
Marginal propensity to import
Encyclopedia
The marginal propensity to import (MPM) refers to the change in import expenditure that occurs with a change in disposable income
(income after taxes and transfers). For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to import is 0.2, then of that dollar, the household will spend 20 cents of that dollar on imported goods and services.
Mathematically, the marginal propensity to import (MPM) function is expressed as the derivative
of the import (I) function with respect to disposable income (Y).
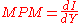
In other words, the marginal propensity to import is measured as the ratio of the change in imports to the change in income, thus giving us a figure between 0 and 1.
Imports are also considered to be automatic stabilisers that work to lessen fluctuations in real GDP
.
The UK government assumes that UK citizens have a high marginal propensity to import and thus will use a decrease in disposable income as a tool to control the current account on the Balance of Payments.
Disposable income
Disposable income is total personal income minus personal current taxes. In national accounts definitions, personal income, minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income...
(income after taxes and transfers). For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to import is 0.2, then of that dollar, the household will spend 20 cents of that dollar on imported goods and services.
Mathematically, the marginal propensity to import (MPM) function is expressed as the derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
of the import (I) function with respect to disposable income (Y).
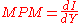
In other words, the marginal propensity to import is measured as the ratio of the change in imports to the change in income, thus giving us a figure between 0 and 1.
Imports are also considered to be automatic stabilisers that work to lessen fluctuations in real GDP
Real GDP
Real Gross Domestic Product is a macroeconomic measure of the value of output economy adjusted for price changes . The adjustment transforms the money-value measure, called nominal GDP, into an index for quantity of total output...
.
The UK government assumes that UK citizens have a high marginal propensity to import and thus will use a decrease in disposable income as a tool to control the current account on the Balance of Payments.
See also
- Marginal propensity to saveMarginal propensity to saveThe marginal propensity to save refers to the increase in saving that results from an increase in income i.e. The marginal propensity to save might be defined as the proportion of each additional dollar of household income that is used for saving. It is also used as an alternative term for the...
- Marginal propensity to consumeMarginal propensity to consumeIn economics, the marginal propensity to consume is an empirical metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending occurs with an increase in disposable income...
- Automatic stabiliser
- Multiplier ModelMultiplier (economics)In economics, the fiscal multiplier is the ratio of a change in national income to the change in government spending that causes it. More generally, the exogenous spending multiplier is the ratio of a change in national income to any autonomous change in spending In economics, the fiscal...

