Master's degree in Europe
Encyclopedia
This page refers to types of Master's degrees in Europe. Please see Master's degree
for more information.
In order to facilitate the movement of students between European countries, a standardized schedule of higher education diplomas, also known as the Bologna process
, was proposed: an undergraduate degree of at least three years called licence or Bachelor's degree
, followed by a one-year or two-year diploma called Master, then a doctorate
, meant to be obtained in (at least) 3 years. Because of these indicated schedules, the reform is sometimes (erroneously) referred to as 3-5-8. The objective is the European Higher Education Area
.
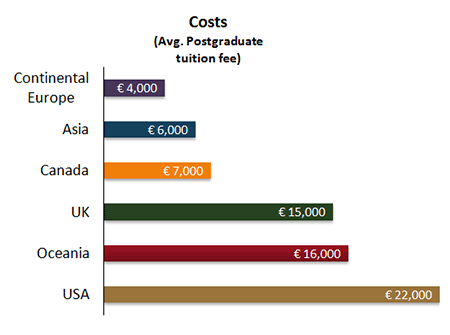
An often cited advantage of the European universities is an advantageous cost/quality ratio. In Europe, especially continental Europe, universities are heavily subsidized by their national governments. In Germany, Scandinavia or Eastern Europe for instance, most Master’s programmes are totally free of charge. Recently, these governments are discussing the introduction of tuition fees. Sweden started charging tuition for non-EU students in 2010.
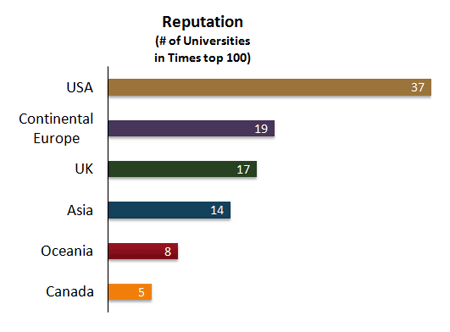
In the recent publication of the Times Higher Education Supplement
, 36 of the top 100 universities in the world are located in Europe. There are large regional differences in the tuition fees in those top 100 universities:
n).
Medicine and dentistry pose an exception; these studies are not divided into Bachelor's and Master's degree, but take 6 years to complete and the degree obtained is called "Dr. med." (However this is not a real doctoral degree, as the name "Dr." might suggest, as you only write a "diploma thesis" and not a "doctoral thesis" or "dissertation".)
Before the Bologna process, the traditional Austria
n equivalent to the Master's degree was the Diplomstudium, leading to the title Diplom-Ingenieur
(female title: Diplom-Ingenieurin)(Abbreviation: "Dipl.-Ing." or "DI") in engineering or Magister
(female: Magistra)(Abbreviation: "Mag.") in almost every discipline. The Diplomstudium took about 4–6 years of study.
, possessing a Master's degree means that you have completed a higher education (usually university or college) programme of 4 or 5 years. Before the Bologna process
most university degrees required 4 years of studies (leading to a licence), but some programmes required 5 years of study. An example in the field of education in business/management was the 5-year programme of "Handelsingenieur" (Dutch/Flemish) or "Ingénieur de Gestion" (French) (English: "Commercial Engineer") with an important amount of mathematics and sciences, and which corresponds to an M.Sc. in Management. This degree co-existed with a graduate degree in business economics (4 years) named "Licentiaat in toegepaste economische wetenschappen" (Dutch/Flemish) or "Licence en sciences économiques appliquées" (French) (English: "Licence in applied economics").
, a Master's degree is awarded. This is just "Master" in Danish; however, MA/M.Sc and Master Courses are distinguished, where MA and M.Sc are known as Candidate degrees ("kandidatgrad"), and are obtained by completing a longer advanced education ("længere videregående uddannelse"), with a typical duration of five years.
A large number of subdivisions exist, usually designating the area of education (e.g. cand.theol.
, cand.arch.
and cand.jur.
), though some have more vague definitions (cand.mag.
, cand.scient.
, cand.polyt.
, and cand.scient.techn., each of which encompass broad, overlapping areas of science).
The Bologna process
has caused most educations to be split into a three-year (180 ECTS
points) substructure, after which a Bachelor's degree
is obtained, followed by a two-year (120 ECTS points) superstructure, at which point the Master's degree is obtained.
, the introduction of the Bologna Process has standardized most of the degrees into the European model. The Master's degree takes 2–3 years (120 ECTS
units) after the Bachelor's degree. In English-speaking usage, the degree title is named after the particular faculty of study. In Finnish, the degree is called maisteri in most fields. When precision is needed, the term ylempi korkeakoulututkinto is used to denote all degrees of Master's level. Literally, this translates into English as higher diploma of higher education.
Medicine-related fields of medicine, dentistry, and veterinary medicine pose an exception to Bologna system. In medical fields, the Licenciate is an equivalent degree, the completion of which takes five (dentistry) or six years (medicine and veterinary), while the Bachelor of Medicine's degree is gained after second year of studies. In fields other than medicine, the Licentiate's degree is a post-graduate degree higher than Master's but lower than doctor's.
In Engineering, the higher degree is either diplomi-insinööri
or arkkitehti although in international use MSc
is used. In Pharmacy
, the degree is proviisori . All such degrees retaining their historical name are classified as Master's degrees (ylempi korkeakoulututkinto) and in English usage, they are always translated as Master's degrees. Some other Master's degrees give the right to use the traditional title of the degree-holder. Most importantly, the degree of Master of Science in Economics and Business Administration gives the right to use the title of ekonomi, while the Masters of Science in Agriculture and Forestry may use the titles of metsänhoitaja (Forester
) or agronomi (Agronomist) depending on their field of study.
and many countries which follow the French model (like the Francophone regions in Switzerland
, Belgium
, Lebanon
, Algeria
, Morocco
, Tunisia
), higher education is divided in three tiers (cycles universitaires), leading to different degrees. The master's degree corresponds to the second tier. A master's degree is awarded to the holders of
France is also host to a number of private American-style universities like The American University of Paris, that offer accredited American Master's degrees in Europe. Admission into these Master's programs requires a completed American undergraduate degree or a similar French/European degree that can be acquired in four years of study.
, the traditional German academic degrees Diplom
and Magister
have mostly been replaced by the undergraduate Bachelor
(3-4 year study programme) and postgraduate Master's degree (1-2 year study programme).
In Germany
the Diplom
(first degree after (usually) 4-6 years - from either a Universität (University
), a Technische Hochschule or a Kunsthochschule with university status) and the Magister
had traditionally been equivalated to the Master's degree, the Magister being a degree after the study of two or three subjects (one main and one or two subsidiary subjects), as common in Humanities
or Liberal Arts
, whereas the Diplom is awarded after the study of one subject, commonly found in Natural Sciences, Social Sciences
, Formal sciences and some Applied Sciences. The Fachhochschule
n or Universities of Applied Sciences conferred the Diplom (FH), whose length of study is between the Bachelor's and Master's degree. Under the harmonised system there is no legal academic difference between the Bachelor's and Master's degrees conferred by the Fachhochschulen and Universitäten.
The German Meister qualification for a master craftsman
is neither a degree nor is it comparable to the academic Master's degree. It, however, qualifies the holder to study at a University
or Fachhochschule
, whether the Meister holds the regular entry qualification (Abitur
or Fachhochschulreife) or not.
(except Trinity College Dublin, where this is an undergraduate degree awarded 21 terms after matriculation, see 'MAs in Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin', below,) or MA
, M.Sc., MBA, MAI, ME/MEng/MEngSc
, MPhil, LLM, MLitt, MArch
, MAgrSc, MSocSc, MCH
, MAcc
, MEconSc.
With respect to NUI post graduate qualifications, in general there is a simple distinction between MA and MPhil. An MA is a combination of taught (classroom) and research-based modules, whilst an MPhil is composed exclusively of research-based learning.
The Magister in Arte Ingeniaria (MAI), literally meaning 'Master in the Art of Engineering', is awarded by the University of Dublin
, Ireland, and is more usually referred to as Master of Engineering. While still available (via two routes), historically it was the engineering Master's degree taken by the university's BAI
graduates. Today the more common engineering Master's degree in the University of Dublin is the M.Sc..
A Master of Business Studies
(MBS) refers to a qualification in the degree of master that can be obtained by students of recognized universities and colleges who complete the relevant approved programmes of study, pass the prescribed examinations, and fulfil all other prescribed conditions. An MBS can be studied in the following areas: Electronic Business,Finance, Human Resource Management, International Business, Management Information System, Management & Organisation Studies, Management Consultancy, Marketing, Project Management, Strategic Management & Planning and can be obtained from many universities in Ireland including University College Dublin
.
The other universities in Ireland usually award a MEngSc, M.E.
, MEng
or M.Sc. for their postgraduate Master's degree in engineering.
, simply called Laurea.
This system was reformed in 1999/2000 to comply to the Bologna process directives. The new university system (Nuovo Ordinamento) includes two levels of degrees: a three year Bachelor's degree
, called Laurea di Primo Livello or just Laurea
(e.g. Laurea di Primo Livello in Ingegneria Elettronica is Bachelor of Science in Electronic Engineering) and a two year course of specialization, leading to a Master's degree called Laurea di Secondo Livello, Laurea Specialistica or Laurea Magistrale (e.g. Laurea Specialistica in Ingegneria Elettronica is Master of Science in Electronic Engineering). Both degrees include a thesis work with final discussion.
A student can apply for the Ph.D. level course, called Dottorato di Ricerca
, only after getting a Master's degree
.
Medicine and some other school ("Facoltà"), notably Law, have adopted the reformed system only partially, keeping the previous unique course. Medicine is therefore still a six year course followed, possibly, by the specialization, requiring from three to six years more.
However, these Facoltà also have other courses organized according to the new system (e.g., Tecniche di radiologia medica for Medicine, Consulente del lavoro for Law)
The first level is Bachelor's degree ("bakalauras"). It is awarded after 4 years of study in a university ("universitetas") or after 3 years of study in a college ("kolegija"). Students of medicine have longer studies.
The second level, Master's degree ("magistras") is awarded after 2 years of further study at university. Bolognia process didn't influence much of the Lithuanian education system because most of it has been there since end of soviet era. One notable change is that now it is possible to apply to Master studies after 3 years study at a college ("kolegija"). Before the Bologna process the 4 years study at a university ("universitetas") was required. One notable exception probably is psychology studies. To enroll to Master of Psychology studies you have to have Bachelor of Psychology degree from university. The Bachelor of Psychology degree from college is not sufficient to enroll in Master of Psychology studies.
After completing Master degree student can study further for the third level - PhD
degree ("daktaras") at a university.
Before the Bachelor/Master system was introduced, HBO graduates received the title baccalaureus (with the corresponding pre-nominal abbreviation "bc."), which was rarely used. On the other hand the HBO graduates with an engineering degree used the degree ingenieur, with pre-nominal abbreviation "ing.
", which was (and still is) used quite commonly. WO degrees consisted of several different titles, such as doctorandus
(pre-nominal abbreviated to drs., corresponds to MA
or MSc
), ingenieur (ir.
for WO level, corresponds to MSc) and meester in de rechten (mr., corresponds to LL.M.) These former titles are no longer granted (although they are still used, protected, and interchangeable with MA and MSc titles). The title of doctor (dr., corresponding to the PhD degree) is still awarded.
Prior to the education reform, a single program leading to the doctorandus, ingenieur or meester degree was in effect, which comprised the same course load as the Bachelor and Master programs put together. Those who had already started the doctorandus, ingenieur or meester program could, upon completing it, opt for the old degree (before their name), or simply use the Master's degree (behind their name) in accordance with the new standard. Since these graduates do not have a separate Bachelor's degree (which is in fact – in retrospect – incorporated into the program), the Master’s degree is their first academic degree.
In the new system, completed college (HBO) degrees are equivalent to a Bachelor's degree and are abbreviated to "B" with a subject suffix. Universities (WO) grant a Bachelor's degree for the general portion of the curriculum. This degree is a "Bachelor of Science" or "Bachelor of Arts" with the appropriate suffix.
Before one is admitted to a Master's program, one must have obtained a Bachelor's degree in the same field of study at the same level (although exceptions to this rule are possible, if the Bachelor's degree has nearly been obtained). This means that someone with a HBO Bachelor's degree cannot start a WO Master program; still, many universities offer a so-called 'bridge year', in which HBO degree holders can attain the WO Bachelor and continue into the WO Master program.
All fully completed curricula in the Netherlands are equivalent to Master's degrees with the addition of a "of Science" or "of Arts" to distinguish them from HBO Master's degrees, which are known simply as Master. WO Master's degrees focus on specialization in a sub-area of the general Bachelor's degree subject and typically take 1 year except for engineering studies where the Master takes 2 years.
HBO Master's are usually started only after several years of work and are similarly focusses on specialization. The title is signified by the abbreviation M and therefore an MBA would indicate a HBO Master's degree in business administration, but use of the MBA title is protected and it can only be granted by accredited schools.
As a result of the Bologna-process and the Quality reform, the degree system of Norwegian higher education consists of the two main levels Bachelor's degree and Master's degree. A Bachelor's degree at a Norwegian university/university college is equivalent to an undergraduate degree and takes three years (with the exception of the teaching courses, where a Bachelor's degree lasts for four years). The Master's degrees are either fully integrated five-year programmes (admission does not require undergraduate degree) leading up to a graduate degree, or two-year courses at graduate level which require an already completed undergraduate degree. Following the graduate level, education is given at the doctoral level, usually through a four year research fellowship leading to a PhD.
Before the implementation of this system, various titles were given in accordance with the field of study and the length of the course. For instance, a three year undergraduate degree in engineering would give the title "høgskoleingeniør" (Bachelor's degree), and a 4,5 to 5 year graduate degree in engineering would give the title "sivilingeniør" (Master's degree). That being said, these titles are still very common and are, although formally abolished, degrees granted earlier (see Academic degree#Norway for a complete list) are still being used, also by academic personnel.
.
In the traditional model, a Master's degree is awarded after completion of a university curriculum — a 5 year programme in science courses at a university or other similar institution, with a project in the final year called magisterium (it can be translated as a Master of Arts or a Master of Science thesis) that often requires carrying out research in a given field. An MA degree is called a magister (abbreviated mgr) except for medical education, where it is called a lekarz (this gives the holder the right to use the title of physician and surgeon), a lekarz weterynarii in the veterinary field and a dentysta in field of dentistry. Universities of technology usually give the title of magister inżynier (abbreviated mgr inż.) corresponding to an MSc Eng degree.
More and more institutions introduce another model, which as of 2005 is still less popular. In this model, following the Bologna process
directives, higher education is split into a 3 to 4-year Bachelor programme ending with a title of licencjat (non-technical) or inżynier (technical fields), and a 2-year programme (uzupełniające studia magisterskie) giving the title of magister or magister inżynier. Nevertheless, even in these institutions, it is often possible to bridge the Bachelor education directly into the Master programme, without formally obtaining the licencjat degree, thus shortening the time needed for completing the education slightly.
Depending on field and school, the timing may be slightly different.
could be divided between 'kandidat' (three years), 'magister' (four years), 'licentiat' ('magister' + 2–3 years of postgraduate studies) and 'doktor' ('magister' + 4–5 years of postgraduate studies). In engineering disciplines M.Sc was called 'civilingenjör', a four and a half year academic program concluded with a thesis. There was no direct equivalent to a B.Sc, however, a three year engineering degree with a more practical focus called 'högskoleingenjör' was close.
With the full implementation of the Bologna process in July 2007, a 'Master' (five years) was introduced in line with the criteria for the second cycle
. The 'magister' will still exist alongside the new 'Master', but is expected to be largely neglected in favour of the new, internationally recognized degree. The M.Sc of engineering, 'civilingenjör', was expanded to five years and a new B.Sc was introduced to coexist with the unaltered 'högskoleingenjör'.
, many universities now have four-year undergraduate programmes (or five-year in Scotland) mainly in the sciences or in engineering
with a research project or Dissertation in the final year. The awards for these are named after the subject, so a course in mathematics
would earn a Master in Mathematics degree, (abbreviated to MMath), or have a general title such as MSci (Master in Science at most universities but Master of Natural Sciences at Cambridge
), MBiomed, MBiochem, MChem, MComp, MPharm
, MEng
, MMath, MPhys, MInf, MML, MDes, etc.
In content the first two years they are generally identical to those of the equivalent Bachelor's degree while the third and fourth years are a combination of higher-level taught courses and a research project.
An example of an undergraduate master's degree in the professions in the United Kingdom
is Pharmacy. In order to become a pharmacist, the undergraduate MPharm
must be completed, followed by one year of pre-registration experience. A similar situation exists as regards Engineering
.
The ancient universities of Scotland
(St Andrews
, Glasgow
, Aberdeen
, Edinburgh
) and Dundee
award a Master of Arts
(MA) as a prestigious undergraduate degree after four years of study in Arts, Humanities or Social Sciences.
The Master of Arts
(MA) is awarded by the universities of Oxford
, Cambridge
and Trinity College, Dublin
—without further examination— to those entitled to the degree of Bachelor of Arts
.
, MA
, LL.M., MLitt, MSSc, MSt
, MEnt
etc.)
The most common types of postgraduate taught Master's degrees are the Master of Arts
(MA) awarded in Arts
, Humanities
, Theology
and Social Sciences
and the Master of Science
(MSc) awarded in pure and applied
Science
. A number of taught programs in Social Sciences
also receive the Master of Science
(MSc) degree (e.g. MSc Development Studies
at the London School of Economics
and University of Bath
).
However, some universities - particularly those in Scotland
- award the Master of Letters
(MLitt) to students in the Arts
, Humanities
, Divinity
and Social Sciences
, often with the suffix (T) to indicate it is a taught degree, to avoid confusion with the MLitt (see Research postgraduate Master's degrees below). In the universities of Cambridge
and Oxford
on the other hand, the MPhil is a taught master's degree (normally also including a short research component), whereas the MLitt and the MSc degrees are offered as pure research degrees only. Some other universities, such as the University of Glasgow
, previously used the designation MPhil for both taught and research Master's degrees, but have recently changed the taught appellation to MLitt.
In Law
the standard taught degree is the Master of Laws, but certain courses may lead to the award of MA or MLitt.
Until recently, both the undergraduate and postgraduate Master's degrees were awarded without grade or class (like the class of an honours degree). Nowadays however, Master's degrees may be classified into a maximum of four categories (Distinction, Merit, Pass or Fail), while others can have a more simplified form of assessment by only distinguishing between a Pass or a Fail.
The Master of Philosophy (MPhil) is a research degree awarded for the completion of a thesis. It is a shorter version of the Ph.D.
and some universities routinely enter potential PhD students into the MPhil programme and allow them to upgrade to the full PhD programme a year or two into the course. Advanced candidates for a taught postgraduate Master's sometimes undertake the MPhil as it is considered a more prestigious degree, but it may also mean that the student could not afford or could not complete the full PhD.
The Master of Research (MRes) degree is a more structured and organised version of the MPhil, usually designed to prepare a student for a career in research. For example, an MRes may combine individual research with periods of work placement in research establishments. MRes is considered a really prestigious degree.
The Master of Letters (MLitt) degree is a two-year research degree at many universities, including Cambridge and the ancient Scottish universities, and is generally awarded when a student cannot or will not complete the final year(s) of their PhD
and so writes their research up for the MLitt. Because MLitt is also used for a taught degree, the suffix (T) or (R) for taught or research is often added, so the more prestigious two-year research degree is called MLitt (R).
Like the PhD, the MPhil and MRes degrees are generally awarded without class or grade as a pass (the standard grade) or can, rarely, be awarded with a distinction.
, Cambridge
and Dublin
award Master's degrees to BAs without further examination, where seven years after matriculation
have passed, and (in some but not all cases) upon payment of a nominal fee. It is commonplace for recipients of the degree to have graduated several years previously and to have had little official contact with the university or academic life since then. The only real significance of these degrees is that they historically conferred voting rights in University elections, it was seen as the point at which one became eligible to teach at the University and certain other privileges e.g. the right to dine at the holder's college's high table. They still do confer some restricted and rarely used voting rights. The MAs awarded by Oxford and Cambridge are colloquially known as the Oxbridge MA
, and that from Dublin as the Trinity MA, and would be usually distinguished respectively: MA (Oxon.), MA (Cantab.) and MA (Dubl.). "Oxon." here is short for Oxoniensis, "Cantab." for Cantabrigiensis, "Dubl." for Dubliniensis, meaning "of Oxford", "of Cambridge", and "of Dublin" respectively. The Universities of Cambridge and Dublin also offer an MA to certain senior staff - both academic and non-academic - after a number of years' employment with the university.
Until the advent of the modern research university in the mid 19th century, several other British and American universities also gave such degrees "in course".
the first degree in Arts
, Fine Art
, Humanities
and Social Sciences awarded by the ancient universities of Scotland
is the Master of Arts
. It should be noted the Science
and Law
faculties of Scottish universities award the BSc
and LLB degrees respectively and the New Universities
generally award the BA. The Scottish MA is roughly equivalent to an advanced BA from a University elsewhere in the United Kingdom, as it is an undergraduate degree. However, Scottish university courses are four years in length rather than the usual UK degrees, which last for only three years (but this is also true of Scottish BSc and LLB degrees). Trinity College Dublin courses are also four years in length.
, the process is not yet fully accomplished. Differences in methodology and curricula are still widely different in some cases. To mitigate this, several initiatives and approaches are currently tried, some of them with the support of the European Union
institutions. Either in partnership or as private consortia, networks of universities in different countries are trying to work out shared curricula and adopt similar methodologies. In niche educational areas like translation
and interpreting
this has proved successful and the networks have become functional, i.e. European Master's in Translation
and the European Master's in Conference Interpreting . While these are not mainstream developments, it may be noted that in these networks of universities a similar Master's degree certificate is offered for a given field, and the network/consortium collectively guarantees that these degrees have a high level of convergence.
Master's degree
A master's is an academic degree granted to individuals who have undergone study demonstrating a mastery or high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice...
for more information.
In order to facilitate the movement of students between European countries, a standardized schedule of higher education diplomas, also known as the Bologna process
Bologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
, was proposed: an undergraduate degree of at least three years called licence or Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
, followed by a one-year or two-year diploma called Master, then a doctorate
Doctorate
A doctorate is an academic degree or professional degree that in most countries refers to a class of degrees which qualify the holder to teach in a specific field, A doctorate is an academic degree or professional degree that in most countries refers to a class of degrees which qualify the holder...
, meant to be obtained in (at least) 3 years. Because of these indicated schedules, the reform is sometimes (erroneously) referred to as 3-5-8. The objective is the European Higher Education Area
European Higher Education Area
The European Higher Education Area was launched along with the Bologna Process' decade anniversary, in March 2010, during the Budapest-Vienna Ministerial Conference....
.
The European Master's Market
As indicated in the sections below, the Bologna process is far from accomplished. There are still large differences between the national higher education systems of the European nations (see the comprehensive report 'Bologna with student eyes' from ESIB). Through the Bologna initiatives and support of the European Union, Europe is unifying and standardising especially the structure of their Master's programmes, making them more and more accessible to foreign students.An often cited advantage of the European universities is an advantageous cost/quality ratio. In Europe, especially continental Europe, universities are heavily subsidized by their national governments. In Germany, Scandinavia or Eastern Europe for instance, most Master’s programmes are totally free of charge. Recently, these governments are discussing the introduction of tuition fees. Sweden started charging tuition for non-EU students in 2010.
In the recent publication of the Times Higher Education Supplement
The Times Higher Education Supplement
The Times Higher Education , formerly Times Higher Education Supplement , is a weekly British magazine based in London reporting specifically on news and other issues related to higher education...
, 36 of the top 100 universities in the world are located in Europe. There are large regional differences in the tuition fees in those top 100 universities:


Austria
In Austria you obtain a Bachelor's degree after 3 years of study and a Master's degree after 2 more years of study. This is true for both the "research-oriented university" sector as well as the "university of applied sciences" sector which had been established in the 1990s (see also FachhochschuleFachhochschule
A Fachhochschule or University of Applied Sciences is a German type of tertiary education institution, sometimes specialized in certain topical areas . Fachhochschulen were founded in Germany and later adopted by Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Greece...
n).
Medicine and dentistry pose an exception; these studies are not divided into Bachelor's and Master's degree, but take 6 years to complete and the degree obtained is called "Dr. med." (However this is not a real doctoral degree, as the name "Dr." might suggest, as you only write a "diploma thesis" and not a "doctoral thesis" or "dissertation".)
Before the Bologna process, the traditional Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
n equivalent to the Master's degree was the Diplomstudium, leading to the title Diplom-Ingenieur
Diplom
A Diplom is an academic degree in the German-speaking countries Germany, Austria, and Switzerland and a similarly named degree in some other European countries including Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Estonia, Finland , Greece, Hungary, Russia, Serbia, Macedonia, Slovenia, and Ukraine...
(female title: Diplom-Ingenieurin)(Abbreviation: "Dipl.-Ing." or "DI") in engineering or Magister
Magister (degree)
Magister is an academic degree used in various systems of higher education.-Argentina:...
(female: Magistra)(Abbreviation: "Mag.") in almost every discipline. The Diplomstudium took about 4–6 years of study.
Belgium
In BelgiumBelgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, possessing a Master's degree means that you have completed a higher education (usually university or college) programme of 4 or 5 years. Before the Bologna process
Bologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
most university degrees required 4 years of studies (leading to a licence), but some programmes required 5 years of study. An example in the field of education in business/management was the 5-year programme of "Handelsingenieur" (Dutch/Flemish) or "Ingénieur de Gestion" (French) (English: "Commercial Engineer") with an important amount of mathematics and sciences, and which corresponds to an M.Sc. in Management. This degree co-existed with a graduate degree in business economics (4 years) named "Licentiaat in toegepaste economische wetenschappen" (Dutch/Flemish) or "Licence en sciences économiques appliquées" (French) (English: "Licence in applied economics").
Denmark
In DenmarkDenmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, a Master's degree is awarded. This is just "Master" in Danish; however, MA/M.Sc and Master Courses are distinguished, where MA and M.Sc are known as Candidate degrees ("kandidatgrad"), and are obtained by completing a longer advanced education ("længere videregående uddannelse"), with a typical duration of five years.
A large number of subdivisions exist, usually designating the area of education (e.g. cand.theol.
Theology
Theology is the systematic and rational study of religion and its influences and of the nature of religious truths, or the learned profession acquired by completing specialized training in religious studies, usually at a university or school of divinity or seminary.-Definition:Augustine of Hippo...
, cand.arch.
Architecture
Architecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
and cand.jur.
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
), though some have more vague definitions (cand.mag.
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
, cand.scient.
Natural science
The natural sciences are branches of science that seek to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world by using empirical and scientific methods...
, cand.polyt.
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
, and cand.scient.techn., each of which encompass broad, overlapping areas of science).
The Bologna process
Bologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
has caused most educations to be split into a three-year (180 ECTS
European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System
This page describes ECTS-credits. For information about the ECTS grading system go to ECTS grading scale.European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System is a standard for comparing the study attainment and performance of students of higher education across the European Union and other...
points) substructure, after which a Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
is obtained, followed by a two-year (120 ECTS points) superstructure, at which point the Master's degree is obtained.
Finland
In FinlandFinland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, the introduction of the Bologna Process has standardized most of the degrees into the European model. The Master's degree takes 2–3 years (120 ECTS
European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System
This page describes ECTS-credits. For information about the ECTS grading system go to ECTS grading scale.European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System is a standard for comparing the study attainment and performance of students of higher education across the European Union and other...
units) after the Bachelor's degree. In English-speaking usage, the degree title is named after the particular faculty of study. In Finnish, the degree is called maisteri in most fields. When precision is needed, the term ylempi korkeakoulututkinto is used to denote all degrees of Master's level. Literally, this translates into English as higher diploma of higher education.
Medicine-related fields of medicine, dentistry, and veterinary medicine pose an exception to Bologna system. In medical fields, the Licenciate is an equivalent degree, the completion of which takes five (dentistry) or six years (medicine and veterinary), while the Bachelor of Medicine's degree is gained after second year of studies. In fields other than medicine, the Licentiate's degree is a post-graduate degree higher than Master's but lower than doctor's.
In Engineering, the higher degree is either diplomi-insinööri
Diplomi-insinööri
Diplomi-insinööri is a Finnish Master's level academic degree with a nominal length of 300 ECTS credits. The official English translation of the degree is Master of Science in Engineering, Master of Science and Master of Science in Technology. The Finnish name derives from the old German degree...
or arkkitehti although in international use MSc
MSC
- Computers:* Mario Strikers Charged* Microsoft Common Console Document, file for the Microsoft Management Console* Microelectronics Support Centre* Microsoft Corporation* MIDI Show Control* Message Sequence Chart...
is used. In Pharmacy
Pharmacy
Pharmacy is the health profession that links the health sciences with the chemical sciences and it is charged with ensuring the safe and effective use of pharmaceutical drugs...
, the degree is proviisori . All such degrees retaining their historical name are classified as Master's degrees (ylempi korkeakoulututkinto) and in English usage, they are always translated as Master's degrees. Some other Master's degrees give the right to use the traditional title of the degree-holder. Most importantly, the degree of Master of Science in Economics and Business Administration gives the right to use the title of ekonomi, while the Masters of Science in Agriculture and Forestry may use the titles of metsänhoitaja (Forester
Forester
250px|thumb|right|Foresters of [[Southern University of Chile|UACh]] in the [[Valdivian forest]]s of San Pablo de Tregua, ChileA forester is a person who practices forestry, the science, art, and profession of managing forests. Foresters engage in a broad range of activities including timber...
) or agronomi (Agronomist) depending on their field of study.
France
In FranceFrance
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and many countries which follow the French model (like the Francophone regions in Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
, Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
), higher education is divided in three tiers (cycles universitaires), leading to different degrees. The master's degree corresponds to the second tier. A master's degree is awarded to the holders of
- master's diploma (diplôme de master). It is the more common master's degree. It is awarded mainly by universities in two principal qualifications
- Master of ResearchMaster of ResearchIn the UK and Ireland, the Master of Research degree is an advanced postgraduate degree available in a range of academic disciplines. Although a relatively new degree, the MRes is becoming increasingly popular with a number of the Russell Group Universities such as Imperial College London,...
(master recherche) the science-oriented degree, necessary step to proceed to doctoral studies. It can be a largely research degree, a taught one or a mix between the two. - vocational master (master professionnel) aimed at gaining working qualification. Usually a taught degree with internship required.
- Master of Research
- grandes écolesGrandes écolesThe grandes écoles of France are higher education establishments outside the main framework of the French university system. The grandes écoles select students for admission based chiefly on national ranking in competitive written and oral exams...
diploma. Not all grandes écoles diplomas programs are accreditated by the State. Some grandes écoles deliver also master's diplomas, but their own diploma remains more prestigious. - Engineer's degreeEngineer's degreeAn engineer's degree is an advanced academic degree in engineering that is conferred in Europe, some countries of Latin America, and a few institutions in the United States....
. - Architect's degree.
- Some degrees from Schools of Fine Arts.
France is also host to a number of private American-style universities like The American University of Paris, that offer accredited American Master's degrees in Europe. Admission into these Master's programs requires a completed American undergraduate degree or a similar French/European degree that can be acquired in four years of study.
Germany
Due to the EU-wide Bologna processBologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
, the traditional German academic degrees Diplom
Diplom
A Diplom is an academic degree in the German-speaking countries Germany, Austria, and Switzerland and a similarly named degree in some other European countries including Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Estonia, Finland , Greece, Hungary, Russia, Serbia, Macedonia, Slovenia, and Ukraine...
and Magister
Magister (degree)
Magister is an academic degree used in various systems of higher education.-Argentina:...
have mostly been replaced by the undergraduate Bachelor
Bachelor
A bachelor is a man above the age of majority who has never been married . Unlike his female counterpart, the spinster, a bachelor may have had children...
(3-4 year study programme) and postgraduate Master's degree (1-2 year study programme).
In Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
the Diplom
Diplom
A Diplom is an academic degree in the German-speaking countries Germany, Austria, and Switzerland and a similarly named degree in some other European countries including Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Estonia, Finland , Greece, Hungary, Russia, Serbia, Macedonia, Slovenia, and Ukraine...
(first degree after (usually) 4-6 years - from either a Universität (University
University
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
), a Technische Hochschule or a Kunsthochschule with university status) and the Magister
Magister (degree)
Magister is an academic degree used in various systems of higher education.-Argentina:...
had traditionally been equivalated to the Master's degree, the Magister being a degree after the study of two or three subjects (one main and one or two subsidiary subjects), as common in Humanities
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
or Liberal Arts
Liberal arts
The term liberal arts refers to those subjects which in classical antiquity were considered essential for a free citizen to study. Grammar, Rhetoric and Logic were the core liberal arts. In medieval times these subjects were extended to include mathematics, geometry, music and astronomy...
, whereas the Diplom is awarded after the study of one subject, commonly found in Natural Sciences, Social Sciences
Social sciences
Social science is the field of study concerned with society. "Social science" is commonly used as an umbrella term to refer to a plurality of fields outside of the natural sciences usually exclusive of the administrative or managerial sciences...
, Formal sciences and some Applied Sciences. The Fachhochschule
Fachhochschule
A Fachhochschule or University of Applied Sciences is a German type of tertiary education institution, sometimes specialized in certain topical areas . Fachhochschulen were founded in Germany and later adopted by Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Greece...
n or Universities of Applied Sciences conferred the Diplom (FH), whose length of study is between the Bachelor's and Master's degree. Under the harmonised system there is no legal academic difference between the Bachelor's and Master's degrees conferred by the Fachhochschulen and Universitäten.
The German Meister qualification for a master craftsman
Master craftsman
A master craftsman or master tradesman was a member of a guild. In the European guild system, only masters were allowed to be members of the guild....
is neither a degree nor is it comparable to the academic Master's degree. It, however, qualifies the holder to study at a University
University
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
or Fachhochschule
Fachhochschule
A Fachhochschule or University of Applied Sciences is a German type of tertiary education institution, sometimes specialized in certain topical areas . Fachhochschulen were founded in Germany and later adopted by Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland and Greece...
, whether the Meister holds the regular entry qualification (Abitur
Abitur
Abitur is a designation used in Germany, Finland and Estonia for final exams that pupils take at the end of their secondary education, usually after 12 or 13 years of schooling, see also for Germany Abitur after twelve years.The Zeugnis der Allgemeinen Hochschulreife, often referred to as...
or Fachhochschulreife) or not.
Ireland
Postgraduate Master's degrees in Ireland can either be taught degrees involving lectures, examination and a short dissertation, or research degrees. They usually are one of: MAMaster of Arts (Oxbridge)
In the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin, Bachelors of Arts of these universities are admitted to the degree of Master of Arts or Master in Arts on application after six or seven years' seniority as members of the university .There is no examination or study required for the degree...
(except Trinity College Dublin, where this is an undergraduate degree awarded 21 terms after matriculation, see 'MAs in Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin', below,) or MA
Master of Arts (Oxbridge)
In the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin, Bachelors of Arts of these universities are admitted to the degree of Master of Arts or Master in Arts on application after six or seven years' seniority as members of the university .There is no examination or study required for the degree...
, M.Sc., MBA, MAI, ME/MEng/MEngSc
Master of Engineering
A Master of Engineering or Master of Technology or Master of Science in Engineering A Master of Engineering (Magister in Ingeniaria) (abbreviated M.Eng., ME or MEng) or Master of Technology (abbreviated M.Tech. or MTech) or Master of Science in Engineering A Master of Engineering (Magister in...
, MPhil, LLM, MLitt, MArch
March
March is in present time held to be the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. It is one of the seven months which are 31 days long....
, MAgrSc, MSocSc, MCH
Master of Surgery
The Master of Surgery is an advanced qualification in surgery. It is most commonly abbreviated Ch.M. or M.S., as well as M.Ch. and M.Chir. from its Latin name, Magister Chirurgiae or the English form of Master of Surgery....
, MAcc
MACC
MACC is an acronym that can stand for the following items:*Master of Accountancy, a graduate professional degree designed to prepare students for public accounting....
, MEconSc.
With respect to NUI post graduate qualifications, in general there is a simple distinction between MA and MPhil. An MA is a combination of taught (classroom) and research-based modules, whilst an MPhil is composed exclusively of research-based learning.
The Magister in Arte Ingeniaria (MAI), literally meaning 'Master in the Art of Engineering', is awarded by the University of Dublin
University of Dublin
The University of Dublin , corporately designated the Chancellor, Doctors and Masters of the University of Dublin , located in Dublin, Ireland, was effectively founded when in 1592 Queen Elizabeth I issued a charter for Trinity College, Dublin, as "the mother of a university" – this date making it...
, Ireland, and is more usually referred to as Master of Engineering. While still available (via two routes), historically it was the engineering Master's degree taken by the university's BAI
Bachelor of Engineering
The Bachelor of Engineering is an undergraduate academic degree awarded to a student after three to five years of studying engineering at universities in Armenia, Australia, Bangladesh, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Denmark, Egypt, Finland , Germany, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Ireland, Jordan, Korea,...
graduates. Today the more common engineering Master's degree in the University of Dublin is the M.Sc..
A Master of Business Studies
Master of Business Studies
A Master of Business Studies refers to a qualification in the degree of master that can be obtained by students of recognized universities and colleges who complete the relevant approved programmes of study, pass the prescribed examinations, and fulfil all other prescribed conditions.- Typical...
(MBS) refers to a qualification in the degree of master that can be obtained by students of recognized universities and colleges who complete the relevant approved programmes of study, pass the prescribed examinations, and fulfil all other prescribed conditions. An MBS can be studied in the following areas: Electronic Business,Finance, Human Resource Management, International Business, Management Information System, Management & Organisation Studies, Management Consultancy, Marketing, Project Management, Strategic Management & Planning and can be obtained from many universities in Ireland including University College Dublin
University College Dublin
University College Dublin ) - formally known as University College Dublin - National University of Ireland, Dublin is the Republic of Ireland's largest, and Ireland's second largest, university, with over 1,300 faculty and 17,000 students...
.
The other universities in Ireland usually award a MEngSc, M.E.
Master of Engineering
A Master of Engineering or Master of Technology or Master of Science in Engineering A Master of Engineering (Magister in Ingeniaria) (abbreviated M.Eng., ME or MEng) or Master of Technology (abbreviated M.Tech. or MTech) or Master of Science in Engineering A Master of Engineering (Magister in...
, MEng
Meng
Meng can refer to the following:* Master of Engineering , an academic or professional master's degree in the field of engineering, the symbol used for the labiodental nasal consonantal sound...
or M.Sc. for their postgraduate Master's degree in engineering.
Italy
The old university system (Vecchio Ordinamento) consisted in a unique course, extended from four to five years or maximum of six (only Medicine), with a variable period (six-twelve months usually) for the thesis work. After the thesis discussion, students got the Master's DegreeMaster's degree
A master's is an academic degree granted to individuals who have undergone study demonstrating a mastery or high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice...
, simply called Laurea.
This system was reformed in 1999/2000 to comply to the Bologna process directives. The new university system (Nuovo Ordinamento) includes two levels of degrees: a three year Bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
, called Laurea di Primo Livello or just Laurea
Laurea
In Italy, the laurea is the main post-secondary academic degree.-Reforms due to the Bologna process:Spurred by the Bologna process, a major reform was instituted in 1999 to introduce easier university degrees comparable to the bachelors...
(e.g. Laurea di Primo Livello in Ingegneria Elettronica is Bachelor of Science in Electronic Engineering) and a two year course of specialization, leading to a Master's degree called Laurea di Secondo Livello, Laurea Specialistica or Laurea Magistrale (e.g. Laurea Specialistica in Ingegneria Elettronica is Master of Science in Electronic Engineering). Both degrees include a thesis work with final discussion.
A student can apply for the Ph.D. level course, called Dottorato di Ricerca
Dottorato di ricerca
The dottorato di ricerca is the highest Italian academic degree, the equivalent of a Ph.D.The dottorato is a relatively recent addition to the Italian academic landscape, having been instituted in 1980....
, only after getting a Master's degree
Master's degree
A master's is an academic degree granted to individuals who have undergone study demonstrating a mastery or high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice...
.
Medicine and some other school ("Facoltà"), notably Law, have adopted the reformed system only partially, keeping the previous unique course. Medicine is therefore still a six year course followed, possibly, by the specialization, requiring from three to six years more.
However, these Facoltà also have other courses organized according to the new system (e.g., Tecniche di radiologia medica for Medicine, Consulente del lavoro for Law)
Lithuania
There are three levels of degrees in Lithuania.The first level is Bachelor's degree ("bakalauras"). It is awarded after 4 years of study in a university ("universitetas") or after 3 years of study in a college ("kolegija"). Students of medicine have longer studies.
The second level, Master's degree ("magistras") is awarded after 2 years of further study at university. Bolognia process didn't influence much of the Lithuanian education system because most of it has been there since end of soviet era. One notable change is that now it is possible to apply to Master studies after 3 years study at a college ("kolegija"). Before the Bologna process the 4 years study at a university ("universitetas") was required. One notable exception probably is psychology studies. To enroll to Master of Psychology studies you have to have Bachelor of Psychology degree from university. The Bachelor of Psychology degree from college is not sufficient to enroll in Master of Psychology studies.
After completing Master degree student can study further for the third level - PhD
PHD
PHD may refer to:*Ph.D., a doctorate of philosophy*Ph.D. , a 1980s British group*PHD finger, a protein sequence*PHD Mountain Software, an outdoor clothing and equipment company*PhD Docbook renderer, an XML renderer...
degree ("daktaras") at a university.
Netherlands
In 2002, the Dutch degree system was changed to abide by international standards. This process was complicated by the fact that the Dutch higher education system has two separate branches, Hoger Beroeps Onderwijs (HBO, which indicates College or "University of Professional Education" level), and Wetenschappelijk Onderwijs (WO, which indicates University level). HBO level education focuses more on practical and professional education while WO is academic and scientific.Before the Bachelor/Master system was introduced, HBO graduates received the title baccalaureus (with the corresponding pre-nominal abbreviation "bc."), which was rarely used. On the other hand the HBO graduates with an engineering degree used the degree ingenieur, with pre-nominal abbreviation "ing.
Engineer's degree
An engineer's degree is an advanced academic degree in engineering that is conferred in Europe, some countries of Latin America, and a few institutions in the United States....
", which was (and still is) used quite commonly. WO degrees consisted of several different titles, such as doctorandus
Doctorandus
Doctorandus is a Dutch academic title according to the pre-bachelor-master system. The title is acquired by passing the doctoraalexamen, traditionally a matriculation exam for admission to study at doctoral level....
(pre-nominal abbreviated to drs., corresponds to MA
Master of Arts (postgraduate)
A Master of Arts from the Latin Magister Artium, is a type of Master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The M.A. is usually contrasted with the M.S. or M.Sc. degrees...
or MSc
MSC
- Computers:* Mario Strikers Charged* Microsoft Common Console Document, file for the Microsoft Management Console* Microelectronics Support Centre* Microsoft Corporation* MIDI Show Control* Message Sequence Chart...
), ingenieur (ir.
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
for WO level, corresponds to MSc) and meester in de rechten (mr., corresponds to LL.M.) These former titles are no longer granted (although they are still used, protected, and interchangeable with MA and MSc titles). The title of doctor (dr., corresponding to the PhD degree) is still awarded.
Prior to the education reform, a single program leading to the doctorandus, ingenieur or meester degree was in effect, which comprised the same course load as the Bachelor and Master programs put together. Those who had already started the doctorandus, ingenieur or meester program could, upon completing it, opt for the old degree (before their name), or simply use the Master's degree (behind their name) in accordance with the new standard. Since these graduates do not have a separate Bachelor's degree (which is in fact – in retrospect – incorporated into the program), the Master’s degree is their first academic degree.
In the new system, completed college (HBO) degrees are equivalent to a Bachelor's degree and are abbreviated to "B" with a subject suffix. Universities (WO) grant a Bachelor's degree for the general portion of the curriculum. This degree is a "Bachelor of Science" or "Bachelor of Arts" with the appropriate suffix.
Before one is admitted to a Master's program, one must have obtained a Bachelor's degree in the same field of study at the same level (although exceptions to this rule are possible, if the Bachelor's degree has nearly been obtained). This means that someone with a HBO Bachelor's degree cannot start a WO Master program; still, many universities offer a so-called 'bridge year', in which HBO degree holders can attain the WO Bachelor and continue into the WO Master program.
All fully completed curricula in the Netherlands are equivalent to Master's degrees with the addition of a "of Science" or "of Arts" to distinguish them from HBO Master's degrees, which are known simply as Master. WO Master's degrees focus on specialization in a sub-area of the general Bachelor's degree subject and typically take 1 year except for engineering studies where the Master takes 2 years.
HBO Master's are usually started only after several years of work and are similarly focusses on specialization. The title is signified by the abbreviation M and therefore an MBA would indicate a HBO Master's degree in business administration, but use of the MBA title is protected and it can only be granted by accredited schools.
Norway
A complete overview of the degrees before the Quality reform of 2003 is to be found at the Academic degree#Norway page.As a result of the Bologna-process and the Quality reform, the degree system of Norwegian higher education consists of the two main levels Bachelor's degree and Master's degree. A Bachelor's degree at a Norwegian university/university college is equivalent to an undergraduate degree and takes three years (with the exception of the teaching courses, where a Bachelor's degree lasts for four years). The Master's degrees are either fully integrated five-year programmes (admission does not require undergraduate degree) leading up to a graduate degree, or two-year courses at graduate level which require an already completed undergraduate degree. Following the graduate level, education is given at the doctoral level, usually through a four year research fellowship leading to a PhD.
Before the implementation of this system, various titles were given in accordance with the field of study and the length of the course. For instance, a three year undergraduate degree in engineering would give the title "høgskoleingeniør" (Bachelor's degree), and a 4,5 to 5 year graduate degree in engineering would give the title "sivilingeniør" (Master's degree). That being said, these titles are still very common and are, although formally abolished, degrees granted earlier (see Academic degree#Norway for a complete list) are still being used, also by academic personnel.
Poland
Currently there are two models of higher education in PolandPoland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
.
In the traditional model, a Master's degree is awarded after completion of a university curriculum — a 5 year programme in science courses at a university or other similar institution, with a project in the final year called magisterium (it can be translated as a Master of Arts or a Master of Science thesis) that often requires carrying out research in a given field. An MA degree is called a magister (abbreviated mgr) except for medical education, where it is called a lekarz (this gives the holder the right to use the title of physician and surgeon), a lekarz weterynarii in the veterinary field and a dentysta in field of dentistry. Universities of technology usually give the title of magister inżynier (abbreviated mgr inż.) corresponding to an MSc Eng degree.
More and more institutions introduce another model, which as of 2005 is still less popular. In this model, following the Bologna process
Bologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
directives, higher education is split into a 3 to 4-year Bachelor programme ending with a title of licencjat (non-technical) or inżynier (technical fields), and a 2-year programme (uzupełniające studia magisterskie) giving the title of magister or magister inżynier. Nevertheless, even in these institutions, it is often possible to bridge the Bachelor education directly into the Master programme, without formally obtaining the licencjat degree, thus shortening the time needed for completing the education slightly.
Depending on field and school, the timing may be slightly different.
Sweden
Prior to the full implementation of the Bologna Process in July 2007 degrees in SwedenSweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
could be divided between 'kandidat' (three years), 'magister' (four years), 'licentiat' ('magister' + 2–3 years of postgraduate studies) and 'doktor' ('magister' + 4–5 years of postgraduate studies). In engineering disciplines M.Sc was called 'civilingenjör', a four and a half year academic program concluded with a thesis. There was no direct equivalent to a B.Sc, however, a three year engineering degree with a more practical focus called 'högskoleingenjör' was close.
With the full implementation of the Bologna process in July 2007, a 'Master' (five years) was introduced in line with the criteria for the second cycle
Bologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
. The 'magister' will still exist alongside the new 'Master', but is expected to be largely neglected in favour of the new, internationally recognized degree. The M.Sc of engineering, 'civilingenjör', was expanded to five years and a new B.Sc was introduced to coexist with the unaltered 'högskoleingenjör'.
With Dissertation
In the UKUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, many universities now have four-year undergraduate programmes (or five-year in Scotland) mainly in the sciences or in engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
with a research project or Dissertation in the final year. The awards for these are named after the subject, so a course in mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
would earn a Master in Mathematics degree, (abbreviated to MMath), or have a general title such as MSci (Master in Science at most universities but Master of Natural Sciences at Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
), MBiomed, MBiochem, MChem, MComp, MPharm
Master of Pharmacy
A Master of Pharmacy is an academic degree in the field of pharmacy, which may be undergraduate or postgraduate depending on the country concerned. In many countries, it has superseded a Bachelor of Pharmacy as the prerequisite for registration to practice as a pharmacist...
, MEng
Meng
Meng can refer to the following:* Master of Engineering , an academic or professional master's degree in the field of engineering, the symbol used for the labiodental nasal consonantal sound...
, MMath, MPhys, MInf, MML, MDes, etc.
In content the first two years they are generally identical to those of the equivalent Bachelor's degree while the third and fourth years are a combination of higher-level taught courses and a research project.
An example of an undergraduate master's degree in the professions in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
is Pharmacy. In order to become a pharmacist, the undergraduate MPharm
Master of Pharmacy
A Master of Pharmacy is an academic degree in the field of pharmacy, which may be undergraduate or postgraduate depending on the country concerned. In many countries, it has superseded a Bachelor of Pharmacy as the prerequisite for registration to practice as a pharmacist...
must be completed, followed by one year of pre-registration experience. A similar situation exists as regards Engineering
Master of Engineering
A Master of Engineering or Master of Technology or Master of Science in Engineering A Master of Engineering (Magister in Ingeniaria) (abbreviated M.Eng., ME or MEng) or Master of Technology (abbreviated M.Tech. or MTech) or Master of Science in Engineering A Master of Engineering (Magister in...
.
The ancient universities of Scotland
Ancient universities of Scotland
The ancient universities of Scotland are medieval and renaissance universities which continue to exist until the present day. The majority of the ancient universities of the British Isles are located within Scotland, and have a number of distinctive features in common, being governed by a series of...
(St Andrews
University of St Andrews
The University of St Andrews, informally referred to as "St Andrews", is the oldest university in Scotland and the third oldest in the English-speaking world after Oxford and Cambridge. The university is situated in the town of St Andrews, Fife, on the east coast of Scotland. It was founded between...
, Glasgow
University of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow is the fourth-oldest university in the English-speaking world and one of Scotland's four ancient universities. Located in Glasgow, the university was founded in 1451 and is presently one of seventeen British higher education institutions ranked amongst the top 100 of the...
, Aberdeen
University of Aberdeen
The University of Aberdeen, an ancient university founded in 1495, in Aberdeen, Scotland, is a British university. It is the third oldest university in Scotland, and the fifth oldest in the United Kingdom and wider English-speaking world...
, Edinburgh
University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh, founded in 1583, is a public research university located in Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland, and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university is deeply embedded in the fabric of the city, with many of the buildings in the historic Old Town belonging to the university...
) and Dundee
University of Dundee
The University of Dundee is a university based in the city and Royal burgh of Dundee on eastern coast of the central Lowlands of Scotland and with a small number of institutions elsewhere....
award a Master of Arts
Master of Arts (Scotland)
A Master of Arts in Scotland can refer to an undergraduate academic degree in humanities and social sciences awarded by the ancient universities of Scotland – the University of St Andrews, the University of Glasgow, the University of Aberdeen and the University of Edinburgh, while the University of...
(MA) as a prestigious undergraduate degree after four years of study in Arts, Humanities or Social Sciences.
Without Dissertation
There exist undergraduate master's courses for which completion of a dissertation is not required, with attainment being measured either purely by examination, or through a combination of testing and shorter written work. One such course is the four-year Oxford MMath course, in which a dissertation is optional.The Master of Arts
Master of Arts (Oxbridge)
In the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin, Bachelors of Arts of these universities are admitted to the degree of Master of Arts or Master in Arts on application after six or seven years' seniority as members of the university .There is no examination or study required for the degree...
(MA) is awarded by the universities of Oxford
University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a university located in Oxford, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest surviving university in the world and the oldest in the English-speaking world. Although its exact date of foundation is unclear, there is evidence of teaching as far back as 1096...
, Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
and Trinity College, Dublin
Trinity College, Dublin
Trinity College, Dublin , formally known as the College of the Holy and Undivided Trinity of Queen Elizabeth near Dublin, was founded in 1592 by letters patent from Queen Elizabeth I as the "mother of a university", Extracts from Letters Patent of Elizabeth I, 1592: "...we...found and...
—without further examination— to those entitled to the degree of Bachelor of Arts
Bachelor of Arts
A Bachelor of Arts , from the Latin artium baccalaureus, is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate course or program in either the liberal arts, the sciences, or both...
.
Postgraduate Master's degrees
Postgraduate Master's degrees in the United Kingdom can either be taught degrees involving lectures, examination and a short dissertation, or research degrees (though the latter have largely been replaced by MPhil and MRes programmes, see below). Taught Master's programmes involve 1 or 2 years of full-time study. The programmes are often very intensive and demanding, and concentrate on one very specialised area of knowledge. Some universities also offer a Master's by Learning Contract scheme, where a candidate can specify his or her own learning objectives; these are submitted to supervising academics for approval, and are assessed by means of written reports, practical demonstrations and presentations.Taught postgraduate Master's degrees
(MScMSC
- Computers:* Mario Strikers Charged* Microsoft Common Console Document, file for the Microsoft Management Console* Microelectronics Support Centre* Microsoft Corporation* MIDI Show Control* Message Sequence Chart...
, MA
Master of Arts (postgraduate)
A Master of Arts from the Latin Magister Artium, is a type of Master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The M.A. is usually contrasted with the M.S. or M.Sc. degrees...
, LL.M., MLitt, MSSc, MSt
MST
MST may refer to:Science and technology* Madison Symmetric Torus, a physics device at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, U.S.* Mean Square for Treatments, in analysis of variance...
, MEnt
MENT
MENT may refer* A brand name for a hormone* Trestolone a synthetic androgen developed for male contraception* Myeloid and erythroid nuclear termination stage specific protein a member of the serpin family of protease inhibitors...
etc.)
The most common types of postgraduate taught Master's degrees are the Master of Arts
Master of Arts (postgraduate)
A Master of Arts from the Latin Magister Artium, is a type of Master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The M.A. is usually contrasted with the M.S. or M.Sc. degrees...
(MA) awarded in Arts
ARts
aRts, which stands for analog Real time synthesizer, is an audio framework that is no longer under development. It is best known for previously being used in KDE to simulate an analog synthesizer....
, Humanities
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
, Theology
Theology
Theology is the systematic and rational study of religion and its influences and of the nature of religious truths, or the learned profession acquired by completing specialized training in religious studies, usually at a university or school of divinity or seminary.-Definition:Augustine of Hippo...
and Social Sciences
Social sciences
Social science is the field of study concerned with society. "Social science" is commonly used as an umbrella term to refer to a plurality of fields outside of the natural sciences usually exclusive of the administrative or managerial sciences...
and the Master of Science
Master of Science
A Master of Science is a postgraduate academic master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The degree is typically studied for in the sciences including the social sciences.-Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay:...
(MSc) awarded in pure and applied
Applied science
Applied science is the application of scientific knowledge transferred into a physical environment. Examples include testing a theoretical model through the use of formal science or solving a practical problem through the use of natural science....
Science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
. A number of taught programs in Social Sciences
Social sciences
Social science is the field of study concerned with society. "Social science" is commonly used as an umbrella term to refer to a plurality of fields outside of the natural sciences usually exclusive of the administrative or managerial sciences...
also receive the Master of Science
Master of Science
A Master of Science is a postgraduate academic master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The degree is typically studied for in the sciences including the social sciences.-Brazil, Argentina and Uruguay:...
(MSc) degree (e.g. MSc Development Studies
Development studies
Development studies is a multidisciplinary branch of social science which addresses issues of concern to developing countries. It has historically placed a particular focus on issues related to social and economic development, and its relevance may therefore extend to communities and regions...
at the London School of Economics
London School of Economics
The London School of Economics and Political Science is a public research university specialised in the social sciences located in London, United Kingdom, and a constituent college of the federal University of London...
and University of Bath
University of Bath
The University of Bath is a campus university located in Bath, United Kingdom. It received its Royal Charter in 1966....
).
However, some universities - particularly those in Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
- award the Master of Letters
Master of Letters
The Master of Letters is a postgraduate degree.- United Kingdom :The MLitt is a postgraduate degree awarded by a select few British and Irish universities, predominantly within the ancient English and Scottish universities.- England :Within the English University system MLitts are not universally...
(MLitt) to students in the Arts
ARts
aRts, which stands for analog Real time synthesizer, is an audio framework that is no longer under development. It is best known for previously being used in KDE to simulate an analog synthesizer....
, Humanities
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
, Divinity
Divinity (academic discipline)
Divinity is the study of Christian and other theology and ministry at a school, divinity school, university, or seminary. The term is sometimes a synonym for theology as an academic, speculative pursuit, and sometimes is used for the study of applied theology and ministry to make a distinction...
and Social Sciences
Social sciences
Social science is the field of study concerned with society. "Social science" is commonly used as an umbrella term to refer to a plurality of fields outside of the natural sciences usually exclusive of the administrative or managerial sciences...
, often with the suffix (T) to indicate it is a taught degree, to avoid confusion with the MLitt (see Research postgraduate Master's degrees below). In the universities of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
and Oxford
University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a university located in Oxford, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest surviving university in the world and the oldest in the English-speaking world. Although its exact date of foundation is unclear, there is evidence of teaching as far back as 1096...
on the other hand, the MPhil is a taught master's degree (normally also including a short research component), whereas the MLitt and the MSc degrees are offered as pure research degrees only. Some other universities, such as the University of Glasgow
University of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow is the fourth-oldest university in the English-speaking world and one of Scotland's four ancient universities. Located in Glasgow, the university was founded in 1451 and is presently one of seventeen British higher education institutions ranked amongst the top 100 of the...
, previously used the designation MPhil for both taught and research Master's degrees, but have recently changed the taught appellation to MLitt.
In Law
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
the standard taught degree is the Master of Laws, but certain courses may lead to the award of MA or MLitt.
Until recently, both the undergraduate and postgraduate Master's degrees were awarded without grade or class (like the class of an honours degree). Nowadays however, Master's degrees may be classified into a maximum of four categories (Distinction, Merit, Pass or Fail), while others can have a more simplified form of assessment by only distinguishing between a Pass or a Fail.
Research postgraduate Master's degrees
(MPhil and MRes)The Master of Philosophy (MPhil) is a research degree awarded for the completion of a thesis. It is a shorter version of the Ph.D.
Doctor of Philosophy
Doctor of Philosophy, abbreviated as Ph.D., PhD, D.Phil., or DPhil , in English-speaking countries, is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities...
and some universities routinely enter potential PhD students into the MPhil programme and allow them to upgrade to the full PhD programme a year or two into the course. Advanced candidates for a taught postgraduate Master's sometimes undertake the MPhil as it is considered a more prestigious degree, but it may also mean that the student could not afford or could not complete the full PhD.
The Master of Research (MRes) degree is a more structured and organised version of the MPhil, usually designed to prepare a student for a career in research. For example, an MRes may combine individual research with periods of work placement in research establishments. MRes is considered a really prestigious degree.
The Master of Letters (MLitt) degree is a two-year research degree at many universities, including Cambridge and the ancient Scottish universities, and is generally awarded when a student cannot or will not complete the final year(s) of their PhD
PHD
PHD may refer to:*Ph.D., a doctorate of philosophy*Ph.D. , a 1980s British group*PHD finger, a protein sequence*PHD Mountain Software, an outdoor clothing and equipment company*PhD Docbook renderer, an XML renderer...
and so writes their research up for the MLitt. Because MLitt is also used for a taught degree, the suffix (T) or (R) for taught or research is often added, so the more prestigious two-year research degree is called MLitt (R).
Like the PhD, the MPhil and MRes degrees are generally awarded without class or grade as a pass (the standard grade) or can, rarely, be awarded with a distinction.
MAs in Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin
The universities of OxfordUniversity of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a university located in Oxford, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest surviving university in the world and the oldest in the English-speaking world. Although its exact date of foundation is unclear, there is evidence of teaching as far back as 1096...
, Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
and Dublin
University of Dublin
The University of Dublin , corporately designated the Chancellor, Doctors and Masters of the University of Dublin , located in Dublin, Ireland, was effectively founded when in 1592 Queen Elizabeth I issued a charter for Trinity College, Dublin, as "the mother of a university" – this date making it...
award Master's degrees to BAs without further examination, where seven years after matriculation
Matriculation
Matriculation, in the broadest sense, means to be registered or added to a list, from the Latin matricula – little list. In Scottish heraldry, for instance, a matriculation is a registration of armorial bearings...
have passed, and (in some but not all cases) upon payment of a nominal fee. It is commonplace for recipients of the degree to have graduated several years previously and to have had little official contact with the university or academic life since then. The only real significance of these degrees is that they historically conferred voting rights in University elections, it was seen as the point at which one became eligible to teach at the University and certain other privileges e.g. the right to dine at the holder's college's high table. They still do confer some restricted and rarely used voting rights. The MAs awarded by Oxford and Cambridge are colloquially known as the Oxbridge MA
Master of Arts (Oxbridge)
In the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge and Dublin, Bachelors of Arts of these universities are admitted to the degree of Master of Arts or Master in Arts on application after six or seven years' seniority as members of the university .There is no examination or study required for the degree...
, and that from Dublin as the Trinity MA, and would be usually distinguished respectively: MA (Oxon.), MA (Cantab.) and MA (Dubl.). "Oxon." here is short for Oxoniensis, "Cantab." for Cantabrigiensis, "Dubl." for Dubliniensis, meaning "of Oxford", "of Cambridge", and "of Dublin" respectively. The Universities of Cambridge and Dublin also offer an MA to certain senior staff - both academic and non-academic - after a number of years' employment with the university.
Until the advent of the modern research university in the mid 19th century, several other British and American universities also gave such degrees "in course".
Scottish MA
In ScotlandScotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
the first degree in Arts
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
, Fine Art
Fine art
Fine art or the fine arts encompass art forms developed primarily for aesthetics and/or concept rather than practical application. Art is often a synonym for fine art, as employed in the term "art gallery"....
, Humanities
Humanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
and Social Sciences awarded by the ancient universities of Scotland
Ancient universities of Scotland
The ancient universities of Scotland are medieval and renaissance universities which continue to exist until the present day. The majority of the ancient universities of the British Isles are located within Scotland, and have a number of distinctive features in common, being governed by a series of...
is the Master of Arts
Master of Arts (Scotland)
A Master of Arts in Scotland can refer to an undergraduate academic degree in humanities and social sciences awarded by the ancient universities of Scotland – the University of St Andrews, the University of Glasgow, the University of Aberdeen and the University of Edinburgh, while the University of...
. It should be noted the Science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
and Law
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
faculties of Scottish universities award the BSc
BSC
BSC is a three-letter abbreviation that may refer to:Science and technology* Bachelor of Science , an undergraduate degree* Base Station Controller, part of a mobile phone network; see: Base Station subsystem...
and LLB degrees respectively and the New Universities
New Universities
The term new universities has been used informally to refer to several different waves of new universities created or renamed as such in the United Kingdom. As early as 1928, the term was used to describe the then-new civic universities, such as Bristol University and the other "red brick...
generally award the BA. The Scottish MA is roughly equivalent to an advanced BA from a University elsewhere in the United Kingdom, as it is an undergraduate degree. However, Scottish university courses are four years in length rather than the usual UK degrees, which last for only three years (but this is also true of Scottish BSc and LLB degrees). Trinity College Dublin courses are also four years in length.
Other approaches
As indicated above, even though higher education systems in Europe try to comply with the Bologna processBologna process
The purpose of the Bologna Process is the creation of the European Higher Education Area by making academic degree standards and quality assurance standards more comparable and compatible throughout Europe, in particular under the Lisbon Recognition Convention...
, the process is not yet fully accomplished. Differences in methodology and curricula are still widely different in some cases. To mitigate this, several initiatives and approaches are currently tried, some of them with the support of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
institutions. Either in partnership or as private consortia, networks of universities in different countries are trying to work out shared curricula and adopt similar methodologies. In niche educational areas like translation
Translation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. Whereas interpreting undoubtedly antedates writing, translation began only after the appearance of written literature; there exist partial translations of the Sumerian Epic of...
and interpreting
Interpreting
Language interpretation is the facilitating of oral or sign-language communication, either simultaneously or consecutively, between users of different languages...
this has proved successful and the networks have become functional, i.e. European Master's in Translation
European Master's in Translation
The European Master's in Translation is a partnership project between the Directorate-General for Translation and a number of universities from different European countries. The initial project was launched in 2006 and a network was officially formed in December 2009, following a selection...
and the European Master's in Conference Interpreting . While these are not mainstream developments, it may be noted that in these networks of universities a similar Master's degree certificate is offered for a given field, and the network/consortium collectively guarantees that these degrees have a high level of convergence.

