Marshall syndrome
Encyclopedia
Marshall syndrome is a genetic disorder
of the connective tissue
which can cause hearing loss
. The three most common areas to be affected are the eye
s, joint
s and the mouth and facial structures. Marshall syndrome and Stickler syndrome
closely resemble each other; in fact they are so similar, some say they are the same.
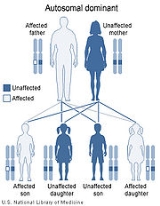
 Stickler syndrome and Marshall syndrome have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. However, there is a great deal of variation within and among families with regard to gene expression. Some may be more severely affected and others may be very mildly affected. Often these syndromes are not recognized in a family until a baby is born with Pierre Robin syndrome
Stickler syndrome and Marshall syndrome have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. However, there is a great deal of variation within and among families with regard to gene expression. Some may be more severely affected and others may be very mildly affected. Often these syndromes are not recognized in a family until a baby is born with Pierre Robin syndrome
or some members have detached retinas or cataract
s at a young age.
Both syndromes where correlated with mutations in the COL2A1
gene.
is the most common eye problem in Marshall syndrome. Cataracts also occur more frequently and detached retina less frequently than in Stickler syndrome. Myopia
also is the most common problem with the eyes in Stickler syndrome
. In the latter syndrome, extreme myopia may lead to severe eye problems such as detached retina more frequently than in Marshall syndrome, and cataracts less frequently than in Marshall syndrome.
. Babies and young children with Stickler syndrome usually have very hyperextensible joints. As an affected child gets older, they may experience pain and stiffness from overuse of a joint. Osteoarthritis
of the large joints often develops during the third or fourth decade. The joint changes in Marshall syndrome are of the same type but to a lesser degree. There also may be changes in the bones that show up on X-ray
but generally are not a problem.
is Pierre Robin syndrome
. This refers to a cleft palate resulting from a very small lower jaw
. During early fetal life, the roof of the mouth is normally open and the sides of the palate
have to come together to close. If the jaw is too small, there is not enough room for the tongue
which is then pushed up and gets in the way of the closing palate. Sometimes the chin is so small the baby has problems with eating and breathing if the tongue blocks the back of the throat
. Cleft palate is found less frequently in Marshall Syndrome than in Stickler syndrome but still more frequently than in the general population.
The facial features of Marshall Syndrome include a flat midface, the appearance of large eyes, short upturned nose, and a round face. The facial features of Stickler syndrome are less prominent but include a rather long flat face, and depressed nasal bridge.
can magnify an existing sensorineural loss and is a frequent problem for children with Stickler or Marshall Syndrome.
or Marshall syndrome. Some families with Stickler syndrome have been shown to have mutations in the Type II collagen gene on chromosome 1. However, other families do not show the linkage to the collagen gene. its an area of active research, also the genetic testing
being expensive supports that the diagnosis is made depending on the features.
tested, and adults should be aware that the hearing loss may not develop until the adult years. Yearly visits to an ophthalmologist or other eye care professional
who has been informed of the diagnosis of Stickler or Marshall syndrome is important for all affected individuals. Children should have the opportunity to have myopia corrected as early as possible, and treatment for cataracts or detached retinas may be more effective with early identification. Support for the joints is especially important during sports, and some recommend that contact sports should be avoided by those who have very loose joints.
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
of the connective tissue
Connective tissue
"Connective tissue" is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues . Connective Tissue is found throughout the body.In fact the whole framework of the skeleton and the different specialized connective tissues from the crown of the head to the toes determine the form of...
which can cause hearing loss
Hearing impairment
-Definition:Deafness is the inability for the ear to interpret certain or all frequencies of sound.-Environmental Situations:Deafness can be caused by environmental situations such as noise, trauma, or other ear defections...
. The three most common areas to be affected are the eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
s, joint
Joint
A joint is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.-Classification:...
s and the mouth and facial structures. Marshall syndrome and Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome is a group of genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. It was first studied and characterized by Gunnar B. Stickler in 1965. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI...
closely resemble each other; in fact they are so similar, some say they are the same.
Genetics

Pierre Robin syndrome
Pierre Robin Sequence , also known as Pierre Robin Malformation, is a congenital condition of facial abnormalities in humans. PRS is a sequence: a chain of certain developmental malformations, one entailing the next...
or some members have detached retinas or cataract
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
s at a young age.
Both syndromes where correlated with mutations in the COL2A1
COL2A1
Collagen, type II, alpha 1 , also known as COL2A1, is a human gene that provides instructions for the production of the pro-alpha1 chain of type II collagen....
gene.
Eyes
MyopiaMyopia
Myopia , "shortsightedness" ) is a refractive defect of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus in front of the retina under conditions of accommodation. In simpler terms, myopia is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in...
is the most common eye problem in Marshall syndrome. Cataracts also occur more frequently and detached retina less frequently than in Stickler syndrome. Myopia
Myopia
Myopia , "shortsightedness" ) is a refractive defect of the eye in which collimated light produces image focus in front of the retina under conditions of accommodation. In simpler terms, myopia is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in...
also is the most common problem with the eyes in Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome is a group of genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. It was first studied and characterized by Gunnar B. Stickler in 1965. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI...
. In the latter syndrome, extreme myopia may lead to severe eye problems such as detached retina more frequently than in Marshall syndrome, and cataracts less frequently than in Marshall syndrome.
Joints
The joint changes include hyperextensibility (double-jointedness) and arthritisArthritis
Arthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation of one or more joints....
. Babies and young children with Stickler syndrome usually have very hyperextensible joints. As an affected child gets older, they may experience pain and stiffness from overuse of a joint. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints, including articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Symptoms may include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, locking, and sometimes an effusion...
of the large joints often develops during the third or fourth decade. The joint changes in Marshall syndrome are of the same type but to a lesser degree. There also may be changes in the bones that show up on X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
but generally are not a problem.
Orofacial Structure
The most severe problem associated with Stickler syndromeStickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome is a group of genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. It was first studied and characterized by Gunnar B. Stickler in 1965. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI...
is Pierre Robin syndrome
Pierre Robin syndrome
Pierre Robin Sequence , also known as Pierre Robin Malformation, is a congenital condition of facial abnormalities in humans. PRS is a sequence: a chain of certain developmental malformations, one entailing the next...
. This refers to a cleft palate resulting from a very small lower jaw
Jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
. During early fetal life, the roof of the mouth is normally open and the sides of the palate
Palate
The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but, in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior...
have to come together to close. If the jaw is too small, there is not enough room for the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
which is then pushed up and gets in the way of the closing palate. Sometimes the chin is so small the baby has problems with eating and breathing if the tongue blocks the back of the throat
Throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the anterior part of the neck, in front of the vertebral column. It consists of the pharynx and larynx...
. Cleft palate is found less frequently in Marshall Syndrome than in Stickler syndrome but still more frequently than in the general population.
The facial features of Marshall Syndrome include a flat midface, the appearance of large eyes, short upturned nose, and a round face. The facial features of Stickler syndrome are less prominent but include a rather long flat face, and depressed nasal bridge.
Hearing loss
The hearing loss associated with Stickler syndrome can be progressive and usually involves the high frequencies. Sensorineural hearing loss has been reported in as many as 100% and as low as 20% of affected individuals. A conductive loss due to otitisOtitis
Otitis is a general term for inflammation or infection of the ear, in both humans and other animals.It is subdivided into the following:*Otitis externa, external otitis, or "swimmer's ear" involves the outer ear and ear canal. In external otitis, the ear hurts when touched or pulled.*Otitis media...
can magnify an existing sensorineural loss and is a frequent problem for children with Stickler or Marshall Syndrome.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made based on features as well as by the very early onset of serious eye and ear disease. Because Marshall syndrome is an autosomal dominant hereditary disease, physicians can also note the characteristic appearance of the biological parent of the child. There are no tests for Stickler syndromeStickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome is a group of genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. It was first studied and characterized by Gunnar B. Stickler in 1965. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI...
or Marshall syndrome. Some families with Stickler syndrome have been shown to have mutations in the Type II collagen gene on chromosome 1. However, other families do not show the linkage to the collagen gene. its an area of active research, also the genetic testing
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
being expensive supports that the diagnosis is made depending on the features.
Treatment
There is no medical treatment for either syndrome but there are some recommendations that can help with prevention or early identification of some of the problems. Children with either syndrome should have their hearingHearing (sense)
Hearing is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations through an organ such as the ear. It is one of the traditional five senses...
tested, and adults should be aware that the hearing loss may not develop until the adult years. Yearly visits to an ophthalmologist or other eye care professional
Eye care professional
An eye care professional is an individual who provides a service related to the eyes or vision. It is a general term that can refer to any healthcare worker involved in eye care, from one with a small amount of post-secondary training to practitioners with a doctoral level of education.-Current...
who has been informed of the diagnosis of Stickler or Marshall syndrome is important for all affected individuals. Children should have the opportunity to have myopia corrected as early as possible, and treatment for cataracts or detached retinas may be more effective with early identification. Support for the joints is especially important during sports, and some recommend that contact sports should be avoided by those who have very loose joints.

