have a similar form of a velocity times a length divided by a diffusivity. The magnetic Reynolds number is related to the magnetic field in an MHD flow, while the Reynolds number is related to the fluid velocity itself, and the Péclet number a related to heat. The dimensionless groups arise in the non-dimensionalization of the respective governing equations, the induction equation, the momentum equation, and the heat equation
Heat equation
The heat equation is an important partial differential equation which describes the distribution of heat in a given region over time...
.
See also
- Lundquist numberLundquist numberIn plasma physics, the Lundquist number is the dimensionless ratio of an Alfvén wave crossing timescale to a resistive diffusion timescale...
- MagnetohydrodynamicsMagnetohydrodynamicsMagnetohydrodynamics is an academic discipline which studies the dynamics of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes...
- Reynolds number
- Péclet numberPéclet numberThe Péclet number is a dimensionless number relevant in the study of transport phenomena in fluid flows. It is named after the French physicist Jean Claude Eugène Péclet. It is defined to be the ratio of the rate of advection of a physical quantity by the flow to the rate of diffusion of the same...