
Mass transfer coefficient
Encyclopedia
In engineering
, the mass transfer coefficient is a diffusion
rate constant that relates the mass transfer
rate, mass transfer area, and concentration gradient as driving force:
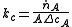
Where:
This can be used to quantify the mass transfer between phase
s, immiscible and partially miscible fluid
mixtures (or between a fluid and a porous solid). Quantifying mass transfer allows for design and manufacture of separation process
equipment that can meet specified requirements, estimate what will happen in real life situations (chemical spill), etc.
Mass transfer coefficients can be estimated from many different theoretical equation
s, correlation
s, and analogies
that are functions of material properties, intensive properties
and flow regime (laminar
or turbulent
flow). Selection of the most applicable model is dependent on the materials and the system, or environment, being studied.
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
, the mass transfer coefficient is a diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
rate constant that relates the mass transfer
Mass transfer
Mass transfer is the net movement of mass from one location, usually meaning a stream, phase, fraction or component, to another. Mass transfer occurs in many processes, such as absorption, evaporation, adsorption, drying, precipitation, membrane filtration, and distillation. Mass transfer is used...
rate, mass transfer area, and concentration gradient as driving force:
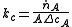
Where:
- kc is the mass transfer coefficient [mol/(s·m2)/(mol/m3), or m/s]
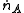 is the mass transfer rate [mol/s]
is the mass transfer rate [mol/s]- A is the effective mass transfer area [m2]
- ΔCA is the driving force concentration difference [mol/m3].
This can be used to quantify the mass transfer between phase
Phase (matter)
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space , throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, and chemical composition...
s, immiscible and partially miscible fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
mixtures (or between a fluid and a porous solid). Quantifying mass transfer allows for design and manufacture of separation process
Separation process
In chemistry and chemical engineering, a separation process, or simply a separation, is any mass transfer process used to convert a mixture of substances into two or more distinct product mixtures, at least one of which is enriched in one or more of the mixture's constituents. In some cases, a...
equipment that can meet specified requirements, estimate what will happen in real life situations (chemical spill), etc.
Mass transfer coefficients can be estimated from many different theoretical equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
s, correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
s, and analogies
Analogy
Analogy is a cognitive process of transferring information or meaning from a particular subject to another particular subject , and a linguistic expression corresponding to such a process...
that are functions of material properties, intensive properties
Intensive and extensive properties
In the physical sciences, an intensive property , is a physical property of a system that does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system: it is scale invariant.By contrast, an extensive property In the physical sciences, an intensive property (also called a bulk...
and flow regime (laminar
Laminar flow
Laminar flow, sometimes known as streamline flow, occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers. At low velocities the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another like playing cards. There are no cross currents...
or turbulent
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
flow). Selection of the most applicable model is dependent on the materials and the system, or environment, being studied.

