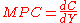Marginal value
Encyclopedia
A marginal value is
(This third case is actual a special case of the second).
In the case of differentiability, at the limit, a marginal change is a mathematical differential, or the corresponding mathematical derivative.
These uses of the term “marginal” are especially common in economics
, and result from conceptualizing constraints as borders or as margins. The sorts of marginal values most common to economic analysis are those associated with unit changes of resources and, in mainstream economics
, those associated with instantaneous changes. Marginal values associated with units are considered because many decisions are made by unit, and marginalism
explains unit price in terms of such marginal values. Mainstream economics uses instantaneous values in much of its analysis for reasons of mathematical tractability.
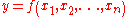
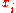 is discretely changed from
is discretely changed from 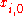 to
to 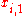 while other independent variables remain unchanged, then the marginal value of the change in
while other independent variables remain unchanged, then the marginal value of the change in 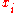 is
is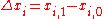
and the “marginal value” of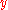 may refer to
may refer to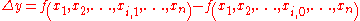
or to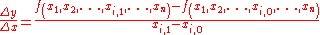
from 2 casks to three casks, then
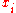 would be
would be 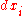 , and the “marginal value” of
, and the “marginal value” of 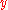 would typically refer to
would typically refer to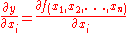
(For a linear functional relationship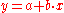 , the marginal value of
, the marginal value of 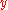 will simply be the co-efficient of
will simply be the co-efficient of  (in this case,
(in this case, 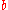 ) and this will not change as
) and this will not change as  changes. However, in the case where the functional relationship is non-linear, say
changes. However, in the case where the functional relationship is non-linear, say 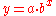 , the marginal value of
, the marginal value of 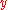 will be different for different values of
will be different for different values of  .)
.)
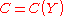
where
Then the marginal propensity to consume
is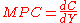
- a valueValue (mathematics)In mathematics, value commonly refers to the 'output' of a function. In the most basic case, that of unary, single-valued functions, there is one input and one output .The function f of the example is real-valued, since each and every possible function value is real...
that holds true given particular constraints, - the change in a value associated with a specific change in some independent variableDependent and independent variablesThe terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
, whether it be of that variable or of a dependent variableDependent and independent variablesThe terms "dependent variable" and "independent variable" are used in similar but subtly different ways in mathematics and statistics as part of the standard terminology in those subjects...
, or - [when underlying values are quantified] the ratioRatioIn mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
of the change of a dependent variable to that of the independent variable.
(This third case is actual a special case of the second).
In the case of differentiability, at the limit, a marginal change is a mathematical differential, or the corresponding mathematical derivative.
These uses of the term “marginal” are especially common in economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, and result from conceptualizing constraints as borders or as margins. The sorts of marginal values most common to economic analysis are those associated with unit changes of resources and, in mainstream economics
Mainstream economics
Mainstream economics is a loose term used to refer to widely-accepted economics as taught in prominent universities and in contrast to heterodox economics...
, those associated with instantaneous changes. Marginal values associated with units are considered because many decisions are made by unit, and marginalism
Marginalism
Marginalism refers to the use of marginal concepts in economic theory. Marginalism is associated with arguments concerning changes in the quantity used of a good or service, as opposed to some notion of the over-all significance of that class of good or service, or of some total quantity...
explains unit price in terms of such marginal values. Mainstream economics uses instantaneous values in much of its analysis for reasons of mathematical tractability.
Quantified conception
Assume a functional relationship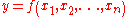
Discrete change
If the value of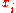 is discretely changed from
is discretely changed from 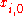 to
to 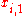 while other independent variables remain unchanged, then the marginal value of the change in
while other independent variables remain unchanged, then the marginal value of the change in 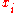 is
is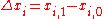
and the “marginal value” of
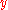 may refer to
may refer to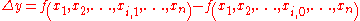
or to
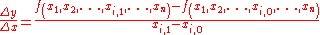
Example
If an individual saw her income increase from $50000 to $55000 per annum, and part of her response was to increase yearly purchases of amontilladoAmontillado
Amontillado is a variety of sherry, characterized by being darker than fino but lighter than oloroso. It is named for the Montilla region of Spain, where the style originated in the 18th century, although the name 'amontillado' is sometimes used commercially as a simple measure of colour to label...
from 2 casks to three casks, then
- the marginal increase in her income was $5000
- the marginal effect on her purchase of amontillado was an increase of 1 cask, or of 1 cask per $5000.
Instantaneous margins
If instantaneous values are considered, then a marginal value of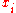 would be
would be 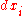 , and the “marginal value” of
, and the “marginal value” of 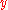 would typically refer to
would typically refer to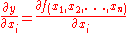
(For a linear functional relationship
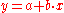 , the marginal value of
, the marginal value of 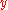 will simply be the co-efficient of
will simply be the co-efficient of  (in this case,
(in this case,  ) and this will not change as
) and this will not change as  changes. However, in the case where the functional relationship is non-linear, say
changes. However, in the case where the functional relationship is non-linear, say 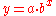 , the marginal value of
, the marginal value of 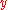 will be different for different values of
will be different for different values of  .)
.)Example
Assume that, in some economy, aggregate consumption is well-approximated by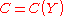
where
 is aggregate incomeMeasures of national income and outputA variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product , gross national product , and net national income . All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and...
is aggregate incomeMeasures of national income and outputA variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product , gross national product , and net national income . All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and...
.
Then the marginal propensity to consume
Marginal propensity to consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume is an empirical metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending occurs with an increase in disposable income...
is