
Management control system
Encyclopedia
A management control systems (MCS) is a system which gathers and uses information to evaluate the performance of different organizational resources like human, physical, financial and also the organization as a whole considering the organizational strategies. Finally, MCS influences the behavior of organizational resources to implement organizational strategies. MCS might be formal or informal. The term ‘management control’ was given of its current connotations by Robert N. Anthony (Otley, 1994).
Robert N. Anthony (2007) defined Management Control is the process by which managers influence other members of the organization to implement the organization’s strategies. Management control systems are tools to aid management for steering an organization toward its strategic objectives and competitive advantage. Management controls are only one of the tools which managers use in implementing desired strategies. However strategies get implemented through management controls, organizational structure, human resources management and culture. Anthony & Young (1999) showed management control system as a black box. The term black box is used to describe an operation whose exact nature cannot be observed. MCS involves the behavior of managers and these behaviors cannot be expressed by equations. Anthony & Young (1999) showed that management accounting has three major subdivisions: full cost accounting
, differential accounting and management control or responsibility accounting.
According to Horngren et al. (2005), management control system is an integrated technique for collecting and using information to motivate employee behavior and to evaluate performance. . According to Simons (1995), Management Control Systems are the formal, information-based routines and procedures managers use to maintain or alter patterns in organizational activities
Chenhall (2003) mentioned that the terms management accounting (MA), management accounting systems (MAS), management control systems (MCS), and organizational controls (OC) are sometimes used interchangeably. In this case, MA refers to a collection of practices such as budgeting or product costing. But MAS refers to the systematic use of MA to achieve some goal and MCS is a broader term that encompasses MAS and also includes other controls such as personal or clan controls. Finally OC is sometimes used to refer to controls built into activities and processes such as statistical quality control, just-in-time management.
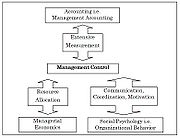
According to Maciariello et al. (1994), management control is concerned with coordination, resource allocation, motivation, and performance measurement. The practice of management control and the design of management control systems draws upon a number of academic disciplines. Management control involves extensive measurement and it is therefore related to and requires contributions from accounting especially management accounting. Second, it involves resource allocation decisions and is therefore related to and requires contribution from economics especially managerial economics. Third, it involves communication, and motivation which means it is related to and must draw contributions from social psychology especially organizational behavior (see Exhibit#1).
 Management control systems use many techniques such as
Management control systems use many techniques such as
Robert N. Anthony (2007) defined Management Control is the process by which managers influence other members of the organization to implement the organization’s strategies. Management control systems are tools to aid management for steering an organization toward its strategic objectives and competitive advantage. Management controls are only one of the tools which managers use in implementing desired strategies. However strategies get implemented through management controls, organizational structure, human resources management and culture. Anthony & Young (1999) showed management control system as a black box. The term black box is used to describe an operation whose exact nature cannot be observed. MCS involves the behavior of managers and these behaviors cannot be expressed by equations. Anthony & Young (1999) showed that management accounting has three major subdivisions: full cost accounting
Full cost accounting
Full cost accounting generally refers to the process of collecting and presenting information - about environmental, social, and economic costs and benefits/advantages - for each proposed alternative when a decision is necessary. It is a conventional method of cost accounting that traces direct...
, differential accounting and management control or responsibility accounting.
According to Horngren et al. (2005), management control system is an integrated technique for collecting and using information to motivate employee behavior and to evaluate performance. . According to Simons (1995), Management Control Systems are the formal, information-based routines and procedures managers use to maintain or alter patterns in organizational activities
Chenhall (2003) mentioned that the terms management accounting (MA), management accounting systems (MAS), management control systems (MCS), and organizational controls (OC) are sometimes used interchangeably. In this case, MA refers to a collection of practices such as budgeting or product costing. But MAS refers to the systematic use of MA to achieve some goal and MCS is a broader term that encompasses MAS and also includes other controls such as personal or clan controls. Finally OC is sometimes used to refer to controls built into activities and processes such as statistical quality control, just-in-time management.
According to Maciariello et al. (1994), management control is concerned with coordination, resource allocation, motivation, and performance measurement. The practice of management control and the design of management control systems draws upon a number of academic disciplines. Management control involves extensive measurement and it is therefore related to and requires contributions from accounting especially management accounting. Second, it involves resource allocation decisions and is therefore related to and requires contribution from economics especially managerial economics. Third, it involves communication, and motivation which means it is related to and must draw contributions from social psychology especially organizational behavior (see Exhibit#1).

- Balanced scorecardBalanced scorecardThe Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management tool - a semi-standard structured report, supported by proven design methods and automation tools, that can be used by managers to keep track of the execution of activities by the staff within their control and to monitor the...
- Total quality managementTotal Quality ManagementTotal quality management or TQM is an integrative philosophy of management for continuously improving the quality of products and processes....
(TQM) - KaizenKaizen, Japanese for "improvement", or "change for the better" refers to philosophy or practices that focus upon continuous improvement of processes in manufacturing, engineering, game development, and business management. It has been applied in healthcare, psychotherapy, life-coaching, government,...
(Continuous Improvement) - Activity-based costingActivity-based costingActivity-based costing is a special costing model that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity with resources to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each...
- Target costingTarget costingTarget costing is a pricing method used by firms. It is defined as "a cost management tool for reducing the overall cost of a product over its entire life-cycle with the help of production, engineering, research and design"...
- BenchmarkingBenchmarkingBenchmarking is the process of comparing one's business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and/or best practices from other industries. Dimensions typically measured are quality, time and cost...
and Benchtrending - JITJITJIT may refer to:* Various meanings of Just In Time:** Just-in-time compilation - a technique for improving the performance of virtual machines in computing.** Just-in-time - a business inventory strategy.* Jabber ICQ Transport....
- Budgeting
- Capital budgetingCapital budgetingCapital budgeting is the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term investments such as new machinery, replacement machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects are worth pursuing...
- Program management techniques, etc.

