Marcus Gunn phenomenon
Encyclopedia
Marcus Gunn phenomenon (a.k.a. Marcus Gunn Jaw-Winking or Trigemino-oculomotor Synkineses) is an autosomal-dominant condition with incomplete penetrance, in which nursing infants will have rhythmic upward jerking of their upper eyelid. This condition is characterized as a synkinesis
: when two or more muscles that are independently innervated have either simultaneous or coordinated movements.
Common physiologic examples of synkineses occur during sucking, chewing, or conjugate eye movements. There are also several abnormal cranial nerve synkineses, both acquired and congenital. Marcus Gunn jaw-winking is an example of a pathologic congenital synkinesis.
First described by the ophthalmologist Marcus Gunn in 1883, this condition presents in approximately 5% of neonates with congenital ptosis
. This condition has been associated with amblyopia
(in 54% of cases), anisometropia
(26%), and strabismus
(56%).
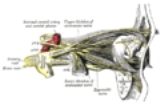
Marcus Gunn jaw-winking is an exaggeration of a very weak physiologic co-contraction that has been disinhibited secondary to a congenital brain stem lesion. The stimulation of the trigeminal nerve by contraction of the pterygoid muscles of jaw results in the excitation of the branch of the oculomotor nerve that innervates the levator palpebrae superioris ipsilaterally (on the same side of the face).
There are two major groups of trigemino-oculomotor synkineses:
1) External pterygoid-levator synkinesis is when the eyelid raises upon:
2) Internal pterygoid-levator synkinesis is when the eyelid raises upon teeth clenching
External pterygoid-levator synkinesis is the more common group.
Synkinesis
Synkinesis is the result from miswiring of nerves after trauma. This result is manifested through involuntary muscular movements accompanying voluntary movements...
: when two or more muscles that are independently innervated have either simultaneous or coordinated movements.
Common physiologic examples of synkineses occur during sucking, chewing, or conjugate eye movements. There are also several abnormal cranial nerve synkineses, both acquired and congenital. Marcus Gunn jaw-winking is an example of a pathologic congenital synkinesis.
First described by the ophthalmologist Marcus Gunn in 1883, this condition presents in approximately 5% of neonates with congenital ptosis
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis is a drooping of the upper or lower eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer, when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to amblyopia...
. This condition has been associated with amblyopia
Amblyopia
Amblyopia, also known as lazy eye, is a disorder of the visual system that is characterized by a vision deficiency in an eye that is otherwise physically normal, or out of proportion to associated structural abnormalities of the eye...
(in 54% of cases), anisometropia
Anisometropia
Anisometropia is the condition in which the two eyes have unequal refractive power; that is, are in different states of myopia , hyperopia or in the extreme, antimetropia , the unequal refractive states cause unequal rotations thus leading to diplopia and asthenopia.Anisometropia can adversely...
(26%), and strabismus
Strabismus
Strabismus is a condition in which the eyes are not properly aligned with each other. It typically involves a lack of coordination between the extraocular muscles, which prevents bringing the gaze of each eye to the same point in space and preventing proper binocular vision, which may adversely...
(56%).
Pathophysiology
It has been postulated that the synkinesis is due to damage to cranial nerve nuclei, caused by peripheral nerve injury and the nuclear lesion releases evolutionarily older [neural] mechanisms with their tendency toward associated movements, and so primitive reflexes are not inhibited.Marcus Gunn jaw-winking is an exaggeration of a very weak physiologic co-contraction that has been disinhibited secondary to a congenital brain stem lesion. The stimulation of the trigeminal nerve by contraction of the pterygoid muscles of jaw results in the excitation of the branch of the oculomotor nerve that innervates the levator palpebrae superioris ipsilaterally (on the same side of the face).
There are two major groups of trigemino-oculomotor synkineses:
1) External pterygoid-levator synkinesis is when the eyelid raises upon:
- Jaw thrust to opposite side (homolateral external pterygoid)
- Jaw is projected forward (bilateral external pterygoid)
- Mouth is opened widely
2) Internal pterygoid-levator synkinesis is when the eyelid raises upon teeth clenching
External pterygoid-levator synkinesis is the more common group.
Treatment
Treatment is usually unnecessary. In severe cases, surgery with a bilateral levator excision and frontalis brow suspension may be used.Behavioral and Social Implications
Although treatment may be unnecessary, there may be social implications, especially in young children when venturing from a supportive home environment to a public environment (e.g., starting school). Continued support, including monitoring behavior and educating the child about his or her appearance as seen by others, is encouraged. Gradual or sudden withdrawal from interaction with others is a sign that may or may not be related to such behavior. Studies are being conducted to elucidate these implications.Inverse Marcus Gunn Phenomenon
Inverse Marcus Gunn phenomenon is a rare condition that causes the eyelid to fall upon opening of the mouth. In this case, trigeminal innervation to the pterygoid muscles of the jaw is associated with an inhibition of the branch of the oculomotor nerve to the levator palpebrae superioris, as opposed to stimulation in Marcus Gunn jaw-winking.External links
- Animation at mrcophth.com
- The Marcus Gunn Foundation ~ A Non-Profit International Support Network
- http://www.mdjunction.com/marcus-gunn-jaw-winking-syndrome Forum with personal accounts (not a substitute for medical advice)

