
McDonald-Kreitman test
Encyclopedia
The McDonald–Kreitman Test looks for ancient selection
over long periods, as opposed to the steady accumulation of mutations that confer no selective advantage predicted by the Neutral theory
. It was first devised by John McDonald and Martin Kreitman
in 1991, based on an investigation of differences in amino acid sequence of the alcohol dehydrogenase
gene of Drosophila
species. Nucleotide differences between the coding regions of homologous genes of related species are enumerated and sorted into four categories, as shown below:
Sites are classed as polymorphic if they show any variation within species, while they are classed as fixed if they differ between species but not within them. If the ratio of fixed differences to polymorphisms is much higher for nonsynonymous changes (i.e. Dn/Pn >> Ds/Ps), this indicates that genetic changes have been subject to positive selection
.
The McDonald-Kreitman test itself consists of the G-test
performed on the numbers in the table above, which would indicate whether the two ratios are significantly different.
As an extension of this, the proportion of base substitutions fixed by natural selection, α, can be estimated:
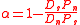
45% of amino acid differences between Drosophila simulans
and D. yakuba are estimated to have been fixed by selection, while 35% of amino acid differences between primates are estimated to be fixed by selection.
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
over long periods, as opposed to the steady accumulation of mutations that confer no selective advantage predicted by the Neutral theory
Neutral theory of molecular evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution states that the vast majority of evolutionary changes at the molecular level are caused by random drift of selectively neutral mutants . The theory was introduced by Motoo Kimura in the late 1960s and early 1970s...
. It was first devised by John McDonald and Martin Kreitman
Martin Kreitman
Martin Kreitman is an American geneticist, and Professor at the University of Chicago.He graduated from Stony Brook University with a B.S. Biology, in 1975, and from University of Florida with a M.S. Zoology, in 1977, and from Harvard University with a Ph.D...
in 1991, based on an investigation of differences in amino acid sequence of the alcohol dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenases are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide...
gene of Drosophila
Drosophila
Drosophila is a genus of small flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "fruit flies" or more appropriately pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit...
species. Nucleotide differences between the coding regions of homologous genes of related species are enumerated and sorted into four categories, as shown below:
| Fixed | Polymorphic | |
|---|---|---|
| Synonymous | Ds | Ps |
| Nonsynonymous | Dn | Pn |
Sites are classed as polymorphic if they show any variation within species, while they are classed as fixed if they differ between species but not within them. If the ratio of fixed differences to polymorphisms is much higher for nonsynonymous changes (i.e. Dn/Pn >> Ds/Ps), this indicates that genetic changes have been subject to positive selection
Directional selection
In population genetics, directional selection is a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction...
.
The McDonald-Kreitman test itself consists of the G-test
G-test
In statistics, G-tests are likelihood-ratio or maximum likelihood statistical significance tests that are increasingly being used in situations where chi-squared tests were previously recommended....
performed on the numbers in the table above, which would indicate whether the two ratios are significantly different.
As an extension of this, the proportion of base substitutions fixed by natural selection, α, can be estimated:
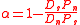
45% of amino acid differences between Drosophila simulans
Drosophila simulans
Drosophila simulans is a species of fly closely related to D. melanogaster and which belongs to the same melanogaster species subgroup. Its closest relatives are D. mauritiana and D. sechellia...
and D. yakuba are estimated to have been fixed by selection, while 35% of amino acid differences between primates are estimated to be fixed by selection.

