
Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution
Encyclopedia
In economics
, the Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution (MRTS) - or Technical Rate of Substitution (TRS) - is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced (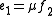 ) when one extra unit of another input is used (
) when one extra unit of another input is used (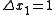 ), so that output remains constant (
), so that output remains constant (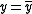 ).
).
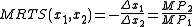
where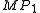 and
and 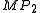 are the marginal product
are the marginal product
s of input 1 and input 2, respectively, and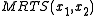 is Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution of the input
is Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution of the input 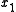 for
for 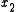 .
.
Along an isoquant, the MRTS shows the rate at which one input (e.g. capital or labor) may be substituted for another, while maintaining the same level of output. The MRTS can also be seen as the slope of an isoquant
at the point in question.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, the Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution (MRTS) - or Technical Rate of Substitution (TRS) - is the amount by which the quantity of one input has to be reduced (
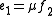 ) when one extra unit of another input is used (
) when one extra unit of another input is used (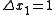 ), so that output remains constant (
), so that output remains constant (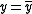 ).
).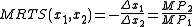
where
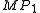 and
and 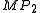 are the marginal product
are the marginal productMarginal product
In economics and in particular neoclassical economics, the marginal product or marginal physical product of an input is the extra output that can be produced by using one more unit of the input , assuming that the quantities of no other inputs to production...
s of input 1 and input 2, respectively, and
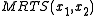 is Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution of the input
is Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution of the input 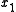 for
for 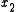 .
.Along an isoquant, the MRTS shows the rate at which one input (e.g. capital or labor) may be substituted for another, while maintaining the same level of output. The MRTS can also be seen as the slope of an isoquant
Isoquant
In economics, an isoquant is a contour line drawn through the set of points at which the same quantity of output is produced while changing the quantities of two or more inputs...
at the point in question.
See also
- Marginal rate of substitutionMarginal rate of substitutionIn economics, the marginal rate of substitution is the rate at which a consumer is ready to give up one good in exchange for another good while maintaining the same level of utility.-Marginal rate of substitution as the slope of indifference curve:...
(the same concept on consumption side)

