
Maximum power point tracker
Encyclopedia
Grid tie inverter
A grid-tie inverter is a special type of inverter that converts direct current electricity into alternating current electricity and feeds it into an existing electrical grid...
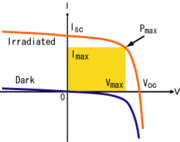
s, solar battery chargers and similar devices use to get the maximum possible power from the PV array. Solar cells have a complex relationship between solar irradiation, temperature and total resistance that produces a non-linear output efficiency known as the I-V curve. It is the purpose of the MPPT system to sample the output of the cells and apply a resistance (load) to obtain maximum power for any given environmental conditions. Essentially, this defines the current that the inverter should draw from the PV in order to get the maximum possible power (since power equals voltage times current).
I-V curve
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
they can produce. The fill factor
Fill factor
Fill factor may refer to:*Fill factor , the ratio of maximum obtainable power to the product of the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current*In vision science, the ratio of view areas to the object visible areas....
, more commonly known by its abbreviation FF, is a parameter which characterizes the non-linear electrical behavior of the solar cell. Fill factor
Fill factor
Fill factor may refer to:*Fill factor , the ratio of maximum obtainable power to the product of the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current*In vision science, the ratio of view areas to the object visible areas....
is defined as the ratio of the maximum power from the solar cell to the product of Voc and Isc, and in tabulated data it is often used to estimate the power that a cell can provide with an optimal load under given conditions, P=FF*Voc*Isc. For most purposes, FF, Voc, and Isc are enough information to give a useful approximate model of the electrical behavior of a photovoltaic cell under typical conditions.
For any given set of operational conditions, cells usually have a single operating point where the values of the current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
(I) and Voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
(V) of the cell result in a maximum power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
output. These values correspond to a particular load resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
, which is equal to V/I as specified by Ohm's Law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
. The power P is given by P=V*I. A photovoltaic cell has an approximately exponential relationship between current and voltage (taking all the device physics into account, the model can become substantially more complicated though). As is well known from basic circuit theory, the power delivered from or to a device is optimized where the derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
(graphically, the slope) dI/dV of the I-V curve is equal and opposite the I/V ratio (where dP/dV=0). This is known as the maximum power point (MPP) and corresponds to the "knee" of the curve.
A load with resistance R=V/I equal to the reciprocal of this value is the load which draws maximum power from the device, and this is sometimes called the characteristic resistance of the cell. Note however that this is a dynamic quantity which changes depending on the level of illumination, as well as other factors such as temperature and the age of the cell. If the resistance is lower or higher than this value, the power drawn will be less than the maximum available, and thus the cell will not be used as efficiently as it could be. Maximum power point trackers utilize different types of control circuit or logic to search for this point and thus to allow the converter circuit to extract the maximum power available from a cell.
Classification
There are three main types of MPPT algorithms: perturb-and-observe, incremental conductance and constant voltage. The first two methods are often referred to as hill climbing methods, because they depend on the fact that on the left side of the MPP, the curve is rising (dP/dV > 0) while on the right side of the MPP the curve is falling (dP/dV < 0).Perturb-and-observe (P&O) method
This method is the most common. The algorithm perturbs the operating voltage in a given direction and samples dP/dV. If dP/dV is positive, then the algorithm knows it adjusted the voltage in the direction toward the MPP. It keeps adjusting the voltage in that direction until dP/dV is negative.P&O algorithms are easy to implement, but they sometimes result in oscillations around the MPP in steady-state operation. They also have slow response times and can even track in the wrong direction under rapidly changing atmospheric conditions.
Incremental conductance (INC) method
This method uses the PV array's incremental conductanceConductance
Conductance may refer to:* Electrical conductance, the ability for electricity to flow a certain path* Fluid conductance, the ability for fluid to transmit through materials* Thermal conductivity, the ability for temperatures to transmit through materials...
dI/dV to compute the sign of dP/dV. INC tracks rapidly changing irradiance
Irradiance
Irradiance is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area incident on a surface. Radiant emittance or radiant exitance is the power per unit area radiated by a surface. The SI units for all of these quantities are watts per square meter , while the cgs units are ergs per square centimeter...
conditions more accurately than the P&O method. However, like the P&O method, it can produce oscillations and be confused by rapidly changing atmospheric conditions. Another disadvantage is that its increased complexity increases computational time and slows down the sampling frequency.
Constant voltage method
This method makes use of the fact that the ratio of maximum power point voltage to the open circuit voltage is often close to a constant value, with 0.76 being a common estimate. One problem with this method arises from the fact that it requires momentarily setting the PV array current to 0 to measure the array's open circuit voltage. The array's operating voltage is then set to (for example) 76% of this measured value. But during the time the array is disconnected, the available energy is wasted. It has also been found that while 76% of the open circuit voltage is often a very good approximation, it does not always coincide with the maximum power point. Thus this method may not give as much efficiency as others, especially if conditions are highly variable or the physical behavior of the cell deviates from expectations. Its main advantage is that it is relatively simple to implement and thus usually less expensive.MPPT placement
Traditional solar inverters perform MPPT for an entire array as a whole. In such systems the same current, dictated by the inverter, flows through all panels in the string. But because different panels have different IV curves, i.e. different MPPs (due to manufacturing tolerance, partial shading, etc.) this architecture means some panels will be performing below their MPP, resulting in the loss of energy.Some companies (see power optimizer
Power optimizer
A power optimizer is a DC to DC converter technology developed to maximize the energy harvest from solar photovoltaic or wind turbine systems. They do this by individually tuning the performance of the panel or wind turbine through maximum power point tracking, and optionally tuning the output to...
) are now placing peak power point converters into individual panels, allowing each to operate at peak efficiency despite uneven shading, soiling or electrical mismatch.
Operation with batteries
At night, an off-grid PV power system uses batteries to supply its loads. Although the battery pack voltage when fully charged may be close to the PV array's peak power point, this is unlikely to be true at sunrise when the battery is partially discharged. Charging may begin at a voltage considerably below the array peak power point, and a MPPT can resolve this mismatch.When the batteries in an off-grid system are full and PV production exceeds local loads, a MPPT can no longer operate the array at its peak power point as the excess power has nowhere to go. The MPPT must then shift the array operating point away from the peak power point until production exactly matches demand. (An alternative approach commonly used in spacecraft is to divert surplus PV power into a resistive load, allowing the array to operate continuously at its peak power point.)
In a grid-tied photovoltaic system, the grid is essentially a battery with near infinite capacity. The grid can always absorb surplus PV power, and it can cover shortfalls in PV production (e.g., at night). Batteries are thus needed only for protection from grid outages. The MPPT in a grid tied PV system will always operate the array at its peak power point unless the grid fails when the batteries are full and there are insufficient local loads. It would then have to back the array away from its peak power point as in the off-grid case (which it has temporarily become).
MPPT as a motor drive
MPPTs can be designed to drive an electric motorElectric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
without a storage battery. They provide significant advantages, especially when starting a motor under load. This can require a starting current that is well above the short-circuit rating of the PV panel. A MPPT can step the panel's relatively high voltage and low current down to the low voltage and high current needed to start the motor. Once the motor is running and its current requirements have dropped, the MPPT will automatically increase the voltage to normal. In this application, the MPPT can be seen as an electrical analogue to the transmission
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
in a car; the low gears provide extra torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
to the wheels until the car is up to speed.
External links
DIY MPPT projects- Arduino PPT solar charger (ArduinoArduinoArduino is an open-source single-board microcontroller, descendant of the open-source Wiring platform, designed to make the process of using electronics in multidisciplinary projects more accessible. The hardware consists of a simple open hardware design for the Arduino board with an Atmel AVR...
based) - MPPT tracker by Daniel F. Butay (Microchip PIC based)

