
Liberal arts
Encyclopedia
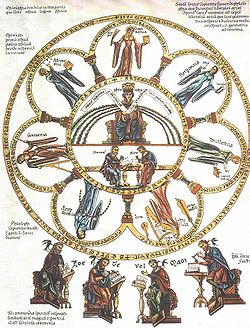
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
were considered essential for a free citizen to study. Grammar
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of structural rules that govern the composition of clauses, phrases, and words in any given natural language. The term refers also to the study of such rules, and this field includes morphology, syntax, and phonology, often complemented by phonetics, semantics,...
, Rhetoric
Rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of discourse, an art that aims to improve the facility of speakers or writers who attempt to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences in specific situations. As a subject of formal study and a productive civic practice, rhetoric has played a central role in the Western...
and Logic
Logic
In philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
were the core liberal arts. In medieval times
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
these subjects (called the Trivium) were extended to include mathematics, geometry, music and astronomy (which included the study of astrology
Astrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
). This extended curriculum was called the Quadrivium. Together the Trivium and Quadrivium constituted the seven liberal arts of the medieval university curriculum.
In modern times liberal arts refers to an educational curriculum that is designed to produce a well-rounded individual suitable for citizenship. Therefore a liberal arts education imparts general knowledge to develop the student’s intellectual ability to reason and argue, unlike the professional
Professional
A professional is a person who is paid to undertake a specialised set of tasks and to complete them for a fee. The traditional professions were doctors, lawyers, clergymen, and commissioned military officers. Today, the term is applied to estate agents, surveyors , environmental scientists,...
, vocational, and technical
Technical
Technical may refer to:*Technical , a fighting vehicle based on a pickup truck*Technical analysis, a discipline for forecasting the future direction of prices through the study of past market data*Technical drawing, also known as drafting...
curricula which emphasize specialization. The contemporary liberal arts comprise studying literature
Literature
Literature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
, languages, philosophy
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
, history
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
, mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, psychology
Psychology
Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society...
, and science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
.
History
In classical antiquityClassical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
, the "liberal arts" denoted those subjects of study that were considered essential for a free person (Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
: liber, "free") to master in order to acquire those qualities that distinguished a free person from slaves
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
- the latter of whom formed the greater number of the population in the classical world. Contrary to popular belief, freeborn girls were as likely to receive formal education as boys, especially during the Roman Empire—unlike the lack-of-education, or purely manual/technical skills, proper to a slave
Slavery in ancient Rome
The institution of slavery in ancient Rome played an important role in society and the Roman economy. Besides manual labor on farms and in mines, slaves performed many domestic services and a variety of other tasks, such as accounting...
. The "liberal arts" or "liberal pursuits" (Latin liberalia studia) were already so called in formal education during the Roman Empire; for example, Seneca the Younger
Seneca the Younger
Lucius Annaeus Seneca was a Roman Stoic philosopher, statesman, dramatist, and in one work humorist, of the Silver Age of Latin literature. He was tutor and later advisor to emperor Nero...
discusses liberal arts in education from a critical Stoic point of view in Moral Epistle 88. The subjects that would become the standard "Liberal Arts" in Roman and Medieval times already comprised the basic curriculum in the enkuklios paideia or "education in a circle" of late Classical and Hellenistic Greece.
In the 5th century AD, Martianus Capella
Martianus Capella
Martianus Minneus Felix Capella was a pagan writer of Late Antiquity, one of the earliest developers of the system of the seven liberal arts that structured early medieval education...
defined the seven Liberal Arts as: grammar
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of structural rules that govern the composition of clauses, phrases, and words in any given natural language. The term refers also to the study of such rules, and this field includes morphology, syntax, and phonology, often complemented by phonetics, semantics,...
, dialectic
Dialectic
Dialectic is a method of argument for resolving disagreement that has been central to Indic and European philosophy since antiquity. The word dialectic originated in Ancient Greece, and was made popular by Plato in the Socratic dialogues...
, rhetoric
Rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of discourse, an art that aims to improve the facility of speakers or writers who attempt to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences in specific situations. As a subject of formal study and a productive civic practice, rhetoric has played a central role in the Western...
, arithmetic
Arithmetic
Arithmetic or arithmetics is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple day-to-day counting to advanced science and business calculations. It involves the study of quantity, especially as the result of combining numbers...
, geometry
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, music
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
, and astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
. In the medieval Western university
Medieval university
Medieval university is an institution of higher learning which was established during High Middle Ages period and is a corporation.The first institutions generally considered to be universities were established in Italy, France, and England in the late 11th and the 12th centuries for the study of...
, the seven liberal arts were divided in two parts:
- the Trivium
- grammarGrammarIn linguistics, grammar is the set of structural rules that govern the composition of clauses, phrases, and words in any given natural language. The term refers also to the study of such rules, and this field includes morphology, syntax, and phonology, often complemented by phonetics, semantics,...
- logicLogicIn philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
- rhetoricRhetoricRhetoric is the art of discourse, an art that aims to improve the facility of speakers or writers who attempt to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences in specific situations. As a subject of formal study and a productive civic practice, rhetoric has played a central role in the Western...
- the QuadriviumQuadriviumThe quadrivium comprised the four subjects, or arts, taught in medieval universities, after teaching the trivium. The word is Latin, meaning "the four ways" , and its use for the 4 subjects has been attributed to Boethius or Cassiodorus in the 6th century...
- arithmeticArithmeticArithmetic or arithmetics is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple day-to-day counting to advanced science and business calculations. It involves the study of quantity, especially as the result of combining numbers...
- geometryGeometryGeometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
- musicMusicMusic is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
- astronomyAstronomyAstronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, often called astrologyAstrologyAstrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
; both modern senses were covered
Basics
Mathematics, science, arts, and language are all parts of the liberal arts. In the middle ages, the liberal arts were synonymous with introductory courses in branches of the sciences, mathematics, and in the study of writing. Some subsections of the liberal arts are trivium-the verbal arts- logic, grammar, and rhetoric, and quadrivium-the numerical arts- mathematics, geometry, music, and astronomy. Analyzing and interpreting information is also studied. Experience in Liberal Arts gives experience forming and expressing well rounded opinions.Academic areas that are included within the Liberal arts
Liberal arts
The term liberal arts refers to those subjects which in classical antiquity were considered essential for a free citizen to study. Grammar, Rhetoric and Logic were the core liberal arts. In medieval times these subjects were extended to include mathematics, geometry, music and astronomy...
include:
- Great BooksGreat BooksGreat Books refers primarily to a group of books that tradition, and various institutions and authorities, have regarded as constituting or best expressing the foundations of Western culture ; derivatively the term also refers to a curriculum or method of education based around a list of such books...
- HistoryHistoryHistory is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
- LanguageLanguageLanguage may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
s including English - LinguisticsLinguisticsLinguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
- LiteratureLiteratureLiterature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
- MathematicsMathematicsMathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
- MusicMusic educationMusic education is a field of study associated with the teaching and learning of music. It touches on all domains of learning, including the psychomotor domain , the cognitive domain , and, in particular and significant ways,the affective domain, including music appreciation and sensitivity...
- PhilosophyPhilosophyPhilosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
- Political SciencePolitical sciencePolitical Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
- PsychologyPsychologyPsychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society...
- Religious studiesReligious studiesReligious studies is the academic field of multi-disciplinary, secular study of religious beliefs, behaviors, and institutions. It describes, compares, interprets, and explains religion, emphasizing systematic, historically based, and cross-cultural perspectives.While theology attempts to...
- ScienceScienceScience is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
- TheaterDrama schoolA drama school or theatre school is an undergraduate and/or graduate school or department at a college or university; or a free-standing institution ; which specialises in the pre-professional training in drama and theatre arts, such as acting, design and technical theatre, arts administration, and...
In the United States
In the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, liberal arts college
Liberal arts college
A liberal arts college is one with a primary emphasis on undergraduate study in the liberal arts and sciences.Students in the liberal arts generally major in a particular discipline while receiving exposure to a wide range of academic subjects, including sciences as well as the traditional...
s are schools emphasizing undergraduate study in the liberal arts. Traditionally earned over four years of full-time study, the student earned either a Bachelor of Arts
Bachelor of Arts
A Bachelor of Arts , from the Latin artium baccalaureus, is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate course or program in either the liberal arts, the sciences, or both...
degree or a Bachelor of Science
Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science is an undergraduate academic degree awarded for completed courses that generally last three to five years .-Australia:In Australia, the BSc is a 3 year degree, offered from 1st year on...
degree; on completing undergraduate study, students might progress to either a graduate school or a professional school
Professional school
A professional school is a school type that prepares students for careers in specific fields.Examples of this type of school include:* Architecture school* Business school* Dental school* Education school* Journalism school* Law school* Library school...
(public administration
Public administration
Public Administration houses the implementation of government policy and an academic discipline that studies this implementation and that prepares civil servants for this work. As a "field of inquiry with a diverse scope" its "fundamental goal.....
, engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
, business
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
, law
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
, medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
, theology
Theology
Theology is the systematic and rational study of religion and its influences and of the nature of religious truths, or the learned profession acquired by completing specialized training in religious studies, usually at a university or school of divinity or seminary.-Definition:Augustine of Hippo...
). The teaching is Socratic
Socratic method
The Socratic method , named after the classical Greek philosopher Socrates, is a form of inquiry and debate between individuals with opposing viewpoints based on asking and answering questions to stimulate critical thinking and to illuminate ideas...
, typically with small classes, and often boasts a lower teacher-to-student ratio than at large universities; professors teaching classes are allowed to concentrate more on their teaching responsibilities than primary research professors
Professors in the United States
In the U.S., "Professors" commonly occupy any of several positions in academia, typically the ranks of Assistant Professor, Associate Professor or Full Professor....
or graduate student teaching assistants, in contrast to the instruction common in universities. Despite the European origin of the liberal arts college, the term liberal arts college usually denotes liberal arts colleges in the United States
Liberal arts colleges in the United States
Liberal arts colleges in the United States are certain undergraduate institutions of higher education in the United States. The Encyclopædia Britannica Concise offers a definition of the liberal arts as a "college or university curriculum aimed at imparting general knowledge and developing general...
. Only recently, some efforts have been undertaken to "re-import" liberal arts education to continental Europe, as with University College Utrecht
University College Utrecht
University College Utrecht is an international Honors College of Utrecht University . UCU is a selective liberal arts, undergraduate college of 700 students within Utrecht University. Located between the two UU sites, Uithof and City Center, it has its own residential campus in the city of...
, University College Maastricht
University College Maastricht
University College Maastricht is an English language, internationally oriented, liberal arts and sciences college housed in the 15th century Nieuwenhof monastery in Maastricht, the Netherlands. Founded in 2002, it is the second of its kind in the Netherlands...
, Amsterdam University College
Amsterdam University College
Amsterdam University College was established in 2009 as a joint excellence initiative of the VU University and University of Amsterdam. AUC’s motto is Excellence and Diversity in a Global City. The college offers a three-year English taught Bachelor honours programme in the liberal arts and...
, Roosevelt Academy
Roosevelt Academy
Roosevelt Academy is a small liberal arts college located in Middelburg in the Netherlands. It offers a residential setting and is an international honors college of Utrecht University.-History:...
, and the European College of Liberal Arts
European College of Liberal Arts
The European College of Liberal Arts is a private, non-profit institution of higher education in Berlin, Germany. It was founded as a non-profit association in 1999 under the leadership of Stephan Gutzeit. The founding dean was Erika Anita Kiss. Since 2003, Peter Hajnal and Thomas Norgaard have...
Berlin. As well as the colleges listed above, some universities in the Netherlands offer bachelors programmes in Liberal Arts and Sciences (Tilburg University), as will King's College London
King's College London
King's College London is a public research university located in London, United Kingdom and a constituent college of the federal University of London. King's has a claim to being the third oldest university in England, having been founded by King George IV and the Duke of Wellington in 1829, and...
and University College London
University College London
University College London is a public research university located in London, United Kingdom and the oldest and largest constituent college of the federal University of London...
in the United Kingdom from 2012. It is the curriculum of Forman Christian College
Forman Christian College
Forman Christian College University, or FCCU, is a chartered university in Lahore, Pakistan, named after its American-born founder, Dr. Charles William Forman.- History :...
in Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
for Bachelors, the only institute in the country which offers this program.
See also
- Bachelor of ArtsBachelor of ArtsA Bachelor of Arts , from the Latin artium baccalaureus, is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate course or program in either the liberal arts, the sciences, or both...
- Bachelor of General StudiesBachelor of General StudiesA Bachelor of General Studies degree is an undergraduate degree, offered by many universities in the Western World. It is very similar to a Bachelor of Arts or Liberal Arts degree, although there are often fewer requirements for studies in humanities and social sciences...
- Bachelor of Liberal ArtsBachelor of Liberal ArtsThe Bachelor of Liberal Arts is the title of an undergraduate academic degree. Generally, it is awarded to students who major in liberal arts, pursue interdisciplinary studies, or design their own concentrations....
- Bachelor of Liberal StudiesBachelor of Liberal StudiesThe purpose of the Bachelor of Liberal Studies degree is to provide students with a solid multidisciplinary preparation in the Humanities, Natural Sciences, Social Sciences and the Arts, subsequently allowing them to pursue careers in education, business, government, and other such fields...
- Doctor of Liberal StudiesDoctor of Liberal StudiesThe Doctor of Liberal Studies degree, abbreviated ,for the Latin Doctor Liberalium Studiorum, is an advanced academic degree. Georgetown University in Washington, D.C was the first university in the world to offer the Doctor of Liberal Studies degree. The Doctor of Liberal Studies degree is...
- Great Books Program
- Great Books Programs in CanadaGreat Books Programs in CanadaGreat Books Programs in Canada are university/college programs inspired by the Great Books movement begun in the United States in the 1920s. The aim of such programs is to return to the Western Liberal Arts tradition in education...
- Liberal arts collegeLiberal arts collegeA liberal arts college is one with a primary emphasis on undergraduate study in the liberal arts and sciences.Students in the liberal arts generally major in a particular discipline while receiving exposure to a wide range of academic subjects, including sciences as well as the traditional...
- Liberal educationLiberal educationA Liberal education is a system or course of education suitable for the cultivation of a free human being. It is based on the medieval concept of the liberal arts or, more commonly now, the liberalism of the Age of Enlightenment...
- Master of Liberal Studies
- The Mechanical ArtsArtes Mechanicae"Mechanical arts": a medieval concept of ordered practices or skills, often juxtaposed to the traditional seven liberal arts Artes liberales. Also called "servile" and considered "vulgar", from antiquity they had been deemed unbecoming for a free man, as ministering to baser needs.Already Johannes...
Further reading
- Blaich, Charles, Anne Bost, Ed Chan, and Richard Lynch. "Defining Liberal Arts Education." Center of Inquiry in the Liberal Arts, 2004.
- Blanshard, BrandBrand BlanshardPercy Brand Blanshard was an American philosopher known primarily for his defense of reason. A powerful polemicist, by all accounts he comported himself with courtesy and grace in philosophical controversies and exemplified the "rational temper" he advocated.-Life:Brand Blanshard was born August...
. The Uses of a Liberal Education: And Other Talks to Students. (Open Court, 1973. ISBN 0-8126-9429-5) - Friedlander, Jack. Measuring the Benefits of Liberal Arts Education in Washington's Community Colleges. Los Angeles: Center for the Study of Community Colleges, 1982a. (ED 217 918)
- Joseph, Sister MiriamSister Miriam JosephSister Miriam Joseph Rauh, C.S.C, Ph.D. was a member of the Sisters of the Holy Cross. She received her doctorate from Columbia University and was professor of English at Saint Mary's College from 1931 to 1960. She is the author of several books including The Trivium which is a text she developed...
. The Trivium: The Liberal Arts of Logic, Grammar, and Rhetoric. Paul Dry Books Inc, 2002. - Pfnister, Allen O. "The Role of the Liberal Arts College." The Journal of Higher Education. Vol. 55, No. 2 (March/April 1984): 145–170.
- Reeves, Floyd W. "The Liberal-Arts College." The Journal of Higher Education. Vol. 1, No. 7 (1930): 373–380.
- Seidel, George. "Saving the Small College." The Journal of Higher Education. Vol. 39, No. 6 (1968): 339–342.
- Winterer, Caroline.The Culture of Classicism: Ancient Greece and Rome in American Intellectual Life, 1780–1910. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2002.
- Wriston, Henry M.Henry WristonHenry Merritt Wriston was a United States' educator, presidential advisor, and served as president at both Brown University and Lawrence University.-Biography:...
The Nature of a Liberal College. Lawrence University Press, 1937.
External links
- The Annapolis Group/College News
- The Classical Liberal Arts Academy
- Philosophy of Liberal Education
- Liberal Arts at the Community College
- A Descriptive Analysis of the Community College Liberal Arts Curriculum
- The Center of Inquiry in the Liberal Arts
- Academic Commons
- Trivium Education
- CatholiCity: Catholic Encyclopedia
- What are the liberal arts? at liberalartsadvantage.com

