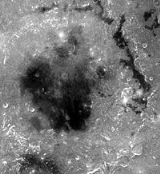
Mare Orientale
Encyclopedia

Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
features, resembling a target ring bull's-eye. Located on the extreme western edge of the lunar nearside, this impact basin
Impact crater
In the broadest sense, the term impact crater can be applied to any depression, natural or manmade, resulting from the high velocity impact of a projectile with a larger body...
is difficult to see from an Earthbound perspective.
Material from this basin was not sampled by the Apollo program so the basin's precise age is not known. However, it may be the freshest impact basin on the Moon and is believed to be slightly younger than the Imbrium Basin
Mare Imbrium
Mare Imbrium, Latin for "Sea of Showers" or "Sea of Rains", is a vast lunar mare filling a basin on Earth's Moon and one of the larger craters in the Solar System. Mare Imbrium was created when lava flooded the giant crater formed when a very large object hit the Moon long ago...
, which formed about 3.85 billion years ago. The surrounding basin material is of the Lower Imbrian
Lower Imbrian
In the lunar geologic timescale, the Early Imbrian epoch occurred between 3850 million years ago to about 3800 million years ago. It overlaps the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment of the inner solar system. The impact which created the huge Mare Imbrium basin occurred at the start of the epoch...
epoch
Epoch (geology)
An epoch is a subdivision of the geologic timescale based on rock layering. In order, the higher subdivisions are periods, eras and eons. We are currently living in the Holocene epoch...
with the mare material being of the Upper Imbrian
Upper Imbrian
In the Lunar geologic timescale, the Late Imbrian epoch occurred between 3800 million years ago to about 3200 million years ago. It was the epoch during which the mantle below the lunar basins partially melted and filled them with basalt...
epoch.
The mare is about 900 kilometres (559.2 mi) across and was formed by the impact of an asteroid-sized object. Unlike most other basins on the Moon, Orientale is relatively unflooded by mare basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
s, exposing much of the basin structure to view; the central portion of Mare Orientale is covered by a thin layer of mare basalt probably less than 1 kilometer deep, much less than in other nearside mare basins. The collision caused ripples in the lunar crust, resulting in the three concentric circular features. The innermost rings of this vast, multi-ringed crater are the inner and outer Montes Rook
Montes Rook
Montes Rook is a ring-shaped mountain range that lies along the western limb of the Moon, crossing over to the far side. It completely encircles the Mare Orientale, and forms part of a massive impact basin feature...
, and the outermost ring are the Montes Cordillera
Montes Cordillera
Montes Cordillera is a mountain range on the Moon. This feature forms the outer wall of peaks that surround the Mare Orientale impact basin, the inner ring being formed by the Montes Rook...
, 930 km in diameter. Basin ejecta begins just outside the Montes Cordillera and extends up to 500 kilometers beyond the base of the mountains. This ejecta has a rough, hummocky texture and contains linear patterns that point back at the center of Orientale.
Located at the antipode
Antipodal point
In mathematics, the antipodal point of a point on the surface of a sphere is the point which is diametrically opposite to it — so situated that a line drawn from the one to the other passes through the centre of the sphere and forms a true diameter....
of Mare Orientale is Mare Marginis
Mare Marginis
Mare Marginis is a lunar mare that lies on the very edge of the lunar nearside. The selenographic coordinates of this feature are 13.3° N, 86.1° E, and the diameter is 420 km. The name is Latin for "Sea of the Edge"....
.
Name
This feature is believed to have first been given its modern name by the GermanGermany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
Julius Franz
Julius Heinrich Franz
Julius Heinrich Franz was a German astronomer.Franz was educated in Berlin, after which he was the principal astronomer at the Royal Observatory in Königsberg. In 1882 he was a member of a team sent to the town of Aiken, South Carolina, to observe the transit of Venus...
in his 1906 book Der Mond (DE: The Moon). However, in his book On the Moon, Patrick Moore
Patrick Moore
Sir Patrick Alfred Caldwell-Moore, CBE, FRS, FRAS is a British amateur astronomer who has attained prominent status in astronomy as a writer, researcher, radio commentator and television presenter of the subject, and who is credited as having done more than any other person to raise the profile of...
later claimed to have discovered and named this same feature in 1946. In an earlier edition (1976) of the book (then titled Guide to the Moon) Moore describes how it was he and H P Wilkins who discovered it. Moore does, however, credit Franz as discoverer in his 2009 Yearbook of Astronomy (p.133-135).
However, in their paper that appeared in the Journal of the British Astronomical Association (vol.117, no 3, 129-135) Ewan Whitaker and Richard Baum tell the story of the 'discovery' and naming of the Mare, and it is credited to Julius Franz.
During the 1960s, rectified images of this area by Gerard Kuiper
Gerard Kuiper
Gerard Peter Kuiper , Netherlands – December 24, 1973, Mexico City) was a Dutch-American astronomer after whom the Kuiper belt was named.-Early life:...
at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
The Lunar and Planetary Laboratory is a research center for planetary science located in Tucson, Arizona. It is also a graduate school, constituting the Department of Planetary Sciences at the University of Arizona...
gave rise to the notion of this being an impact crater.
At the time this formation was named it was located on what by convention was considered the eastern side of the Moon, hence the latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
name for "Eastern Sea". In 1961, however, the International Astronomical Union
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
adopted the astronautic convention for East and West on the Moon and this limb became the western edge.

