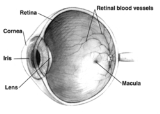
Mammalian eye
Overview
Along a line through the nodal (central) point of the eye is the optic axis, which is slightly five degrees toward the nose from the visual axis (i.e., that going towards the focused point to the fovea.
The structure of the mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
ian eye can be divided into three main layers or tunics whose names reflect their basic functions: the fibrous tunic, the vascular tunic, and the nervous tunic.
- The fibrous tunic, also known as the tunica fibrosa oculi, is the outer layer of the eyeball consisting of the corneaCorneaThe cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Together with the lens, the cornea refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is...
and scleraScleraThe sclera , also known as the white or white of the eye, is the opaque , fibrous, protective, outer layer of the eye containing collagen and elastic fiber. In the development of the embryo, the sclera is derived from the neural crest...
.
Unanswered Questions

