
Markov information source
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a Markov information source, or simply, a Markov source, is an information source
whose underlying dynamics are given by a stationary finite Markov chain
.
s ranging over a finite alphabet Γ, having a stationary distribution
.
A Markov information source is then a (stationary) Markov chain M, together with a function
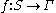
that maps states S in the Markov chain to letters in the alphabet Γ.
A unifilar Markov source is a Markov source for which the values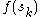 are distinct whenever each of the states
are distinct whenever each of the states 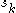 are reachable, in one step, from a common prior state. Unifilar sources are notable in that many of their properties are far more easily analyzed, as compared to the general case.
are reachable, in one step, from a common prior state. Unifilar sources are notable in that many of their properties are far more easily analyzed, as compared to the general case.
, as a model of a transmitter
. Markov sources also occur in natural language processing
, where they are used to represent hidden meaning in a text. Given the output of a Markov source, whose underlying Markov chain is unknown, the task of solving for the underlying chain is undertaken by the techniques of hidden Markov model
s, such as the Viterbi algorithm
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a Markov information source, or simply, a Markov source, is an information source
Information source (mathematics)
In mathematics, an information source is a sequence of random variables ranging over a finite alphabet Γ, having a stationary distribution.The uncertainty, or entropy rate, of an information source is defined as...
whose underlying dynamics are given by a stationary finite Markov chain
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
.
Formal definition
An information source is a sequence of random variableRandom variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s ranging over a finite alphabet Γ, having a stationary distribution
Stationary distribution
Stationary distribution may refer to:* The limiting distribution in a Markov chain* The marginal distribution of a stationary process or stationary time series* The set of joint probability distributions of a stationary process or stationary time series...
.
A Markov information source is then a (stationary) Markov chain M, together with a function
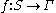
that maps states S in the Markov chain to letters in the alphabet Γ.
A unifilar Markov source is a Markov source for which the values
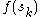 are distinct whenever each of the states
are distinct whenever each of the states 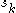 are reachable, in one step, from a common prior state. Unifilar sources are notable in that many of their properties are far more easily analyzed, as compared to the general case.
are reachable, in one step, from a common prior state. Unifilar sources are notable in that many of their properties are far more easily analyzed, as compared to the general case.Applications
Markov sources are commonly used in communication theoryCommunication theory
Communication theory is a field of information and mathematics that studies the technical process of information and the human process of human communication.- History :- Origins :...
, as a model of a transmitter
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications a transmitter or radio transmitter is an electronic device which, with the aid of an antenna, produces radio waves. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating...
. Markov sources also occur in natural language processing
Natural language processing
Natural language processing is a field of computer science and linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and human languages; it began as a branch of artificial intelligence....
, where they are used to represent hidden meaning in a text. Given the output of a Markov source, whose underlying Markov chain is unknown, the task of solving for the underlying chain is undertaken by the techniques of hidden Markov model
Hidden Markov model
A hidden Markov model is a statistical Markov model in which the system being modeled is assumed to be a Markov process with unobserved states. An HMM can be considered as the simplest dynamic Bayesian network. The mathematics behind the HMM was developed by L. E...
s, such as the Viterbi algorithm
Viterbi algorithm
The Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states – called the Viterbi path – that results in a sequence of observed events, especially in the context of Markov information sources, and more generally, hidden Markov models...
.

