
Maurotoxin
Encyclopedia
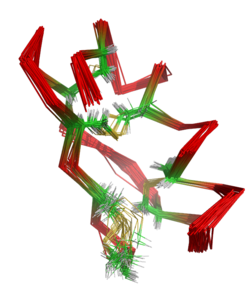

Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
toxin
Toxin
A toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
from the venom of the Tunisian chactoid scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
Scorpio maurus palmatus, from which it was first isolated and from which the chemical gets its name. It acts by blocking several types of voltage-gated potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channel
Voltage-gated potassium channels are transmembrane channels specific for potassium and sensitive to voltage changes in the cell's membrane potential. During action potentials, they play a crucial role in returning the depolarized cell to a resting state....
.
Chemistry
Maurotoxin is a peptide of 34 amino acidAmino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s cross-linked by four disulfide bridges, with an atypical pattern of organization compared with other scorpion toxins; this unusual pairing of cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
residues may be mediated by the presence of adjacent proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
s. The peptide contains an alpha helix
Alpha helix
A common motif in the secondary structure of proteins, the alpha helix is a right-handed coiled or spiral conformation, in which every backbone N-H group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid four residues earlier...
linked by two disulfide bridges to a two-stranded antiparallel beta sheet
Beta sheet
The β sheet is the second form of regular secondary structure in proteins, only somewhat less common than the alpha helix. Beta sheets consist of beta strands connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet...
.
Target
Scorpion toxins constitute the largest group of potassiumPotassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
(K+) channel blockers and are useful pharmacological probes to investigate ion channels and their functions.
Maurotoxin (MTX) blocks various K+ -channels:
- ApaminApaminApamin is an 18 amino acid peptide neurotoxin found in apitoxin . It selectively blocks SK channels, a type of Ca2+-activated K+ channel expressed in the central nervous system and smooth muscle...
-sensitive small conductance Ca2+CalciumCalcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
- activated K+PotassiumPotassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
channels (SK) - Intermediate conductance Ca2+ - activated K+ channels (IK)
- Several types of voltage-gated potassium channelVoltage-gated potassium channelVoltage-gated potassium channels are transmembrane channels specific for potassium and sensitive to voltage changes in the cell's membrane potential. During action potentials, they play a crucial role in returning the depolarized cell to a resting state....
s (Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.3 and shaker B)
The structural and pharmacological features of MTX suggest that MTX belongs to a new class of natural K+ channel blockers structurally intermediate between the Na+ (60–70 residues and four disulfide bridges) and K+ channel scorpion toxin families (less than 40 residues and three disulfide bridges).
The intermediate conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (IK) channel is present in peripheral tissues, including secretory epithelia and blood cell
Blood cell
A blood cell, also called a hematocyte, is a cell normally found in blood. In mammals, these fall into three general categories:* red blood cells — Erythrocytes* white blood cells — Leukocytes* platelets — Thrombocytes...
s. An important physiological role of the IK channel is to help maintain large electrical gradients for the sustained transport of ions such as Ca2+ that controls T lymphocyte (T cell) proliferation. Thus IK blockers could be potential immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressant
An immunosuppressant is any substance that performs immunosuppression of the immune system. They may be either exogenous, as immunosuppressive drugs, or endogenous, as ,e. g., testosterone...
s for the treatment of autoimmune disorders (such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis).
Mode of action
MTX occludes the pore region of various potassium channels (Kv1.2, IKCa1, Kv1.3) by establishing strong interactions between its lysineLysine
Lysine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH4NH2. It is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body cannot synthesize it. Its codons are AAA and AAG....
-23 residue and the glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
-tyrosine
Tyrosine
Tyrosine or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine, is one of the 22 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. Its codons are UAC and UAU. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group...
-glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
-aspartate (GYGD) motif of the channel. MTX thus blocks the channels by binding in the external vestibule of the pore to block the ion conduction pathway. Although Kv1.1, Kv1.2, and Kv1.3 have a very similar pore structure, they display different pharmacological sensitivity to MTX.

