
McCallum rule
Encyclopedia
In monetary policy
, the McCallum rule specifies a target for the monetary base
(M0) which could be used by a central bank. The McCallum rule was proposed by Bennett T. McCallum at Carnegie Mellon University
's Tepper School of Business
. It is an alternative to the well known Taylor rule
.

where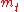 is the natural logarithm
is the natural logarithm
of M0 at time t (in quarters);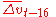 is the average quarterly increase of the velocity
is the average quarterly increase of the velocity
of M0 over a four year period from t-16 to t;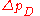 is desired rate of inflation, i.e. the desired quarterly increase in the natural logarithm of the price level;
is desired rate of inflation, i.e. the desired quarterly increase in the natural logarithm of the price level;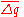 is the long-run average quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the real GDP
is the long-run average quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the real GDP
; and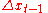 is the quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the nominal GDP from t-1 to t.
is the quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the nominal GDP from t-1 to t.

where: M is the money supply (in our case, the monetary base, M0); and X is the aggregate money traded for goods or services (in our case, the nominal GDP for the quarter in question).
Let us define the price level, P, (in our case, the GDP deflator
divided by 100) by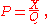
where Q is the quantity of goods or services exchanged (in our case, the real GDP during the quarter).
Together, these definitions yield the so-called equation of exchange
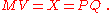
Now, define m, v, x, p, and q as the natural logarithms of M, V, X, P, and Q. Then the equation becomes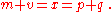
These quantities are functions of time, t, which we will take to be an integer
which counts the quarters of years. So mt means the (average) value of m during the t quarter. The forward difference operator, is defined by
is defined by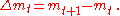
If we apply the forward difference operator, we get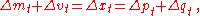
and so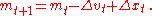
The velocity of money changes due to changes in technology and regulation. McCallum assumes that these changes tend to occur at the same rate over a period of a few years. He averages over four years to get a forecast of the average growth rate of velocity over the foreseeable future. Thus one approximates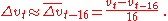
The velocity term is not intended to reflect current conditions in the business cycle
.
We assume that when the rate of inflation is held near its desired value,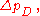 for an extended period, then the growth rate of real GDP will be near to its long-run average,
for an extended period, then the growth rate of real GDP will be near to its long-run average, 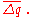 And thus that the growth rate of nominal GDP will be close to their sum
And thus that the growth rate of nominal GDP will be close to their sum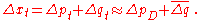
However, it is not obvious what that desired value of inflation should be.
McCallum takes the long-run average rate of growth of real GDP to be 3 percent per year which amounts to
on a quarterly basis. He expects the Federal Reserve to choose an inflation target of 2 percent per year which amounts to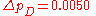
on a quarterly basis (although he would personally prefer a lower inflation target).
So the target for the monetary base should be given by a rule of the form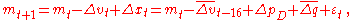
where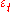 is a correction term which can only depend on information available at time t. The correction term is intended to compensate for current cyclical conditions. It should be positive when recent growth of output and the price level has been slow.
is a correction term which can only depend on information available at time t. The correction term is intended to compensate for current cyclical conditions. It should be positive when recent growth of output and the price level has been slow.
If one takes the correction to be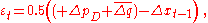
then the result is McCallum's rule. A large resulting increase in M0 tends to generate or support a rapid rate of increase in broader monetary aggregates and thereby stimulate aggregate demand for goods and services.
The figures used for the monetary base (M0) should be the adjusted base as calculated by the Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis
. The adjustments serve to take account of changes in legal reserve requirements that alter the quantity of medium-of-exchange money (such as M1) that can be supported by a given quantity of the base.
Monetary policy
Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting a rate of interest for the purpose of promoting economic growth and stability. The official goals usually include relatively stable prices and low unemployment...
, the McCallum rule specifies a target for the monetary base
Monetary base
In economics, the monetary base is a term relating to the money supply , the amount of money in the economy...
(M0) which could be used by a central bank. The McCallum rule was proposed by Bennett T. McCallum at Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States....
's Tepper School of Business
Tepper School of Business
The Tepper School of Business is a private business school located on Carnegie Mellon University’s campus in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA.The school consistently ranks highly among the top business schools in the U.S., as well as in a wide range of specializations, such as finance,...
. It is an alternative to the well known Taylor rule
Taylor rule
In economics, a Taylor rule is a monetary-policy rule that stipulates how much the central bank should change the nominal interest rate in response to changes in inflation, output, or other economic conditions. In particular, the rule stipulates that for each one-percent increase in inflation, the...
.
Rule
The rule gives a target for the monetary base in the next quarter (about 13 weeks). The target is:
where
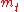 is the natural logarithm
is the natural logarithmNatural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
of M0 at time t (in quarters);
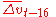 is the average quarterly increase of the velocity
is the average quarterly increase of the velocityVelocity of money
300px|thumb|Similar chart showing the velocity of a broader measure of money that covers M2 plus large institutional deposits, M3. The US no longer publishes official M3 measures, so the chart only runs through 2005....
of M0 over a four year period from t-16 to t;
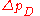 is desired rate of inflation, i.e. the desired quarterly increase in the natural logarithm of the price level;
is desired rate of inflation, i.e. the desired quarterly increase in the natural logarithm of the price level;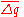 is the long-run average quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the real GDP
is the long-run average quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the real GDPGross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
; and
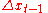 is the quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the nominal GDP from t-1 to t.
is the quarterly increase of the natural logarithm of the nominal GDP from t-1 to t.Explanation
Let us define the velocity of (base) money, V, by
where: M is the money supply (in our case, the monetary base, M0); and X is the aggregate money traded for goods or services (in our case, the nominal GDP for the quarter in question).
Let us define the price level, P, (in our case, the GDP deflator
GDP deflator
In economics, the GDP deflator is a measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy...
divided by 100) by
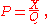
where Q is the quantity of goods or services exchanged (in our case, the real GDP during the quarter).
Together, these definitions yield the so-called equation of exchange
Equation of exchange
In economics, the equation of exchange is the relation:M\cdot V = P\cdot Qwhere, for a given period,M\, is the total nominal amount of money in circulation on average in an economy.V\, is the velocity of money, that is the average frequency with which a unit of money is spent.P\, is the price...
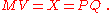
Now, define m, v, x, p, and q as the natural logarithms of M, V, X, P, and Q. Then the equation becomes

These quantities are functions of time, t, which we will take to be an integer
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
which counts the quarters of years. So mt means the (average) value of m during the t quarter. The forward difference operator,
 is defined by
is defined by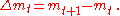
If we apply the forward difference operator, we get
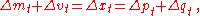
and so
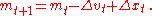
The velocity of money changes due to changes in technology and regulation. McCallum assumes that these changes tend to occur at the same rate over a period of a few years. He averages over four years to get a forecast of the average growth rate of velocity over the foreseeable future. Thus one approximates
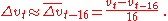
The velocity term is not intended to reflect current conditions in the business cycle
Business cycle
The term business cycle refers to economy-wide fluctuations in production or economic activity over several months or years...
.
We assume that when the rate of inflation is held near its desired value,
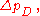 for an extended period, then the growth rate of real GDP will be near to its long-run average,
for an extended period, then the growth rate of real GDP will be near to its long-run average, 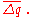 And thus that the growth rate of nominal GDP will be close to their sum
And thus that the growth rate of nominal GDP will be close to their sum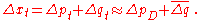
However, it is not obvious what that desired value of inflation should be.
McCallum takes the long-run average rate of growth of real GDP to be 3 percent per year which amounts to

on a quarterly basis. He expects the Federal Reserve to choose an inflation target of 2 percent per year which amounts to
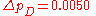
on a quarterly basis (although he would personally prefer a lower inflation target).
So the target for the monetary base should be given by a rule of the form
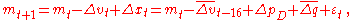
where
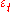 is a correction term which can only depend on information available at time t. The correction term is intended to compensate for current cyclical conditions. It should be positive when recent growth of output and the price level has been slow.
is a correction term which can only depend on information available at time t. The correction term is intended to compensate for current cyclical conditions. It should be positive when recent growth of output and the price level has been slow.If one takes the correction to be
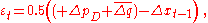
then the result is McCallum's rule. A large resulting increase in M0 tends to generate or support a rapid rate of increase in broader monetary aggregates and thereby stimulate aggregate demand for goods and services.
The figures used for the monetary base (M0) should be the adjusted base as calculated by the Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis
Federal Reserve Bank of St Louis
The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis is one of 12 regional Reserve Banks that, along with the Board of Governors in Washington, D.C., make up the nation's central bank. Missouri is the only state to have two Federal Reserve Banks . The St...
. The adjustments serve to take account of changes in legal reserve requirements that alter the quantity of medium-of-exchange money (such as M1) that can be supported by a given quantity of the base.
External links
- Policy-Rule Retrospective on the Greenspan Era
- The Use of Policy Rules in Monetary Policy Analysis
- Alternative Monetary Policy Rules: A Comparison with Historical Settings for the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan
- Federal Reserve paper on Taylor rule & McCallum rule
- `Home' Base and Monetary Base Rules

